The University of Colorado decision diagram package. More...
#include <inttypes.h>
Go to the source code of this file.
Macros | |
| #define | CUDD_TRUE 1 |
| #define | CUDD_FALSE 0 |
| #define | CUDD_OUT_OF_MEM -1 |
| Value returned my many functions when memory is exhausted. | |
| #define | CUDD_UNIQUE_SLOTS 256 |
| #define | CUDD_CACHE_SLOTS 262144 |
| #define | CUDD_RESIDUE_DEFAULT 0 |
| #define | CUDD_RESIDUE_MSB 1 |
| #define | CUDD_RESIDUE_TC 2 |
| #define | Cudd_Not(node) ((DdNode *)((uintptr_t)(node) ^ (uintptr_t) 01)) |
| Complements a DD. More... | |
| #define | Cudd_NotCond(node, c) ((DdNode *)((uintptr_t)(node) ^ (uintptr_t) (c))) |
| Complements a DD if a condition is true. More... | |
| #define | Cudd_Regular(node) ((DdNode *)((uintptr_t)(node) & ~(uintptr_t) 01)) |
| Returns the regular version of a pointer. More... | |
| #define | Cudd_Complement(node) ((DdNode *)((uintptr_t)(node) | (uintptr_t) 01)) |
| Returns the complemented version of a pointer. More... | |
| #define | Cudd_IsComplement(node) ((int) ((uintptr_t) (node) & (uintptr_t) 01)) |
| Returns 1 if a pointer is complemented. More... | |
| #define | Cudd_ReadIndex(dd, index) (Cudd_ReadPerm(dd,index)) |
| Returns the current position in the order of variable index. More... | |
| #define | Cudd_ForeachCube(manager, f, gen, cube, value) |
| Iterates over the cubes of a decision diagram. More... | |
| #define | Cudd_ForeachPrime(manager, l, u, gen, cube) |
| Iterates over the primes of a Boolean function. More... | |
| #define | Cudd_ForeachNode(manager, f, gen, node) |
| Iterates over the nodes of a decision diagram. More... | |
| #define | Cudd_zddForeachPath(manager, f, gen, path) |
| Iterates over the paths of a ZDD. More... | |
Typedefs | |
| typedef double | CUDD_VALUE_TYPE |
| Type of the value of a terminal node. | |
| typedef struct DdNode | DdNode |
| Type of the decision diagram node. | |
| typedef DdNode * | DdNodePtr |
| Type of a pointer to a decision diagram node. | |
| typedef struct DdManager | DdManager |
| CUDD manager. | |
| typedef struct DdGen | DdGen |
| CUDD generator. | |
| typedef uint32_t | DdApaDigit |
| Type of an arbitrary precision integer "digit.". | |
| typedef DdApaDigit * | DdApaNumber |
| Type of an arbitrary precision intger, which is an array of digits. | |
| typedef DdApaDigit const * | DdConstApaNumber |
| Type of a const-qualified arbitrary precision integer. | |
| typedef struct DdTlcInfo | DdTlcInfo |
| Return type for function computing two-literal clauses. | |
| typedef int(* | DD_HFP) (DdManager *, const char *, void *) |
| Type of hook function. | |
| typedef DdNode *(* | DD_PRFP) (DdManager *, int, DdNode **, DdNode **, DdNode **) |
| Type of priority function. | |
| typedef DdNode *(* | DD_AOP) (DdManager *, DdNode **, DdNode **) |
| Type of apply operator. | |
| typedef DdNode *(* | DD_MAOP) (DdManager *, DdNode *) |
| Type of monadic apply operator. | |
| typedef DdNode *(* | DD_CTFP) (DdManager *, DdNode *, DdNode *) |
| Type of two-operand cache tag functions. | |
| typedef DdNode *(* | DD_CTFP1) (DdManager *, DdNode *) |
| Type of one-operand cache tag functions. | |
| typedef void(* | DD_OOMFP) (size_t) |
| Type of memory-out function. | |
| typedef int(* | DD_QSFP) (const void *, const void *) |
| Type of comparison function for qsort. | |
| typedef int(* | DD_THFP) (const void *) |
| Type of termination handler. | |
| typedef void(* | DD_TOHFP) (DdManager *, void *) |
| Type of timeout handler. | |
Enumerations | |
| enum | Cudd_ReorderingType { CUDD_REORDER_SAME, CUDD_REORDER_NONE, CUDD_REORDER_RANDOM, CUDD_REORDER_RANDOM_PIVOT, CUDD_REORDER_SIFT, CUDD_REORDER_SIFT_CONVERGE, CUDD_REORDER_SYMM_SIFT, CUDD_REORDER_SYMM_SIFT_CONV, CUDD_REORDER_WINDOW2, CUDD_REORDER_WINDOW3, CUDD_REORDER_WINDOW4, CUDD_REORDER_WINDOW2_CONV, CUDD_REORDER_WINDOW3_CONV, CUDD_REORDER_WINDOW4_CONV, CUDD_REORDER_GROUP_SIFT, CUDD_REORDER_GROUP_SIFT_CONV, CUDD_REORDER_ANNEALING, CUDD_REORDER_GENETIC, CUDD_REORDER_LINEAR, CUDD_REORDER_LINEAR_CONVERGE, CUDD_REORDER_LAZY_SIFT, CUDD_REORDER_EXACT } |
| Type of reordering algorithm. | |
| enum | Cudd_AggregationType { CUDD_NO_CHECK, CUDD_GROUP_CHECK, CUDD_GROUP_CHECK2, CUDD_GROUP_CHECK3, CUDD_GROUP_CHECK4, CUDD_GROUP_CHECK5, CUDD_GROUP_CHECK6, CUDD_GROUP_CHECK7, CUDD_GROUP_CHECK8, CUDD_GROUP_CHECK9 } |
| Type of aggregation methods. | |
| enum | Cudd_HookType { CUDD_PRE_GC_HOOK, CUDD_POST_GC_HOOK, CUDD_PRE_REORDERING_HOOK, CUDD_POST_REORDERING_HOOK } |
| Type of hooks. | |
| enum | Cudd_ErrorType { CUDD_NO_ERROR, CUDD_MEMORY_OUT, CUDD_TOO_MANY_NODES, CUDD_MAX_MEM_EXCEEDED, CUDD_TIMEOUT_EXPIRED, CUDD_TERMINATION, CUDD_INVALID_ARG, CUDD_INTERNAL_ERROR } |
| Type of error codes. | |
| enum | Cudd_LazyGroupType { CUDD_LAZY_NONE, CUDD_LAZY_SOFT_GROUP, CUDD_LAZY_HARD_GROUP, CUDD_LAZY_UNGROUP } |
| Group type for lazy sifting. | |
| enum | Cudd_VariableType { CUDD_VAR_PRIMARY_INPUT, CUDD_VAR_PRESENT_STATE, CUDD_VAR_NEXT_STATE } |
| Variable type. More... | |
Functions | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addNewVar (DdManager *dd) |
| Returns a new ADD variable. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addNewVarAtLevel (DdManager *dd, int level) |
| Returns a new ADD variable at a specified level. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddNewVar (DdManager *dd) |
| Returns a new BDD variable. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddNewVarAtLevel (DdManager *dd, int level) |
| Returns a new BDD variable at a specified level. More... | |
| int | Cudd_bddIsVar (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f) |
| Returns 1 if the given node is a BDD variable; 0 otherwise. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addIthVar (DdManager *dd, int i) |
| Returns the ADD variable with index i. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddIthVar (DdManager *dd, int i) |
| Returns the BDD variable with index i. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_zddIthVar (DdManager *dd, int i) |
| Returns the ZDD variable with index i. More... | |
| int | Cudd_zddVarsFromBddVars (DdManager *dd, int multiplicity) |
| Creates one or more ZDD variables for each BDD variable. More... | |
| unsigned int | Cudd_ReadMaxIndex (void) |
| Returns the maximum possible index for a variable. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addConst (DdManager *dd, CUDD_VALUE_TYPE c) |
| Returns the ADD for constant c. More... | |
| int | Cudd_IsConstant (DdNode *node) |
| Returns 1 if the node is a constant node. More... | |
| int | Cudd_IsNonConstant (DdNode *f) |
| Returns 1 if a DD node is not constant. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_T (DdNode *node) |
| Returns the then child of an internal node. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_E (DdNode *node) |
| Returns the else child of an internal node. More... | |
| CUDD_VALUE_TYPE | Cudd_V (DdNode *node) |
| Returns the value of a constant node. More... | |
| unsigned long | Cudd_ReadStartTime (DdManager *unique) |
| Returns the start time of the manager. More... | |
| unsigned long | Cudd_ReadElapsedTime (DdManager *unique) |
| Returns the time elapsed since the start time of the manager. More... | |
| void | Cudd_SetStartTime (DdManager *unique, unsigned long st) |
| Sets the start time of the manager. More... | |
| void | Cudd_ResetStartTime (DdManager *unique) |
| Resets the start time of the manager. More... | |
| unsigned long | Cudd_ReadTimeLimit (DdManager *unique) |
| Returns the time limit for the manager. More... | |
| unsigned long | Cudd_SetTimeLimit (DdManager *unique, unsigned long tl) |
| Sets the time limit for the manager. More... | |
| void | Cudd_UpdateTimeLimit (DdManager *unique) |
| Updates the time limit for the manager. More... | |
| void | Cudd_IncreaseTimeLimit (DdManager *unique, unsigned long increase) |
| Increases the time limit for the manager. More... | |
| void | Cudd_UnsetTimeLimit (DdManager *unique) |
| Unsets the time limit for the manager. More... | |
| int | Cudd_TimeLimited (DdManager *unique) |
| Returns true if the time limit for the manager is set. More... | |
| void | Cudd_RegisterTerminationCallback (DdManager *unique, DD_THFP callback, void *callback_arg) |
| Installs a termination callback. More... | |
| void | Cudd_UnregisterTerminationCallback (DdManager *unique) |
| Unregisters a termination callback. More... | |
| DD_OOMFP | Cudd_RegisterOutOfMemoryCallback (DdManager *unique, DD_OOMFP callback) |
| Installs an out-of-memory callback. More... | |
| void | Cudd_UnregisterOutOfMemoryCallback (DdManager *unique) |
| Unregister an out-of-memory callback. More... | |
| void | Cudd_RegisterTimeoutHandler (DdManager *unique, DD_TOHFP handler, void *arg) |
| Register a timeout handler function. More... | |
| DD_TOHFP | Cudd_ReadTimeoutHandler (DdManager *unique, void **argp) |
| Read the current timeout handler function. More... | |
| void | Cudd_AutodynEnable (DdManager *unique, Cudd_ReorderingType method) |
| Enables automatic dynamic reordering of BDDs and ADDs. More... | |
| void | Cudd_AutodynDisable (DdManager *unique) |
| Disables automatic dynamic reordering. More... | |
| int | Cudd_ReorderingStatus (DdManager *unique, Cudd_ReorderingType *method) |
| Reports the status of automatic dynamic reordering of BDDs and ADDs. More... | |
| void | Cudd_AutodynEnableZdd (DdManager *unique, Cudd_ReorderingType method) |
| Enables automatic dynamic reordering of ZDDs. More... | |
| void | Cudd_AutodynDisableZdd (DdManager *unique) |
| Disables automatic dynamic reordering of ZDDs. More... | |
| int | Cudd_ReorderingStatusZdd (DdManager *unique, Cudd_ReorderingType *method) |
| Reports the status of automatic dynamic reordering of ZDDs. More... | |
| int | Cudd_zddRealignmentEnabled (DdManager *unique) |
| Tells whether the realignment of ZDD order to BDD order is enabled. More... | |
| void | Cudd_zddRealignEnable (DdManager *unique) |
| Enables realignment of ZDD order to BDD order. More... | |
| void | Cudd_zddRealignDisable (DdManager *unique) |
| Disables realignment of ZDD order to BDD order. More... | |
| int | Cudd_bddRealignmentEnabled (DdManager *unique) |
| Tells whether the realignment of BDD order to ZDD order is enabled. More... | |
| void | Cudd_bddRealignEnable (DdManager *unique) |
| Enables realignment of BDD order to ZDD order. More... | |
| void | Cudd_bddRealignDisable (DdManager *unique) |
| Disables realignment of ZDD order to BDD order. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_ReadOne (DdManager *dd) |
| Returns the one constant of the manager. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_ReadZddOne (DdManager *dd, int i) |
| Returns the ZDD for the constant 1 function. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_ReadZero (DdManager *dd) |
| Returns the zero constant of the manager. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_ReadLogicZero (DdManager *dd) |
| Returns the logic zero constant of the manager. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_ReadPlusInfinity (DdManager *dd) |
| Reads the plus-infinity constant from the manager. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_ReadMinusInfinity (DdManager *dd) |
| Reads the minus-infinity constant from the manager. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_ReadBackground (DdManager *dd) |
| Reads the background constant of the manager. More... | |
| void | Cudd_SetBackground (DdManager *dd, DdNode *bck) |
| Sets the background constant of the manager. More... | |
| unsigned int | Cudd_ReadCacheSlots (DdManager *dd) |
| Reads the number of slots in the cache. More... | |
| double | Cudd_ReadCacheUsedSlots (DdManager *dd) |
| Reads the fraction of used slots in the cache. More... | |
| double | Cudd_ReadCacheLookUps (DdManager *dd) |
| Returns the number of cache look-ups. More... | |
| double | Cudd_ReadCacheHits (DdManager *dd) |
| Returns the number of cache hits. More... | |
| double | Cudd_ReadRecursiveCalls (DdManager *dd) |
| Returns the number of recursive calls. More... | |
| unsigned int | Cudd_ReadMinHit (DdManager *dd) |
| Reads the hit rate that causes resizinig of the computed table. More... | |
| void | Cudd_SetMinHit (DdManager *dd, unsigned int hr) |
| Sets the hit rate that causes resizinig of the computed table. More... | |
| unsigned int | Cudd_ReadLooseUpTo (DdManager *dd) |
| Reads the looseUpTo parameter of the manager. More... | |
| void | Cudd_SetLooseUpTo (DdManager *dd, unsigned int lut) |
| Sets the looseUpTo parameter of the manager. More... | |
| unsigned int | Cudd_ReadMaxCache (DdManager *dd) |
| Returns the soft limit for the cache size. More... | |
| unsigned int | Cudd_ReadMaxCacheHard (DdManager *dd) |
| Reads the maxCacheHard parameter of the manager. More... | |
| void | Cudd_SetMaxCacheHard (DdManager *dd, unsigned int mc) |
| Sets the maxCacheHard parameter of the manager. More... | |
| int | Cudd_ReadSize (DdManager *dd) |
| Returns the number of BDD variables in existance. More... | |
| int | Cudd_ReadZddSize (DdManager *dd) |
| Returns the number of ZDD variables in existance. More... | |
| unsigned int | Cudd_ReadSlots (DdManager *dd) |
| Returns the total number of slots of the unique table. More... | |
| double | Cudd_ReadUsedSlots (DdManager *dd) |
| Reads the fraction of used slots in the unique table. More... | |
| double | Cudd_ExpectedUsedSlots (DdManager *dd) |
| Computes the expected fraction of used slots in the unique table. More... | |
| unsigned int | Cudd_ReadKeys (DdManager *dd) |
| Returns the number of nodes in the unique table. More... | |
| unsigned int | Cudd_ReadDead (DdManager *dd) |
| Returns the number of dead nodes in the unique table. More... | |
| unsigned int | Cudd_ReadMinDead (DdManager *dd) |
| Reads the minDead parameter of the manager. More... | |
| unsigned int | Cudd_ReadReorderings (DdManager *dd) |
| Returns the number of times reordering has occurred. More... | |
| unsigned int | Cudd_ReadMaxReorderings (DdManager *dd) |
| Returns the maximum number of times reordering may be invoked. More... | |
| void | Cudd_SetMaxReorderings (DdManager *dd, unsigned int mr) |
| Sets the maximum number of times reordering may be invoked. More... | |
| long | Cudd_ReadReorderingTime (DdManager *dd) |
| Returns the time spent in reordering. More... | |
| int | Cudd_ReadGarbageCollections (DdManager *dd) |
| Returns the number of times garbage collection has occurred. More... | |
| long | Cudd_ReadGarbageCollectionTime (DdManager *dd) |
| Returns the time spent in garbage collection. More... | |
| double | Cudd_ReadNodesFreed (DdManager *dd) |
| Returns the number of nodes freed. More... | |
| double | Cudd_ReadNodesDropped (DdManager *dd) |
| Returns the number of nodes dropped. More... | |
| double | Cudd_ReadUniqueLookUps (DdManager *dd) |
| Returns the number of look-ups in the unique table. More... | |
| double | Cudd_ReadUniqueLinks (DdManager *dd) |
| Returns the number of links followed in the unique table. More... | |
| int | Cudd_ReadSiftMaxVar (DdManager *dd) |
| Reads the siftMaxVar parameter of the manager. More... | |
| void | Cudd_SetSiftMaxVar (DdManager *dd, int smv) |
| Sets the siftMaxVar parameter of the manager. More... | |
| int | Cudd_ReadSiftMaxSwap (DdManager *dd) |
| Reads the siftMaxSwap parameter of the manager. More... | |
| void | Cudd_SetSiftMaxSwap (DdManager *dd, int sms) |
| Sets the siftMaxSwap parameter of the manager. More... | |
| double | Cudd_ReadMaxGrowth (DdManager *dd) |
| Reads the maxGrowth parameter of the manager. More... | |
| void | Cudd_SetMaxGrowth (DdManager *dd, double mg) |
| Sets the maxGrowth parameter of the manager. More... | |
| double | Cudd_ReadMaxGrowthAlternate (DdManager *dd) |
| Reads the maxGrowthAlt parameter of the manager. More... | |
| void | Cudd_SetMaxGrowthAlternate (DdManager *dd, double mg) |
| Sets the maxGrowthAlt parameter of the manager. More... | |
| int | Cudd_ReadReorderingCycle (DdManager *dd) |
| Reads the reordCycle parameter of the manager. More... | |
| void | Cudd_SetReorderingCycle (DdManager *dd, int cycle) |
| Sets the reordCycle parameter of the manager. More... | |
| unsigned int | Cudd_NodeReadIndex (DdNode *node) |
| Returns the index of the node. More... | |
| int | Cudd_ReadPerm (DdManager *dd, int i) |
| Returns the current position of the i-th variable in the order. More... | |
| int | Cudd_ReadPermZdd (DdManager *dd, int i) |
| Returns the current position of the i-th ZDD variable in the order. More... | |
| int | Cudd_ReadInvPerm (DdManager *dd, int i) |
| Returns the index of the variable currently in the i-th position of the order. More... | |
| int | Cudd_ReadInvPermZdd (DdManager *dd, int i) |
| Returns the index of the ZDD variable currently in the i-th position of the order. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_ReadVars (DdManager *dd, int i) |
| Returns the i-th element of the vars array. More... | |
| CUDD_VALUE_TYPE | Cudd_ReadEpsilon (DdManager *dd) |
| Reads the epsilon parameter of the manager. More... | |
| void | Cudd_SetEpsilon (DdManager *dd, CUDD_VALUE_TYPE ep) |
| Sets the epsilon parameter of the manager to ep. More... | |
| Cudd_AggregationType | Cudd_ReadGroupcheck (DdManager *dd) |
| Reads the groupcheck parameter of the manager. More... | |
| void | Cudd_SetGroupcheck (DdManager *dd, Cudd_AggregationType gc) |
| Sets the parameter groupcheck of the manager to gc. More... | |
| int | Cudd_GarbageCollectionEnabled (DdManager *dd) |
| Tells whether garbage collection is enabled. More... | |
| void | Cudd_EnableGarbageCollection (DdManager *dd) |
| Enables garbage collection. More... | |
| void | Cudd_DisableGarbageCollection (DdManager *dd) |
| Disables garbage collection. More... | |
| int | Cudd_DeadAreCounted (DdManager *dd) |
| Tells whether dead nodes are counted towards triggering reordering. More... | |
| void | Cudd_TurnOnCountDead (DdManager *dd) |
| Causes the dead nodes to be counted towards triggering reordering. More... | |
| void | Cudd_TurnOffCountDead (DdManager *dd) |
| Causes the dead nodes not to be counted towards triggering reordering. More... | |
| int | Cudd_ReadRecomb (DdManager *dd) |
| Returns the current value of the recombination parameter used in group sifting. More... | |
| void | Cudd_SetRecomb (DdManager *dd, int recomb) |
| Sets the value of the recombination parameter used in group sifting. More... | |
| int | Cudd_ReadSymmviolation (DdManager *dd) |
| Returns the current value of the symmviolation parameter used in group sifting. More... | |
| void | Cudd_SetSymmviolation (DdManager *dd, int symmviolation) |
| Sets the value of the symmviolation parameter used in group sifting. More... | |
| int | Cudd_ReadArcviolation (DdManager *dd) |
| Returns the current value of the arcviolation parameter used in group sifting. More... | |
| void | Cudd_SetArcviolation (DdManager *dd, int arcviolation) |
| Sets the value of the arcviolation parameter used in group sifting. More... | |
| int | Cudd_ReadPopulationSize (DdManager *dd) |
| Reads the current size of the population used by the genetic algorithm for variable reordering. More... | |
| void | Cudd_SetPopulationSize (DdManager *dd, int populationSize) |
| Sets the size of the population used by the genetic algorithm for variable reordering. More... | |
| int | Cudd_ReadNumberXovers (DdManager *dd) |
| Reads the current number of crossovers used by the genetic algorithm for variable reordering. More... | |
| void | Cudd_SetNumberXovers (DdManager *dd, int numberXovers) |
| Sets the number of crossovers used by the genetic algorithm for variable reordering. More... | |
| unsigned int | Cudd_ReadOrderRandomization (DdManager *dd) |
| Returns the order randomization factor. More... | |
| void | Cudd_SetOrderRandomization (DdManager *dd, unsigned int factor) |
| Sets the order randomization factor. More... | |
| size_t | Cudd_ReadMemoryInUse (DdManager *dd) |
| Returns the memory in use by the manager measured in bytes. More... | |
| int | Cudd_PrintInfo (DdManager *dd, FILE *fp) |
| Prints out statistics and settings for a CUDD manager. More... | |
| long | Cudd_ReadPeakNodeCount (DdManager *dd) |
| Reports the peak number of nodes. More... | |
| int | Cudd_ReadPeakLiveNodeCount (DdManager *dd) |
| Reports the peak number of live nodes. More... | |
| long | Cudd_ReadNodeCount (DdManager *dd) |
| Reports the number of nodes in BDDs and ADDs. More... | |
| long | Cudd_zddReadNodeCount (DdManager *dd) |
| Reports the number of nodes in ZDDs. More... | |
| int | Cudd_AddHook (DdManager *dd, DD_HFP f, Cudd_HookType where) |
| Adds a function to a hook. More... | |
| int | Cudd_RemoveHook (DdManager *dd, DD_HFP f, Cudd_HookType where) |
| Removes a function from a hook. More... | |
| int | Cudd_IsInHook (DdManager *dd, DD_HFP f, Cudd_HookType where) |
| Checks whether a function is in a hook. More... | |
| int | Cudd_StdPreReordHook (DdManager *dd, const char *str, void *data) |
| Sample hook function to call before reordering. More... | |
| int | Cudd_StdPostReordHook (DdManager *dd, const char *str, void *data) |
| Sample hook function to call after reordering. More... | |
| int | Cudd_EnableReorderingReporting (DdManager *dd) |
| Enables reporting of reordering stats. More... | |
| int | Cudd_DisableReorderingReporting (DdManager *dd) |
| Disables reporting of reordering stats. More... | |
| int | Cudd_ReorderingReporting (DdManager *dd) |
| Returns 1 if reporting of reordering stats is enabled; 0 otherwise. More... | |
| int | Cudd_PrintGroupedOrder (DdManager *dd, const char *str, void *data) |
| Hook function to print the current variable order. More... | |
| int | Cudd_EnableOrderingMonitoring (DdManager *dd) |
| Enables monitoring of ordering. More... | |
| int | Cudd_DisableOrderingMonitoring (DdManager *dd) |
| Disables monitoring of ordering. More... | |
| int | Cudd_OrderingMonitoring (DdManager *dd) |
| Returns 1 if monitoring of ordering is enabled; 0 otherwise. More... | |
| void | Cudd_SetApplicationHook (DdManager *dd, void *value) |
| Sets the application hook. More... | |
| void * | Cudd_ReadApplicationHook (DdManager *dd) |
| Reads the application hook. More... | |
| Cudd_ErrorType | Cudd_ReadErrorCode (DdManager *dd) |
| Returns the code of the last error. More... | |
| void | Cudd_ClearErrorCode (DdManager *dd) |
| Clear the error code of a manager. More... | |
| DD_OOMFP | Cudd_InstallOutOfMemoryHandler (DD_OOMFP newHandler) |
| Installs a handler for failed memory allocations. More... | |
| FILE * | Cudd_ReadStdout (DdManager *dd) |
| Reads the stdout of a manager. More... | |
| void | Cudd_SetStdout (DdManager *dd, FILE *fp) |
| Sets the stdout of a manager. More... | |
| FILE * | Cudd_ReadStderr (DdManager *dd) |
| Reads the stderr of a manager. More... | |
| void | Cudd_SetStderr (DdManager *dd, FILE *fp) |
| Sets the stderr of a manager. More... | |
| unsigned int | Cudd_ReadNextReordering (DdManager *dd) |
| Returns the threshold for the next dynamic reordering. More... | |
| void | Cudd_SetNextReordering (DdManager *dd, unsigned int next) |
| Sets the threshold for the next dynamic reordering. More... | |
| double | Cudd_ReadSwapSteps (DdManager *dd) |
| Reads the number of elementary reordering steps. More... | |
| unsigned int | Cudd_ReadMaxLive (DdManager *dd) |
| Reads the maximum allowed number of live nodes. More... | |
| void | Cudd_SetMaxLive (DdManager *dd, unsigned int maxLive) |
| Sets the maximum allowed number of live nodes. More... | |
| size_t | Cudd_ReadMaxMemory (DdManager *dd) |
| Reads the maximum allowed memory. More... | |
| size_t | Cudd_SetMaxMemory (DdManager *dd, size_t maxMemory) |
| Sets the maximum allowed memory. More... | |
| int | Cudd_bddBindVar (DdManager *dd, int index) |
| Prevents sifting of a variable. More... | |
| int | Cudd_bddUnbindVar (DdManager *dd, int index) |
| Allows the sifting of a variable. More... | |
| int | Cudd_bddVarIsBound (DdManager *dd, int index) |
| Tells whether a variable can be sifted. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addExistAbstract (DdManager *manager, DdNode *f, DdNode *cube) |
| Existentially Abstracts all the variables in cube from f. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addUnivAbstract (DdManager *manager, DdNode *f, DdNode *cube) |
| Universally Abstracts all the variables in cube from f. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addOrAbstract (DdManager *manager, DdNode *f, DdNode *cube) |
| Disjunctively abstracts all the variables in cube from the 0-1 ADD f. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addApply (DdManager *dd, DD_AOP op, DdNode *f, DdNode *g) |
| Applies op to the corresponding discriminants of f and g. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addPlus (DdManager *dd, DdNode **f, DdNode **g) |
| Integer and floating point addition. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addTimes (DdManager *dd, DdNode **f, DdNode **g) |
| Integer and floating point multiplication. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addThreshold (DdManager *dd, DdNode **f, DdNode **g) |
| f if f≥g; 0 if f<g. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addSetNZ (DdManager *dd, DdNode **f, DdNode **g) |
| This operator sets f to the value of g wherever g != 0. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addDivide (DdManager *dd, DdNode **f, DdNode **g) |
| Integer and floating point division. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addMinus (DdManager *dd, DdNode **f, DdNode **g) |
| Integer and floating point subtraction. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addMinimum (DdManager *dd, DdNode **f, DdNode **g) |
| Integer and floating point min. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addMaximum (DdManager *dd, DdNode **f, DdNode **g) |
| Integer and floating point max. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addOneZeroMaximum (DdManager *dd, DdNode **f, DdNode **g) |
| Returns 1 if f > g and 0 otherwise. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addDiff (DdManager *dd, DdNode **f, DdNode **g) |
| Returns plusinfinity if f=g; returns min(f,g) if f!=g. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addAgreement (DdManager *dd, DdNode **f, DdNode **g) |
| f if f==g; background if f!=g. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addOr (DdManager *dd, DdNode **f, DdNode **g) |
| Disjunction of two 0-1 ADDs. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addNand (DdManager *dd, DdNode **f, DdNode **g) |
| NAND of two 0-1 ADDs. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addNor (DdManager *dd, DdNode **f, DdNode **g) |
| NOR of two 0-1 ADDs. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addXor (DdManager *dd, DdNode **f, DdNode **g) |
| XOR of two 0-1 ADDs. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addXnor (DdManager *dd, DdNode **f, DdNode **g) |
| XNOR of two 0-1 ADDs. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addMonadicApply (DdManager *dd, DD_MAOP op, DdNode *f) |
| Applies op to the discriminants of f. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addLog (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f) |
| Natural logarithm of an ADD. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addFindMax (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f) |
| Finds the maximum discriminant of f. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addFindMin (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f) |
| Finds the minimum discriminant of f. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addIthBit (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, int bit) |
| Extracts the i-th bit from an ADD. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addScalarInverse (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *epsilon) |
| Computes the scalar inverse of an ADD. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addIte (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *g, DdNode *h) |
| Implements ITE(f,g,h). More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addIteConstant (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *g, DdNode *h) |
| Implements ITEconstant for ADDs. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addEvalConst (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *g) |
| Checks whether ADD g is constant whenever ADD f is 1. More... | |
| int | Cudd_addLeq (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *g) |
| Determines whether f is less than or equal to g. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addCmpl (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f) |
| Computes the complement of an ADD a la C language. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addNegate (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f) |
| Computes the additive inverse of an ADD. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addRoundOff (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, int N) |
| Rounds off the discriminants of an ADD. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addWalsh (DdManager *dd, DdNode **x, DdNode **y, int n) |
| Generates a Walsh matrix in ADD form. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addResidue (DdManager *dd, int n, int m, int options, int top) |
| Builds an ADD for the residue modulo m of an n-bit number. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddAndAbstract (DdManager *manager, DdNode *f, DdNode *g, DdNode *cube) |
| Takes the AND of two BDDs and simultaneously abstracts the variables in cube. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddAndAbstractLimit (DdManager *manager, DdNode *f, DdNode *g, DdNode *cube, unsigned int limit) |
| Takes the AND of two BDDs and simultaneously abstracts variables unless too many nodes are needed. More... | |
| int | Cudd_ApaNumberOfDigits (int binaryDigits) |
| Returns the number of digits for an arbitrary precision integer. More... | |
| DdApaNumber | Cudd_NewApaNumber (int digits) |
| Allocates memory for an arbitrary precision integer. More... | |
| void | Cudd_FreeApaNumber (DdApaNumber number) |
| Frees an arbitrary precision integer. More... | |
| void | Cudd_ApaCopy (int digits, DdConstApaNumber source, DdApaNumber dest) |
| Makes a copy of an arbitrary precision integer. More... | |
| DdApaDigit | Cudd_ApaAdd (int digits, DdConstApaNumber a, DdConstApaNumber b, DdApaNumber sum) |
| Adds two arbitrary precision integers. More... | |
| DdApaDigit | Cudd_ApaSubtract (int digits, DdConstApaNumber a, DdConstApaNumber b, DdApaNumber diff) |
| Subtracts two arbitrary precision integers. More... | |
| DdApaDigit | Cudd_ApaShortDivision (int digits, DdConstApaNumber dividend, DdApaDigit divisor, DdApaNumber quotient) |
| Divides an arbitrary precision integer by a digit. More... | |
| unsigned int | Cudd_ApaIntDivision (int digits, DdConstApaNumber dividend, unsigned int divisor, DdApaNumber quotient) |
| Divides an arbitrary precision integer by an integer. More... | |
| void | Cudd_ApaShiftRight (int digits, DdApaDigit in, DdConstApaNumber a, DdApaNumber b) |
| Shifts right an arbitrary precision integer by one binary place. More... | |
| void | Cudd_ApaSetToLiteral (int digits, DdApaNumber number, DdApaDigit literal) |
| Sets an arbitrary precision integer to a one-digit literal. More... | |
| void | Cudd_ApaPowerOfTwo (int digits, DdApaNumber number, int power) |
| Sets an arbitrary precision integer to a power of two. More... | |
| int | Cudd_ApaCompare (int digitsFirst, DdConstApaNumber first, int digitsSecond, DdConstApaNumber second) |
| Compares two arbitrary precision integers. More... | |
| int | Cudd_ApaCompareRatios (int digitsFirst, DdConstApaNumber firstNum, unsigned int firstDen, int digitsSecond, DdConstApaNumber secondNum, unsigned int secondDen) |
| Compares the ratios of two arbitrary precision integers to two unsigned ints. More... | |
| int | Cudd_ApaPrintHex (FILE *fp, int digits, DdConstApaNumber number) |
| Prints an arbitrary precision integer in hexadecimal format. More... | |
| int | Cudd_ApaPrintDecimal (FILE *fp, int digits, DdConstApaNumber number) |
| Prints an arbitrary precision integer in decimal format. More... | |
| char * | Cudd_ApaStringDecimal (int digits, DdConstApaNumber number) |
| converts an arbitrary precision integer to a string in decimal format. More... | |
| int | Cudd_ApaPrintExponential (FILE *fp, int digits, DdConstApaNumber number, int precision) |
| Prints an arbitrary precision integer in exponential format. More... | |
| DdApaNumber | Cudd_ApaCountMinterm (DdManager const *manager, DdNode *node, int nvars, int *digits) |
| Counts the number of minterms of a DD. More... | |
| int | Cudd_ApaPrintMinterm (FILE *fp, DdManager const *dd, DdNode *node, int nvars) |
| Prints the number of minterms of a BDD or ADD using arbitrary precision arithmetic. More... | |
| int | Cudd_ApaPrintMintermExp (FILE *fp, DdManager const *dd, DdNode *node, int nvars, int precision) |
| Prints the number of minterms of a BDD or ADD in exponential format using arbitrary precision arithmetic. More... | |
| int | Cudd_ApaPrintDensity (FILE *fp, DdManager *dd, DdNode *node, int nvars) |
| Prints the density of a BDD or ADD using arbitrary precision arithmetic. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_UnderApprox (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, int numVars, int threshold, int safe, double quality) |
| Extracts a dense subset from a BDD with Shiple's underapproximation method. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_OverApprox (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, int numVars, int threshold, int safe, double quality) |
| Extracts a dense superset from a BDD with Shiple's underapproximation method. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_RemapUnderApprox (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, int numVars, int threshold, double quality) |
| Extracts a dense subset from a BDD with the remapping underapproximation method. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_RemapOverApprox (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, int numVars, int threshold, double quality) |
| Extracts a dense superset from a BDD with the remapping underapproximation method. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_BiasedUnderApprox (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *b, int numVars, int threshold, double quality1, double quality0) |
| Extracts a dense subset from a BDD with the biased underapproximation method. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_BiasedOverApprox (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *b, int numVars, int threshold, double quality1, double quality0) |
| Extracts a dense superset from a BDD with the biased underapproximation method. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddExistAbstract (DdManager *manager, DdNode *f, DdNode *cube) |
| Existentially abstracts all the variables in cube from f. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddExistAbstractLimit (DdManager *manager, DdNode *f, DdNode *cube, unsigned int limit) |
| Existentially abstracts all the variables in cube from f. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddXorExistAbstract (DdManager *manager, DdNode *f, DdNode *g, DdNode *cube) |
| Takes the exclusive OR of two BDDs and simultaneously abstracts the variables in cube. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddUnivAbstract (DdManager *manager, DdNode *f, DdNode *cube) |
| Universally abstracts all the variables in cube from f. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddBooleanDiff (DdManager *manager, DdNode *f, int x) |
| Computes the boolean difference of f with respect to x. More... | |
| int | Cudd_bddVarIsDependent (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *var) |
| Checks whether a variable is dependent on others in a function. More... | |
| double | Cudd_bddCorrelation (DdManager *manager, DdNode *f, DdNode *g) |
| Computes the correlation of f and g. More... | |
| double | Cudd_bddCorrelationWeights (DdManager *manager, DdNode *f, DdNode *g, double *prob) |
| Computes the correlation of f and g for given input probabilities. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddIte (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *g, DdNode *h) |
| Implements ITE(f,g,h). More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddIteLimit (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *g, DdNode *h, unsigned int limit) |
| Implements ITE(f,g,h) unless too many nodes are required. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddIteConstant (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *g, DdNode *h) |
| Implements ITEconstant(f,g,h). More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddIntersect (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *g) |
| Returns a function included in the intersection of f and g. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddAnd (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *g) |
| Computes the conjunction of two BDDs f and g. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddAndLimit (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *g, unsigned int limit) |
| Computes the conjunction of two BDDs f and g unless too many nodes are required. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddOr (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *g) |
| Computes the disjunction of two BDDs f and g. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddOrLimit (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *g, unsigned int limit) |
| Computes the disjunction of two BDDs f and g unless too many nodes are required. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddNand (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *g) |
| Computes the NAND of two BDDs f and g. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddNor (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *g) |
| Computes the NOR of two BDDs f and g. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddXor (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *g) |
| Computes the exclusive OR of two BDDs f and g. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddXnor (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *g) |
| Computes the exclusive NOR of two BDDs f and g. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddXnorLimit (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *g, unsigned int limit) |
| Computes the exclusive NOR of two BDDs f and g unless too many nodes are required. More... | |
| int | Cudd_bddLeq (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *g) |
| Checks whether f is less than or equal to g. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addBddThreshold (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, CUDD_VALUE_TYPE value) |
| Converts an ADD to a BDD. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addBddStrictThreshold (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, CUDD_VALUE_TYPE value) |
| Converts an ADD to a BDD. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addBddInterval (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, CUDD_VALUE_TYPE lower, CUDD_VALUE_TYPE upper) |
| Converts an ADD to a BDD. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addBddIthBit (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, int bit) |
| Converts an ADD to a BDD by extracting the i-th bit from the leaves. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_BddToAdd (DdManager *dd, DdNode *B) |
| Converts a BDD to a 0-1 ADD. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addBddPattern (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f) |
| Converts an ADD to a BDD. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddTransfer (DdManager *ddSource, DdManager *ddDestination, DdNode *f) |
| Convert a BDD from a manager to another one. More... | |
| int | Cudd_DebugCheck (DdManager *table) |
| Checks for inconsistencies in the DD heap. More... | |
| int | Cudd_CheckKeys (DdManager *table) |
| Checks for several conditions that should not occur. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddClippingAnd (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *g, int maxDepth, int direction) |
| Approximates the conjunction of two BDDs f and g. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddClippingAndAbstract (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *g, DdNode *cube, int maxDepth, int direction) |
| Approximates the conjunction of two BDDs f and g and simultaneously abstracts the variables in cube. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_Cofactor (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *g) |
| Computes the cofactor of f with respect to g. More... | |
| int | Cudd_CheckCube (DdManager *dd, DdNode *g) |
| Checks whether g is the BDD of a cube. More... | |
| int | Cudd_VarsAreSymmetric (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, int index1, int index2) |
| Checks whether two variables are symmetric in a BDD. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddCompose (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *g, int v) |
| Substitutes g for x_v in the BDD for f. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addCompose (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *g, int v) |
| Substitutes g for x_v in the ADD for f. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addPermute (DdManager *manager, DdNode *node, int *permut) |
| Permutes the variables of an ADD. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addSwapVariables (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode **x, DdNode **y, int n) |
| Swaps two sets of variables of the same size (x and y) in the ADD f. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddPermute (DdManager *manager, DdNode *node, int *permut) |
| Permutes the variables of a BDD. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddVarMap (DdManager *manager, DdNode *f) |
| Remaps the variables of a BDD using the default variable map. More... | |
| int | Cudd_SetVarMap (DdManager *manager, DdNode **x, DdNode **y, int n) |
| Registers a variable mapping with the manager. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddSwapVariables (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode **x, DdNode **y, int n) |
| Swaps two sets of variables of the same size (x and y) in the BDD f. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddAdjPermuteX (DdManager *dd, DdNode *B, DdNode **x, int n) |
| Rearranges a set of variables in the BDD B. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addVectorCompose (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode **vector) |
| Composes an ADD with a vector of 0-1 ADDs. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addGeneralVectorCompose (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode **vectorOn, DdNode **vectorOff) |
| Composes an ADD with a vector of ADDs. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addNonSimCompose (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode **vector) |
| Composes an ADD with a vector of 0-1 ADDs. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddVectorCompose (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode **vector) |
| Composes a BDD with a vector of BDDs. More... | |
| int | Cudd_bddApproxConjDecomp (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode ***conjuncts) |
| Performs two-way conjunctive decomposition of a BDD. More... | |
| int | Cudd_bddApproxDisjDecomp (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode ***disjuncts) |
| Performs two-way disjunctive decomposition of a BDD. More... | |
| int | Cudd_bddIterConjDecomp (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode ***conjuncts) |
| Performs two-way conjunctive decomposition of a BDD. More... | |
| int | Cudd_bddIterDisjDecomp (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode ***disjuncts) |
| Performs two-way disjunctive decomposition of a BDD. More... | |
| int | Cudd_bddGenConjDecomp (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode ***conjuncts) |
| Performs two-way conjunctive decomposition of a BDD. More... | |
| int | Cudd_bddGenDisjDecomp (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode ***disjuncts) |
| Performs two-way disjunctive decomposition of a BDD. More... | |
| int | Cudd_bddVarConjDecomp (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode ***conjuncts) |
| Performs two-way conjunctive decomposition of a BDD. More... | |
| int | Cudd_bddVarDisjDecomp (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode ***disjuncts) |
| Performs two-way disjunctive decomposition of a BDD. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_FindEssential (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f) |
| Finds the essential variables of a DD. More... | |
| int | Cudd_bddIsVarEssential (DdManager *manager, DdNode *f, int id, int phase) |
| Determines whether a given variable is essential with a given phase in a BDD. More... | |
| DdTlcInfo * | Cudd_FindTwoLiteralClauses (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f) |
| Finds the two literal clauses of a DD. More... | |
| int | Cudd_PrintTwoLiteralClauses (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, char **names, FILE *fp) |
| Prints the one- and two-literal clauses of a DD. More... | |
| int | Cudd_ReadIthClause (DdTlcInfo *tlc, int i, unsigned *var1, unsigned *var2, int *phase1, int *phase2) |
| Accesses the i-th clause of a DD. More... | |
| void | Cudd_tlcInfoFree (DdTlcInfo *t) |
| Frees a DdTlcInfo Structure. More... | |
| int | Cudd_DumpBlif (DdManager *dd, int n, DdNode **f, char const *const *inames, char const *const *onames, char *mname, FILE *fp, int mv) |
| Writes a blif file representing the argument BDDs. More... | |
| int | Cudd_DumpBlifBody (DdManager *dd, int n, DdNode **f, char const *const *inames, char const *const *onames, FILE *fp, int mv) |
| Writes a blif body representing the argument BDDs. More... | |
| int | Cudd_DumpDot (DdManager *dd, int n, DdNode **f, char const *const *inames, char const *const *onames, FILE *fp) |
| Writes a dot file representing the argument DDs. More... | |
| int | Cudd_DumpDaVinci (DdManager *dd, int n, DdNode **f, char const *const *inames, char const *const *onames, FILE *fp) |
| Writes a daVinci file representing the argument BDDs. More... | |
| int | Cudd_DumpDDcal (DdManager *dd, int n, DdNode **f, char const *const *inames, char const *const *onames, FILE *fp) |
| Writes a DDcal file representing the argument BDDs. More... | |
| int | Cudd_DumpFactoredForm (DdManager *dd, int n, DdNode **f, char const *const *inames, char const *const *onames, FILE *fp) |
| Writes factored forms representing the argument BDDs. More... | |
| char * | Cudd_FactoredFormString (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, char const *const *inames) |
| Returns a string with the factored form of the argument BDDs. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddConstrain (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *c) |
| Computes f constrain c. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddRestrict (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *c) |
| BDD restrict according to Coudert and Madre's algorithm (ICCAD90). More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddNPAnd (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *c) |
| Computes f non-polluting-and g. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addConstrain (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *c) |
| Computes f constrain c for ADDs. More... | |
| DdNode ** | Cudd_bddConstrainDecomp (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f) |
| BDD conjunctive decomposition as in McMillan's CAV96 paper. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addRestrict (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *c) |
| ADD restrict according to Coudert and Madre's algorithm (ICCAD90). More... | |
| DdNode ** | Cudd_bddCharToVect (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f) |
| Computes a vector of BDDs whose image equals a non-zero function. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddLICompaction (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *c) |
| Performs safe minimization of a BDD. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddSqueeze (DdManager *dd, DdNode *l, DdNode *u) |
| Finds a small BDD in a function interval. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddInterpolate (DdManager *dd, DdNode *l, DdNode *u) |
| Finds an interpolant of two functions. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddMinimize (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *c) |
Finds a small BDD that agrees with f over c. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_SubsetCompress (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, int nvars, int threshold) |
Find a dense subset of BDD f. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_SupersetCompress (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, int nvars, int threshold) |
Find a dense superset of BDD f. More... | |
| int | Cudd_addHarwell (FILE *fp, DdManager *dd, DdNode **E, DdNode ***x, DdNode ***y, DdNode ***xn, DdNode ***yn_, int *nx, int *ny, int *m, int *n, int bx, int sx, int by, int sy, int pr) |
| Reads in a matrix in the format of the Harwell-Boeing benchmark suite. More... | |
| DdManager * | Cudd_Init (unsigned int numVars, unsigned int numVarsZ, unsigned int numSlots, unsigned int cacheSize, size_t maxMemory) |
| Creates a new DD manager. More... | |
| void | Cudd_Quit (DdManager *unique) |
| Deletes resources associated with a DD manager. More... | |
| int | Cudd_PrintLinear (DdManager *table) |
| Prints the linear transform matrix. More... | |
| int | Cudd_ReadLinear (DdManager *table, int x, int y) |
| Reads an entry of the linear transform matrix. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddLiteralSetIntersection (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *g) |
| Computes the intesection of two sets of literals represented as BDDs. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addMatrixMultiply (DdManager *dd, DdNode *A, DdNode *B, DdNode **z, int nz) |
| Calculates the product of two matrices represented as ADDs. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addTimesPlus (DdManager *dd, DdNode *A, DdNode *B, DdNode **z, int nz) |
| Calculates the product of two matrices represented as ADDs. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addTriangle (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *g, DdNode **z, int nz) |
| Performs the triangulation step for the shortest path computation. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addOuterSum (DdManager *dd, DdNode *M, DdNode *r, DdNode *c) |
| Takes the minimum of a matrix and the outer sum of two vectors. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_PrioritySelect (DdManager *dd, DdNode *R, DdNode **x, DdNode **y, DdNode **z, DdNode *Pi, int n, DD_PRFP PiFunc) |
| Selects pairs from R using a priority function. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_Xgty (DdManager *dd, int N, DdNode **z, DdNode **x, DdNode **y) |
| Generates a BDD for the function x > y. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_Xeqy (DdManager *dd, int N, DdNode **x, DdNode **y) |
| Generates a BDD for the function x==y. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addXeqy (DdManager *dd, int N, DdNode **x, DdNode **y) |
| Generates an ADD for the function x==y. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_Dxygtdxz (DdManager *dd, int N, DdNode **x, DdNode **y, DdNode **z) |
| Generates a BDD for the function d(x,y) > d(x,z). More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_Dxygtdyz (DdManager *dd, int N, DdNode **x, DdNode **y, DdNode **z) |
| Generates a BDD for the function d(x,y) > d(y,z). More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_Inequality (DdManager *dd, int N, int c, DdNode **x, DdNode **y) |
| Generates a BDD for the function x - y ≥ c. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_Disequality (DdManager *dd, int N, int c, DdNode **x, DdNode **y) |
| Generates a BDD for the function x - y != c. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddInterval (DdManager *dd, int N, DdNode **x, unsigned int lowerB, unsigned int upperB) |
| Generates a BDD for the function lowerB ≤ x ≤ upperB. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_CProjection (DdManager *dd, DdNode *R, DdNode *Y) |
| Computes the compatible projection of R w.r.t. cube Y. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addHamming (DdManager *dd, DdNode **xVars, DdNode **yVars, int nVars) |
| Computes the Hamming distance ADD. More... | |
| int | Cudd_MinHammingDist (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, int *minterm, int upperBound) |
| Returns the minimum Hamming distance between f and minterm. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddClosestCube (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *g, int *distance) |
| Finds a cube of f at minimum Hamming distance from the minterms of g. More... | |
| int | Cudd_addRead (FILE *fp, DdManager *dd, DdNode **E, DdNode ***x, DdNode ***y, DdNode ***xn, DdNode ***yn_, int *nx, int *ny, int *m, int *n, int bx, int sx, int by, int sy) |
| Reads in a sparse matrix. More... | |
| int | Cudd_bddRead (FILE *fp, DdManager *dd, DdNode **E, DdNode ***x, DdNode ***y, int *nx, int *ny, int *m, int *n, int bx, int sx, int by, int sy) |
| Reads in a graph (without labels) given as a list of arcs. More... | |
| void | Cudd_Ref (DdNode *n) |
| Increases the reference count of a node, if it is not saturated. More... | |
| void | Cudd_RecursiveDeref (DdManager *table, DdNode *n) |
| Decreases the reference count of node n. More... | |
| void | Cudd_IterDerefBdd (DdManager *table, DdNode *n) |
| Decreases the reference count of BDD node n. More... | |
| void | Cudd_DelayedDerefBdd (DdManager *table, DdNode *n) |
| Decreases the reference count of BDD node n. More... | |
| void | Cudd_RecursiveDerefZdd (DdManager *table, DdNode *n) |
| Decreases the reference count of ZDD node n. More... | |
| void | Cudd_Deref (DdNode *node) |
| Decreases the reference count of node. More... | |
| int | Cudd_CheckZeroRef (DdManager *manager) |
| Checks the unique table for nodes with non-zero reference counts. More... | |
| int | Cudd_ReduceHeap (DdManager *table, Cudd_ReorderingType heuristic, int minsize) |
| Main dynamic reordering routine. More... | |
| int | Cudd_ShuffleHeap (DdManager *table, int *permutation) |
| Reorders variables according to given permutation. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_Eval (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, int *inputs) |
| Returns the value of a DD for a given variable assignment. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_ShortestPath (DdManager *manager, DdNode *f, int *weight, int *support, int *length) |
| Finds a shortest path in a DD. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_LargestCube (DdManager *manager, DdNode *f, int *length) |
| Finds a largest cube in a DD. More... | |
| int | Cudd_ShortestLength (DdManager *manager, DdNode *f, int *weight) |
| Find the length of the shortest path(s) in a DD. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_Decreasing (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, int i) |
| Checks whether a BDD is negative unate in a variable. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_Increasing (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, int i) |
| Checks whether a BDD is positive unate in a variable. More... | |
| int | Cudd_EquivDC (DdManager *dd, DdNode *F, DdNode *G, DdNode *D) |
| Tells whether F and G are identical wherever D is 0. More... | |
| int | Cudd_bddLeqUnless (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *g, DdNode *D) |
| Tells whether f is less than of equal to G unless D is 1. More... | |
| int | Cudd_EqualSupNorm (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *g, CUDD_VALUE_TYPE tolerance, int pr) |
| Compares two ADDs for equality within tolerance. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddMakePrime (DdManager *dd, DdNode *cube, DdNode *f) |
| Expands cube to a prime implicant of f. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddMaximallyExpand (DdManager *dd, DdNode *lb, DdNode *ub, DdNode *f) |
| Expands lb to prime implicants of (f and ub). More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddLargestPrimeUnate (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *phaseBdd) |
| Find a largest prime implicant of a unate function. More... | |
| double * | Cudd_CofMinterm (DdManager *dd, DdNode *node) |
| Computes the fraction of minterms in the on-set of all the positive cofactors of a BDD or ADD. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_SolveEqn (DdManager *bdd, DdNode *F, DdNode *Y, DdNode **G, int **yIndex, int n) |
| Implements the solution of F(x,y) = 0. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_VerifySol (DdManager *bdd, DdNode *F, DdNode **G, int *yIndex, int n) |
| Checks the solution of F(x,y) = 0. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_SplitSet (DdManager *manager, DdNode *S, DdNode **xVars, int n, double m) |
| Returns m minterms from a BDD. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_SubsetHeavyBranch (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, int numVars, int threshold) |
| Extracts a dense subset from a BDD with the heavy branch heuristic. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_SupersetHeavyBranch (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, int numVars, int threshold) |
| Extracts a dense superset from a BDD with the heavy branch heuristic. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_SubsetShortPaths (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, int numVars, int threshold, int hardlimit) |
| Extracts a dense subset from a BDD with the shortest paths heuristic. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_SupersetShortPaths (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, int numVars, int threshold, int hardlimit) |
| Extracts a dense superset from a BDD with the shortest paths heuristic. More... | |
| void | Cudd_SymmProfile (DdManager *table, int lower, int upper) |
| Prints statistics on symmetric variables. More... | |
| unsigned int | Cudd_Prime (unsigned int p) |
| Returns the next prime ≥ p. More... | |
| int | Cudd_Reserve (DdManager *manager, int amount) |
| Expand manager without creating variables. More... | |
| int | Cudd_PrintMinterm (DdManager *manager, DdNode *node) |
| Prints a disjoint sum of products. More... | |
| int | Cudd_bddPrintCover (DdManager *dd, DdNode *l, DdNode *u) |
| Prints a sum of prime implicants of a BDD. More... | |
| int | Cudd_PrintDebug (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, int n, int pr) |
| Prints to the manager standard output a DD and its statistics. More... | |
| int | Cudd_PrintSummary (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, int n, int mode) |
| Prints a one-line summary of an ADD or BDD to the manager stdout. More... | |
| int | Cudd_DagSize (DdNode *node) |
| Counts the number of nodes in a DD. More... | |
| int | Cudd_EstimateCofactor (DdManager *dd, DdNode *node, int i, int phase) |
| Estimates the number of nodes in a cofactor of a DD. More... | |
| int | Cudd_EstimateCofactorSimple (DdNode *node, int i) |
| Estimates the number of nodes in a cofactor of a DD. More... | |
| int | Cudd_SharingSize (DdNode **nodeArray, int n) |
| Counts the number of nodes in an array of DDs. More... | |
| double | Cudd_CountMinterm (DdManager *manager, DdNode *node, int nvars) |
| Counts the minterms of an ADD or BDD. More... | |
| long double | Cudd_LdblCountMinterm (DdManager const *manager, DdNode *node, int nvars) |
| Returns the number of minterms of aa ADD or BDD as a long double. More... | |
| int | Cudd_EpdPrintMinterm (DdManager const *dd, DdNode *node, int nvars) |
| Prints the number of minterms of an ADD or BDD with extended range. More... | |
| double | Cudd_CountPath (DdNode *node) |
| Counts the paths of a DD. More... | |
| double | Cudd_CountPathsToNonZero (DdNode *node) |
| Counts the paths to a non-zero terminal of a DD. More... | |
| int | Cudd_SupportIndices (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, int **indices) |
| Finds the variables on which a DD depends. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_Support (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f) |
| Finds the variables on which a DD depends. More... | |
| int * | Cudd_SupportIndex (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f) |
| Finds the variables on which a DD depends. More... | |
| int | Cudd_SupportSize (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f) |
| Counts the variables on which a DD depends. More... | |
| int | Cudd_VectorSupportIndices (DdManager *dd, DdNode **F, int n, int **indices) |
| Finds the variables on which a set of DDs depends. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_VectorSupport (DdManager *dd, DdNode **F, int n) |
| Finds the variables on which a set of DDs depends. More... | |
| int * | Cudd_VectorSupportIndex (DdManager *dd, DdNode **F, int n) |
| Finds the variables on which a set of DDs depends. More... | |
| int | Cudd_VectorSupportSize (DdManager *dd, DdNode **F, int n) |
| Counts the variables on which a set of DDs depends. More... | |
| int | Cudd_ClassifySupport (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *g, DdNode **common, DdNode **onlyF, DdNode **onlyG) |
| Classifies the variables in the support of two DDs. More... | |
| int | Cudd_CountLeaves (DdNode *node) |
| Counts the number of leaves in a DD. More... | |
| int | Cudd_bddPickOneCube (DdManager *ddm, DdNode *node, char *string) |
| Picks one on-set cube randomly from the given DD. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddPickOneMinterm (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode **vars, int n) |
| Picks one on-set minterm randomly from the given DD. More... | |
| DdNode ** | Cudd_bddPickArbitraryMinterms (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode **vars, int n, int k) |
| Picks k on-set minterms evenly distributed from given DD. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_SubsetWithMaskVars (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode **vars, int nvars, DdNode **maskVars, int mvars) |
| Extracts a subset from a BDD. More... | |
| DdGen * | Cudd_FirstCube (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, int **cube, CUDD_VALUE_TYPE *value) |
| Finds the first cube of a decision diagram. More... | |
| int | Cudd_NextCube (DdGen *gen, int **cube, CUDD_VALUE_TYPE *value) |
| Generates the next cube of a decision diagram onset. More... | |
| DdGen * | Cudd_FirstPrime (DdManager *dd, DdNode *l, DdNode *u, int **cube) |
| Finds the first prime of a Boolean function. More... | |
| int | Cudd_NextPrime (DdGen *gen, int **cube) |
| Generates the next prime of a Boolean function. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddComputeCube (DdManager *dd, DdNode **vars, int *phase, int n) |
| Computes the cube of an array of BDD variables. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_addComputeCube (DdManager *dd, DdNode **vars, int *phase, int n) |
| Computes the cube of an array of ADD variables. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_CubeArrayToBdd (DdManager *dd, int *array) |
| Builds the BDD of a cube from a positional array. More... | |
| int | Cudd_BddToCubeArray (DdManager *dd, DdNode *cube, int *array) |
| Builds a positional array from the BDD of a cube. More... | |
| DdGen * | Cudd_FirstNode (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode **node) |
| Finds the first node of a decision diagram. More... | |
| int | Cudd_NextNode (DdGen *gen, DdNode **node) |
| Finds the next node of a decision diagram. More... | |
| int | Cudd_GenFree (DdGen *gen) |
| Frees a CUDD generator. More... | |
| int | Cudd_IsGenEmpty (DdGen *gen) |
| Queries the status of a generator. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_IndicesToCube (DdManager *dd, int *array, int n) |
| Builds a cube of BDD variables from an array of indices. More... | |
| void | Cudd_PrintVersion (FILE *fp) |
| Prints the package version number. More... | |
| double | Cudd_AverageDistance (DdManager *dd) |
| Computes the average distance between adjacent nodes in the manager. More... | |
| int32_t | Cudd_Random (DdManager *dd) |
| Portable random number generator. More... | |
| void | Cudd_Srandom (DdManager *dd, int32_t seed) |
| Initializer for the portable random number generator. More... | |
| double | Cudd_Density (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, int nvars) |
| Computes the density of a BDD or ADD. More... | |
| void | Cudd_OutOfMem (size_t size) |
| Warns that a memory allocation failed. More... | |
| void | Cudd_OutOfMemSilent (size_t size) |
| Doesn not warn that a memory allocation failed. More... | |
| int | Cudd_zddCount (DdManager *zdd, DdNode *P) |
| Counts the number of minterms in a ZDD. More... | |
| double | Cudd_zddCountDouble (DdManager *zdd, DdNode *P) |
| Counts the number of minterms of a ZDD. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_zddProduct (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *g) |
| Computes the product of two covers represented by ZDDs. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_zddUnateProduct (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *g) |
| Computes the product of two unate covers represented as ZDDs. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_zddWeakDiv (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *g) |
| Applies weak division to two covers. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_zddDivide (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *g) |
| Computes the quotient of two unate covers. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_zddWeakDivF (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *g) |
| Modified version of Cudd_zddWeakDiv. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_zddDivideF (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *g) |
| Modified version of Cudd_zddDivide. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_zddComplement (DdManager *dd, DdNode *node) |
| Computes a complement cover for a ZDD node. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_zddIsop (DdManager *dd, DdNode *L, DdNode *U, DdNode **zdd_I) |
| Computes an ISOP in ZDD form from BDDs. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_bddIsop (DdManager *dd, DdNode *L, DdNode *U) |
| Computes a BDD in the interval between L and U with a simple sum-of-product cover. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_MakeBddFromZddCover (DdManager *dd, DdNode *node) |
| Converts a ZDD cover to a BDD. More... | |
| int | Cudd_zddDagSize (DdNode *p_node) |
| Counts the number of nodes in a ZDD. More... | |
| double | Cudd_zddCountMinterm (DdManager *zdd, DdNode *node, int path) |
| Counts the number of minterms of a ZDD. More... | |
| void | Cudd_zddPrintSubtable (DdManager *table) |
| Prints the ZDD table for debugging purposes. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_zddPortFromBdd (DdManager *dd, DdNode *B) |
| Converts a BDD into a ZDD. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_zddPortToBdd (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f) |
| Converts a ZDD into a BDD. More... | |
| int | Cudd_zddReduceHeap (DdManager *table, Cudd_ReorderingType heuristic, int minsize) |
| Main dynamic reordering routine for ZDDs. More... | |
| int | Cudd_zddShuffleHeap (DdManager *table, int *permutation) |
| Reorders ZDD variables according to given permutation. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_zddIte (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f, DdNode *g, DdNode *h) |
| Computes the ITE of three ZDDs. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_zddUnion (DdManager *dd, DdNode *P, DdNode *Q) |
| Computes the union of two ZDDs. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_zddIntersect (DdManager *dd, DdNode *P, DdNode *Q) |
| Computes the intersection of two ZDDs. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_zddDiff (DdManager *dd, DdNode *P, DdNode *Q) |
| Computes the difference of two ZDDs. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_zddDiffConst (DdManager *zdd, DdNode *P, DdNode *Q) |
| Performs the inclusion test for ZDDs (P implies Q). More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_zddSubset1 (DdManager *dd, DdNode *P, int var) |
| Computes the positive cofactor of a ZDD w.r.t. a variable. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_zddSubset0 (DdManager *dd, DdNode *P, int var) |
| Computes the negative cofactor of a ZDD w.r.t. a variable. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_zddChange (DdManager *dd, DdNode *P, int var) |
| Substitutes a variable with its complement in a ZDD. More... | |
| void | Cudd_zddSymmProfile (DdManager *table, int lower, int upper) |
| Prints statistics on symmetric ZDD variables. More... | |
| int | Cudd_zddPrintMinterm (DdManager *zdd, DdNode *node) |
| Prints a disjoint sum of product form for a ZDD. More... | |
| int | Cudd_zddPrintCover (DdManager *zdd, DdNode *node) |
| Prints a sum of products from a ZDD representing a cover. More... | |
| int | Cudd_zddPrintDebug (DdManager *zdd, DdNode *f, int n, int pr) |
| Prints to the standard output a ZDD and its statistics. More... | |
| DdGen * | Cudd_zddFirstPath (DdManager *zdd, DdNode *f, int **path) |
| Finds the first path of a ZDD. More... | |
| int | Cudd_zddNextPath (DdGen *gen, int **path) |
| Generates the next path of a ZDD. More... | |
| char * | Cudd_zddCoverPathToString (DdManager *zdd, int *path, char *str) |
| Converts a path of a ZDD representing a cover to a string. More... | |
| DdNode * | Cudd_zddSupport (DdManager *dd, DdNode *f) |
| Finds the variables on which a ZDD depends. More... | |
| int | Cudd_zddDumpDot (DdManager *dd, int n, DdNode **f, char const *const *inames, char const *const *onames, FILE *fp) |
| Writes a dot file representing the argument ZDDs. More... | |
| int | Cudd_bddSetPiVar (DdManager *dd, int index) |
| Sets a variable type to primary input. More... | |
| int | Cudd_bddSetPsVar (DdManager *dd, int index) |
| Sets a variable type to present state. More... | |
| int | Cudd_bddSetNsVar (DdManager *dd, int index) |
| Sets a variable type to next state. More... | |
| int | Cudd_bddIsPiVar (DdManager *dd, int index) |
| Checks whether a variable is primary input. More... | |
| int | Cudd_bddIsPsVar (DdManager *dd, int index) |
| Checks whether a variable is present state. More... | |
| int | Cudd_bddIsNsVar (DdManager *dd, int index) |
| Checks whether a variable is next state. More... | |
| int | Cudd_bddSetPairIndex (DdManager *dd, int index, int pairIndex) |
| Sets a corresponding pair index for a given index. More... | |
| int | Cudd_bddReadPairIndex (DdManager *dd, int index) |
| Reads a corresponding pair index for a given index. More... | |
| int | Cudd_bddSetVarToBeGrouped (DdManager *dd, int index) |
| Sets a variable to be grouped. More... | |
| int | Cudd_bddSetVarHardGroup (DdManager *dd, int index) |
| Sets a variable to be a hard group. More... | |
| int | Cudd_bddResetVarToBeGrouped (DdManager *dd, int index) |
| Resets a variable not to be grouped. More... | |
| int | Cudd_bddIsVarToBeGrouped (DdManager *dd, int index) |
| Checks whether a variable is set to be grouped. More... | |
| int | Cudd_bddSetVarToBeUngrouped (DdManager *dd, int index) |
| Sets a variable to be ungrouped. More... | |
| int | Cudd_bddIsVarToBeUngrouped (DdManager *dd, int index) |
| Checks whether a variable is set to be ungrouped. More... | |
| int | Cudd_bddIsVarHardGroup (DdManager *dd, int index) |
| Checks whether a variable is set to be in a hard group. More... | |
Detailed Description
The University of Colorado decision diagram package.
External functions and data strucures of the CUDD package.
- To turn on the gathering of statistics, define DD_STATS.
- To turn on additional debugging code, define DD_DEBUG.
- Copyright
Copyright (c) 1995-2015, Regents of the University of Colorado
All rights reserved.
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
Neither the name of the University of Colorado nor the names of its contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from this software without specific prior written permission.
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
Macro Definition Documentation
◆ CUDD_CACHE_SLOTS
| #define CUDD_CACHE_SLOTS 262144 |
Default size of the cache
◆ Cudd_Complement
| #define Cudd_Complement | ( | node | ) | ((DdNode *)((uintptr_t)(node) | (uintptr_t) 01)) |
Returns the complemented version of a pointer.
- Side effects none
- See also
- Cudd_Regular Cudd_IsComplement
◆ CUDD_FALSE
| #define CUDD_FALSE 0 |
readable false
◆ Cudd_ForeachCube
| #define Cudd_ForeachCube | ( | manager, | |
| f, | |||
| gen, | |||
| cube, | |||
| value | |||
| ) |
Iterates over the cubes of a decision diagram.
Iterates over the cubes of a decision diagram f.
Cudd_ForeachCube allocates and frees the generator. Therefore the application should not try to do that. Also, the cube is freed at the end of Cudd_ForeachCube and hence is not available outside of the loop.
CAUTION: It is assumed that dynamic reordering will not occur while there are open generators. It is the user's responsibility to make sure that dynamic reordering does not occur. As long as new nodes are not created during generation, and dynamic reordering is not called explicitly, dynamic reordering will not occur. Alternatively, it is sufficient to disable dynamic reordering. It is a mistake to dispose of a diagram on which generation is ongoing.
- Side effects none
◆ Cudd_ForeachNode
| #define Cudd_ForeachNode | ( | manager, | |
| f, | |||
| gen, | |||
| node | |||
| ) |
Iterates over the nodes of a decision diagram.
Iterates over the nodes of a decision diagram f.
The nodes are returned in a seemingly random order. Cudd_ForeachNode allocates and frees the generator. Therefore the application should not try to do that.
CAUTION: It is assumed that dynamic reordering will not occur while there are open generators. It is the user's responsibility to make sure that dynamic reordering does not occur. As long as new nodes are not created during generation, and dynamic reordering is not called explicitly, dynamic reordering will not occur. Alternatively, it is sufficient to disable dynamic reordering. It is a mistake to dispose of a diagram on which generation is ongoing.
- Side effects none
◆ Cudd_ForeachPrime
| #define Cudd_ForeachPrime | ( | manager, | |
| l, | |||
| u, | |||
| gen, | |||
| cube | |||
| ) |
Iterates over the primes of a Boolean function.
Iterates over the primes of a Boolean function producing a prime, but not necessarily irredundant, cover.
The Boolean function is described by an upper bound and a lower bound. If the function is completely specified, the two bounds coincide. Cudd_ForeachPrime allocates and frees the generator. Therefore the application should not try to do that. Also, the cube is freed at the end of Cudd_ForeachPrime and hence is not available outside of the loop.
CAUTION: It is a mistake to change a diagram on which generation is ongoing.
- Side effects none
◆ Cudd_IsComplement
| #define Cudd_IsComplement | ( | node | ) | ((int) ((uintptr_t) (node) & (uintptr_t) 01)) |
◆ Cudd_Not
| #define Cudd_Not | ( | node | ) | ((DdNode *)((uintptr_t)(node) ^ (uintptr_t) 01)) |
Complements a DD.
Complements a DD by flipping the complement attribute of the pointer (the least significant bit).
- Side effects none
- See also
- Cudd_NotCond
◆ Cudd_NotCond
| #define Cudd_NotCond | ( | node, | |
| c | |||
| ) | ((DdNode *)((uintptr_t)(node) ^ (uintptr_t) (c))) |
Complements a DD if a condition is true.
Complements a DD if condition c is true; c should be either 0 or 1, because it is used directly (for efficiency). If in doubt on the values c may take, use "(c) ? Cudd_Not(node) : node".
- Side effects none
- See also
- Cudd_Not
◆ Cudd_ReadIndex
| #define Cudd_ReadIndex | ( | dd, | |
| index | |||
| ) | (Cudd_ReadPerm(dd,index)) |
Returns the current position in the order of variable index.
Returns the current position in the order of variable index. This macro is obsolete and is kept for compatibility. New applications should use Cudd_ReadPerm instead.
- Side effects none
- See also
- Cudd_ReadPerm
◆ Cudd_Regular
| #define Cudd_Regular | ( | node | ) | ((DdNode *)((uintptr_t)(node) & ~(uintptr_t) 01)) |
Returns the regular version of a pointer.
- Side effects none
- See also
- Cudd_Complement Cudd_IsComplement
◆ CUDD_TRUE
| #define CUDD_TRUE 1 |
readable true
◆ CUDD_UNIQUE_SLOTS
| #define CUDD_UNIQUE_SLOTS 256 |
Initial size of subtables
◆ Cudd_zddForeachPath
| #define Cudd_zddForeachPath | ( | manager, | |
| f, | |||
| gen, | |||
| path | |||
| ) |
Iterates over the paths of a ZDD.
Iterates over the paths of a ZDD f.
Cudd_zddForeachPath allocates and frees the generator. Therefore the application should not try to do that. Also, the path is freed at the end of Cudd_zddForeachPath and hence is not available outside of the loop.
CAUTION: It is assumed that dynamic reordering will not occur while there are open generators. It is the user's responsibility to make sure that dynamic reordering does not occur. As long as new nodes are not created during generation, and dynamic reordering is not called explicitly, dynamic reordering will not occur. Alternatively, it is sufficient to disable dynamic reordering. It is a mistake to dispose of a diagram on which generation is ongoing.
- Side effects none
Enumeration Type Documentation
◆ Cudd_VariableType
| enum Cudd_VariableType |
Variable type.
Used only in lazy sifting.
Function Documentation
◆ Cudd_addAgreement()
f if f==g; background if f!=g.
- Returns
- NULL if not a terminal case; f op g otherwise, where f op g is f if f==g; background if f!=g.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_addApply
◆ Cudd_addApply()
Applies op to the corresponding discriminants of f and g.
- Returns
- a pointer to the result if succssful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_addMonadicApply Cudd_addPlus Cudd_addTimes Cudd_addThreshold Cudd_addSetNZ Cudd_addDivide Cudd_addMinus Cudd_addMinimum Cudd_addMaximum Cudd_addOneZeroMaximum Cudd_addDiff Cudd_addAgreement Cudd_addOr Cudd_addNand Cudd_addNor Cudd_addXor Cudd_addXnor
- Parameters
-
dd manager op operator f first operand g second operand
◆ Cudd_addBddInterval()
| DdNode* Cudd_addBddInterval | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| DdNode * | f, | ||
| CUDD_VALUE_TYPE | lower, | ||
| CUDD_VALUE_TYPE | upper | ||
| ) |
Converts an ADD to a BDD.
Replaces all discriminants greater than or equal to lower and less than or equal to upper with 1, and all other discriminants with 0.
- Returns
- a pointer to the resulting BDD if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_addBddIthBit()
Converts an ADD to a BDD by extracting the i-th bit from the leaves.
Converts an ADD to a BDD by replacing all discriminants whose i-th bit is equal to 1 with 1, and all other discriminants with 0. The i-th bit refers to the integer representation of the leaf value. If the value has a fractional part, it is ignored. Repeated calls to this procedure allow one to transform an integer-valued ADD into an array of BDDs, one for each bit of the leaf values.
- Returns
- a pointer to the resulting BDD if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_addBddPattern()
Converts an ADD to a BDD.
Replaces all discriminants different from 0 with 1.
- Returns
- a pointer to the resulting BDD if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_addBddStrictThreshold()
| DdNode* Cudd_addBddStrictThreshold | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| DdNode * | f, | ||
| CUDD_VALUE_TYPE | value | ||
| ) |
Converts an ADD to a BDD.
Replaces all discriminants STRICTLY greater than value with 1, and all other discriminants with 0.
- Returns
- a pointer to the resulting BDD if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_addBddThreshold()
| DdNode* Cudd_addBddThreshold | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| DdNode * | f, | ||
| CUDD_VALUE_TYPE | value | ||
| ) |
Converts an ADD to a BDD.
Replaces all discriminants greater than or equal to value with 1, and all other discriminants with 0.
- Returns
- a pointer to the resulting BDD if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_addCmpl()
Computes the complement of an ADD a la C language.
The complement of 0 is 1 and the complement of everything else is 0.
- Returns
- a pointer to the resulting ADD if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_addNegate
◆ Cudd_addCompose()
Substitutes g for x_v in the ADD for f.
v is the index of the variable to be substituted. g must be a 0-1 ADD. Cudd_bddCompose passes the corresponding projection function to the recursive procedure, so that the cache may be used.
- Returns
- the composed ADD if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_bddCompose
◆ Cudd_addComputeCube()
Computes the cube of an array of ADD variables.
If non-null, the phase argument indicates which literal of each variable should appear in the cube. If phase[i] is nonzero, then the positive literal is used. If phase is NULL, the cube is positive unate.
- Returns
- a pointer to the result if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects none
- See also
- Cudd_bddComputeCube
◆ Cudd_addConst()
| DdNode* Cudd_addConst | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| CUDD_VALUE_TYPE | c | ||
| ) |
Returns the ADD for constant c.
Retrieves the ADD for constant c if it already exists, or creates a new ADD.
- Returns
- a pointer to the ADD if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_addNewVar Cudd_addIthVar
◆ Cudd_addConstrain()
Computes f constrain c for ADDs.
Computes f constrain c (f @ c), for f an ADD and c a 0-1 ADD. List of special cases:
- F @ 0 = 0
- F @ 1 = F
- 0 @ c = 0
- 1 @ c = 1
- F @ F = 1
- Returns
- a pointer to the result if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_bddConstrain
◆ Cudd_addDiff()
Returns plusinfinity if f=g; returns min(f,g) if f!=g.
- Returns
- NULL if not a terminal case; f op g otherwise, where f op g is plusinfinity if f=g; min(f,g) if f!=g.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_addApply
◆ Cudd_addDivide()
Integer and floating point division.
- Returns
- NULL if not a terminal case; f / g otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_addApply
◆ Cudd_addEvalConst()
Checks whether ADD g is constant whenever ADD f is 1.
f must be a 0-1 ADD. If f is identically 0, the check is assumed to be successful, and the background value is returned. No new nodes are created.
- Returns
- a pointer to the resulting ADD (which may or may not be constant) or DD_NON_CONSTANT.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_addIteConstant Cudd_addLeq
◆ Cudd_addExistAbstract()
Existentially Abstracts all the variables in cube from f.
Abstracts all the variables in cube from f by summing over all possible values taken by the variables.
- Returns
- the abstracted ADD.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_addFindMax()
Finds the maximum discriminant of f.
- Returns
- a pointer to a constant ADD.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_addFindMin()
Finds the minimum discriminant of f.
- Returns
- a pointer to a constant ADD.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_addGeneralVectorCompose()
| DdNode* Cudd_addGeneralVectorCompose | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| DdNode * | f, | ||
| DdNode ** | vectorOn, | ||
| DdNode ** | vectorOff | ||
| ) |
Composes an ADD with a vector of ADDs.
Given a vector of ADDs, creates a new ADD by substituting the ADDs for the variables of the ADD f. vectorOn contains ADDs to be substituted for the x_v and vectorOff the ADDs to be substituted for x_v'. There should be an entry in vector for each variable in the manager. If no substitution is sought for a given variable, the corresponding projection function should be specified in the vector. This function implements simultaneous composition.
- Returns
- a pointer to the resulting ADD if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_addHamming()
Computes the Hamming distance ADD.
The two vectors xVars and yVars identify the variables that form the two arguments.
- Returns
- an ADD that gives the Hamming distance between its two arguments if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_addHarwell()
| int Cudd_addHarwell | ( | FILE * | fp, |
| DdManager * | dd, | ||
| DdNode ** | E, | ||
| DdNode *** | x, | ||
| DdNode *** | y, | ||
| DdNode *** | xn, | ||
| DdNode *** | yn_, | ||
| int * | nx, | ||
| int * | ny, | ||
| int * | m, | ||
| int * | n, | ||
| int | bx, | ||
| int | sx, | ||
| int | by, | ||
| int | sy, | ||
| int | pr | ||
| ) |
Reads in a matrix in the format of the Harwell-Boeing benchmark suite.
The variables are ordered as follows:
x[0] y[0] x[1] y[1] ...
0 is the most significant bit. On input, nx and ny hold the numbers of row and column variables already in existence.
- Returns
- 1 on success; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects On output, nx and ny hold the numbers of row and column
- variables actually used by the matrix. m and n are set to the numbers of rows and columns of the matrix. Their values on input are immaterial. The ADD for the sparse matrix is returned in E, and its reference count is > 0.
- See also
- Cudd_addRead Cudd_bddRead
- Parameters
-
fp pointer to the input file dd DD manager E characteristic function of the graph x array of row variables y array of column variables xn array of complemented row variables yn_ array of complemented column variables nx number or row variables ny number or column variables m number of rows n number of columns bx first index of row variables sx step of row variables by first index of column variables sy step of column variables pr verbosity level
◆ Cudd_AddHook()
| int Cudd_AddHook | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| DD_HFP | f, | ||
| Cudd_HookType | where | ||
| ) |
Adds a function to a hook.
A hook is a list of application-provided functions called on certain occasions by the package.
- Returns
- 1 if the function is successfully added; 2 if the function was already in the list; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_RemoveHook
◆ Cudd_addIte()
Implements ITE(f,g,h).
This procedure assumes that f is a 0-1 ADD.
- Returns
- a pointer to the resulting ADD if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_addIteConstant()
Implements ITEconstant for ADDs.
f must be a 0-1 ADD. No new nodes are created. This function can be used, for instance, to check that g has a constant value (specified by h) whenever f is 1. If the constant value is unknown, then one should use Cudd_addEvalConst.
- Returns
- a pointer to the resulting ADD (which may or may not be constant) or DD_NON_CONSTANT.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_addIthBit()
Extracts the i-th bit from an ADD.
Produces an ADD from another ADD by replacing all discriminants whose i-th bit is equal to 1 with 1, and all other discriminants with 0. The i-th bit refers to the integer representation of the leaf value. If the value has a fractional part, it is ignored. Repeated calls to this procedure allow one to transform an integer-valued ADD into an array of ADDs, one for each bit of the leaf values.
- Returns
- a pointer to the resulting ADD if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_addBddIthBit
◆ Cudd_addIthVar()
Returns the ADD variable with index i.
Retrieves the ADD variable with index i if it already exists, or creates a new ADD variable. An ADD variable differs from a BDD variable because it points to the arithmetic zero, instead of having a complement pointer to 1.
- Returns
- a pointer to the variable if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_addLeq()
Determines whether f is less than or equal to g.
No new nodes are created. This procedure works for arbitrary ADDs. For 0-1 ADDs Cudd_addEvalConst is more efficient.
- Returns
- 1 if f is less than or equal to g; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_addLog()
Natural logarithm of an ADD.
The discriminants of f must be positive double's.
- Returns
- NULL if not a terminal case; log(f) otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_addMonadicApply
◆ Cudd_addMatrixMultiply()
Calculates the product of two matrices represented as ADDs.
This procedure implements the quasiring multiplication algorithm. A is assumed to depend on variables x (rows) and z (columns). B is assumed to depend on variables z (rows) and y (columns). The product of A and B then depends on x (rows) and y (columns). Only the z variables have to be explicitly identified; they are the "summation" variables.
- Returns
- a pointer to the result if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_addMaximum()
Integer and floating point max.
Integer and floating point max for Cudd_addApply.
- Returns
- NULL if not a terminal case; max(f,g) otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_addApply
◆ Cudd_addMinimum()
Integer and floating point min.
Integer and floating point min for Cudd_addApply.
- Returns
- NULL if not a terminal case; min(f,g) otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_addApply
◆ Cudd_addMinus()
Integer and floating point subtraction.
- Returns
- NULL if not a terminal case; f - g otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_addApply
◆ Cudd_addMonadicApply()
Applies op to the discriminants of f.
- Returns
- a pointer to the result if succssful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_addApply Cudd_addLog
◆ Cudd_addNand()
NAND of two 0-1 ADDs.
- Returns
- NULL if not a terminal case; f NAND g otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_addApply
◆ Cudd_addNegate()
Computes the additive inverse of an ADD.
- Returns
- a pointer to the result if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_addCmpl
◆ Cudd_addNewVar()
Returns a new ADD variable.
The new variable has an index equal to the largest previous index plus 1. An ADD variable differs from a BDD variable because it points to the arithmetic zero, instead of having a complement pointer to 1.
- Returns
- a pointer to the new variable if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_addNewVarAtLevel()
Returns a new ADD variable at a specified level.
The new variable has an index equal to the largest previous index plus 1 and is positioned at the specified level in the order.
- Returns
- a pointer to the new variable if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_addNonSimCompose()
Composes an ADD with a vector of 0-1 ADDs.
Given a vector of 0-1 ADDs, creates a new ADD by substituting the 0-1 ADDs for the variables of the ADD f. There should be an entry in vector for each variable in the manager. This function implements non-simultaneous composition. If any of the functions being composed depends on any of the variables being substituted, then the result depends on the order of composition, which in turn depends on the variable order: The variables farther from the roots in the order are substituted first.
- Returns
- a pointer to the resulting ADD if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_addNor()
NOR of two 0-1 ADDs.
- Returns
- NULL if not a terminal case; f NOR g otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_addApply
◆ Cudd_addOneZeroMaximum()
Returns 1 if f > g and 0 otherwise.
Used in conjunction with Cudd_addApply.
- Returns
- NULL if not a terminal case.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_addApply
◆ Cudd_addOr()
Disjunction of two 0-1 ADDs.
- Returns
- NULL if not a terminal case; f OR g otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_addApply
◆ Cudd_addOrAbstract()
Disjunctively abstracts all the variables in cube from the 0-1 ADD f.
Abstracts all the variables in cube from the 0-1 ADD f by taking the disjunction over all possible values taken by the variables.
- Returns
- the abstracted ADD if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_addOuterSum()
Takes the minimum of a matrix and the outer sum of two vectors.
Takes the pointwise minimum of a matrix and the outer sum of two vectors. This procedure is used in the Floyd-Warshall all-pair shortest path algorithm.
- Returns
- a pointer to the result if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_addPermute()
Permutes the variables of an ADD.
Given a permutation in array permut, creates a new ADD with permuted variables. There should be an entry in array permut for each variable in the manager. The i-th entry of permut holds the index of the variable that is to substitute the i-th variable.
- Returns
- a pointer to the resulting ADD if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_bddPermute Cudd_addSwapVariables
◆ Cudd_addPlus()
Integer and floating point addition.
- Returns
- NULL if not a terminal case; f+g otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_addApply
◆ Cudd_addRead()
| int Cudd_addRead | ( | FILE * | fp, |
| DdManager * | dd, | ||
| DdNode ** | E, | ||
| DdNode *** | x, | ||
| DdNode *** | y, | ||
| DdNode *** | xn, | ||
| DdNode *** | yn_, | ||
| int * | nx, | ||
| int * | ny, | ||
| int * | m, | ||
| int * | n, | ||
| int | bx, | ||
| int | sx, | ||
| int | by, | ||
| int | sy | ||
| ) |
Reads in a sparse matrix.
Reads in a sparse matrix specified in a simple format. The first line of the input contains the numbers of rows and columns. The remaining lines contain the elements of the matrix, one per line. Given a background value (specified by the background field of the manager), only the values different from it are explicitly listed. Each foreground element is described by two integers, i.e., the row and column number, and a real number, i.e., the value.
Cudd_addRead produces an ADD that depends on two sets of variables: x and y. The x variables (x[0] ... x[nx-1]) encode the row index and the y variables (y[0] ... y[ny-1]) encode the column index. x[0] and y[0] are the most significant bits in the indices. The variables may already exist or may be created by the function. The index of x[i] is bx+i*sx, and the index of y[i] is by+i*sy.
On input, nx and ny hold the numbers of row and column variables already in existence. On output, they hold the numbers of row and column variables actually used by the matrix. When Cudd_addRead creates the variable arrays, the index of x[i] is bx+i*sx, and the index of y[i] is by+i*sy. When some variables already exist Cudd_addRead expects the indices of the existing x variables to be bx+i*sx, and the indices of the existing y variables to be by+i*sy.
m and n are set to the numbers of rows and columns of the matrix. Their values on input are immaterial. The ADD for the sparse matrix is returned in E, and its reference count is > 0.
- Returns
- 1 in case of success; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects nx and ny are set to the numbers of row and column
- variables. m and n are set to the numbers of rows and columns. x and y are possibly extended to represent the array of row and column variables. Similarly for xn and yn_, which hold on return from Cudd_addRead the complements of the row and column variables.
- See also
- Cudd_addHarwell Cudd_bddRead
- Parameters
-
fp input file pointer dd DD manager E characteristic function of the graph x array of row variables y array of column variables xn array of complemented row variables yn_ array of complemented column variables nx number or row variables ny number or column variables m number of rows n number of columns bx first index of row variables sx step of row variables by first index of column variables sy step of column variables
◆ Cudd_addResidue()
Builds an ADD for the residue modulo m of an n-bit number.
The modulus must be at least 2, and the number of bits at least 1. Parameter options specifies whether the MSB should be on top or the LSB; and whther the number whose residue is computed is in two's complement notation or not. The macro CUDD_RESIDUE_DEFAULT specifies LSB on top and unsigned number. The macro CUDD_RESIDUE_MSB specifies MSB on top, and the macro CUDD_RESIDUE_TC specifies two's complement residue. To request MSB on top and two's complement residue simultaneously, one can OR the two macros: CUDD_RESIDUE_MSB | CUDD_RESIDUE_TC.
- Returns
- a pointer to the resulting ADD if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- Parameters
-
dd manager n number of bits m modulus options options top index of top variable
◆ Cudd_addRestrict()
ADD restrict according to Coudert and Madre's algorithm (ICCAD90).
If application of restrict results in an ADD larger than the input ADD, the input ADD is returned.
- Returns
- the restricted ADD if successful; otherwise NULL.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_addConstrain Cudd_bddRestrict
◆ Cudd_addRoundOff()
Rounds off the discriminants of an ADD.
The discriminants are rounded off to N digits after the decimal.
- Returns
- a pointer to the result ADD if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_addScalarInverse()
Computes the scalar inverse of an ADD.
Computes an n ADD where the discriminants are the multiplicative inverses of the corresponding discriminants of the argument ADD.
- Returns
- a pointer to the resulting ADD in case of success. Returns NULL if any discriminants smaller than epsilon is encountered.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_addSetNZ()
This operator sets f to the value of g wherever g != 0.
- Returns
- NULL if not a terminal case; f op g otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_addApply
◆ Cudd_addSwapVariables()
Swaps two sets of variables of the same size (x and y) in the ADD f.
The size is given by n. The two sets of variables are assumed to be disjoint.
- Returns
- a pointer to the resulting ADD if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_addPermute Cudd_bddSwapVariables
◆ Cudd_addThreshold()
f if f≥g; 0 if f<g.
Threshold operator for Apply (f if f ≥g; 0 if f<g).
- Returns
- NULL if not a terminal case; f op g otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_addApply
◆ Cudd_addTimes()
Integer and floating point multiplication.
This function can be used also to take the AND of two 0-1 ADDs.
- Returns
- NULL if not a terminal case; f * g otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_addApply
◆ Cudd_addTimesPlus()
Calculates the product of two matrices represented as ADDs.
Calculates the product of two matrices, A and B, represented as ADDs, using the CMU matrix by matrix multiplication procedure by Clarke et al.. Matrix A has x's as row variables and z's as column variables, while matrix B has z's as row variables and y's as column variables. The resulting matrix has x's as row variables and y's as column variables.
- Returns
- the pointer to the result if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_addMatrixMultiply
◆ Cudd_addTriangle()
Performs the triangulation step for the shortest path computation.
Implements the semiring multiplication algorithm used in the triangulation step for the shortest path computation. f is assumed to depend on variables x (rows) and z (columns). g is assumed to depend on variables z (rows) and y (columns). The product of f and g then depends on x (rows) and y (columns). Only the z variables have to be explicitly identified; they are the "abstraction" variables.
- Returns
- a pointer to the result if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_addUnivAbstract()
Universally Abstracts all the variables in cube from f.
Abstracts all the variables in cube from f by taking the product over all possible values taken by the variable.
- Returns
- the abstracted ADD if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_addVectorCompose()
Composes an ADD with a vector of 0-1 ADDs.
Given a vector of 0-1 ADDs, creates a new ADD by substituting the 0-1 ADDs for the variables of the ADD f. There should be an entry in vector for each variable in the manager. If no substitution is sought for a given variable, the corresponding projection function should be specified in the vector. This function implements simultaneous composition.
- Returns
- a pointer to the resulting ADD if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_addWalsh()
Generates a Walsh matrix in ADD form.
- Returns
- a pointer to the matrixi if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_addXeqy()
Generates an ADD for the function x==y.
This function generates an ADD for the function x==y. Both x and y are N-bit numbers, x[0] x[1] ... x[N-1] and y[0] y[1] ... y[N-1]. The ADD is built bottom-up. It has 3*N-1 internal nodes, if the variables are ordered as follows: x[0] y[0] x[1] y[1] ... x[N-1] y[N-1].
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_Xeqy
- Parameters
-
dd DD manager N number of x and y variables x array of x variables y array of y variables
◆ Cudd_addXnor()
XNOR of two 0-1 ADDs.
- Returns
- NULL if not a terminal case; f XNOR g otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_addApply
◆ Cudd_addXor()
XOR of two 0-1 ADDs.
- Returns
- NULL if not a terminal case; f XOR g otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_addApply
◆ Cudd_ApaAdd()
| DdApaDigit Cudd_ApaAdd | ( | int | digits, |
| DdConstApaNumber | a, | ||
| DdConstApaNumber | b, | ||
| DdApaNumber | sum | ||
| ) |
Adds two arbitrary precision integers.
- Returns
- the carry out of the most significant digit.
- Side effects The result of the sum is stored in parameter sum.
◆ Cudd_ApaCompare()
| int Cudd_ApaCompare | ( | int | digitsFirst, |
| DdConstApaNumber | first, | ||
| int | digitsSecond, | ||
| DdConstApaNumber | second | ||
| ) |
Compares two arbitrary precision integers.
- Returns
- 1 if the first number is larger; 0 if they are equal; -1 if the second number is larger.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_ApaCompareRatios()
| int Cudd_ApaCompareRatios | ( | int | digitsFirst, |
| DdConstApaNumber | firstNum, | ||
| unsigned int | firstDen, | ||
| int | digitsSecond, | ||
| DdConstApaNumber | secondNum, | ||
| unsigned int | secondDen | ||
| ) |
Compares the ratios of two arbitrary precision integers to two unsigned ints.
- Returns
- 1 if the first number is larger; 0 if they are equal; -1 if the second number is larger.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_ApaCopy()
| void Cudd_ApaCopy | ( | int | digits, |
| DdConstApaNumber | source, | ||
| DdApaNumber | dest | ||
| ) |
Makes a copy of an arbitrary precision integer.
- Side effects Changes parameter dest.
◆ Cudd_ApaCountMinterm()
| DdApaNumber Cudd_ApaCountMinterm | ( | DdManager const * | manager, |
| DdNode * | node, | ||
| int | nvars, | ||
| int * | digits | ||
| ) |
Counts the number of minterms of a DD.
The function is assumed to depend on nvars variables. The minterm count is represented as an arbitrary precision unsigned integer, to allow for any number of variables CUDD supports.
- Returns
- a pointer to the array representing the number of minterms of the function rooted at node if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects The number of digits of the result is returned in
- parameter
digits.
- See also
- Cudd_CountMinterm
◆ Cudd_ApaIntDivision()
| unsigned int Cudd_ApaIntDivision | ( | int | digits, |
| DdConstApaNumber | dividend, | ||
| unsigned int | divisor, | ||
| DdApaNumber | quotient | ||
| ) |
Divides an arbitrary precision integer by an integer.
Divides an arbitrary precision integer by a 32-bit unsigned integer. This procedure relies on the assumption that the number of bits of a DdApaDigit plus the number of bits of an unsigned int is less the number of bits of the mantissa of a double. This guarantees that the product of a DdApaDigit and an unsigned int can be represented without loss of precision by a double. On machines where this assumption is not satisfied, this procedure will malfunction.
- Returns
- the remainder.
- Side effects The quotient is returned in parameter quotient.
- Deprecated:
- The assumption on which the correctness of this function rests is not satisfied by modern-day 64-bit CPUs.
- See also
- Cudd_ApaShortDivision
◆ Cudd_ApaNumberOfDigits()
| int Cudd_ApaNumberOfDigits | ( | int | binaryDigits | ) |
Returns the number of digits for an arbitrary precision integer.
Finds the number of digits for an arbitrary precision integer given the maximum number of binary digits. The number of binary digits should be positive.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_ApaPowerOfTwo()
| void Cudd_ApaPowerOfTwo | ( | int | digits, |
| DdApaNumber | number, | ||
| int | power | ||
| ) |
Sets an arbitrary precision integer to a power of two.
If the power of two is too large to be represented, the number is set to 0.
- Side effects The result is returned in parameter number.
◆ Cudd_ApaPrintDecimal()
| int Cudd_ApaPrintDecimal | ( | FILE * | fp, |
| int | digits, | ||
| DdConstApaNumber | number | ||
| ) |
Prints an arbitrary precision integer in decimal format.
- Returns
- 1 if successful; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_ApaPrintDensity()
Prints the density of a BDD or ADD using arbitrary precision arithmetic.
- Returns
- 1 if successful; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_ApaPrintExponential()
| int Cudd_ApaPrintExponential | ( | FILE * | fp, |
| int | digits, | ||
| DdConstApaNumber | number, | ||
| int | precision | ||
| ) |
Prints an arbitrary precision integer in exponential format.
Prints as an integer if precision is at least the number of digits to be printed. If precision does not allow printing of all digits, rounds to nearest breaking ties so that the last printed digit is even.
- Returns
- 1 if successful; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_ApaPrintHex Cudd_ApaPrintDecimal
< readable false
< readable true
◆ Cudd_ApaPrintHex()
| int Cudd_ApaPrintHex | ( | FILE * | fp, |
| int | digits, | ||
| DdConstApaNumber | number | ||
| ) |
Prints an arbitrary precision integer in hexadecimal format.
- Returns
- 1 if successful; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_ApaPrintMinterm()
Prints the number of minterms of a BDD or ADD using arbitrary precision arithmetic.
- Returns
- 1 if successful; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_ApaPrintMintermExp
◆ Cudd_ApaPrintMintermExp()
| int Cudd_ApaPrintMintermExp | ( | FILE * | fp, |
| DdManager const * | dd, | ||
| DdNode * | node, | ||
| int | nvars, | ||
| int | precision | ||
| ) |
Prints the number of minterms of a BDD or ADD in exponential format using arbitrary precision arithmetic.
Parameter precision controls the number of signficant digits printed.
- Returns
- 1 if successful; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_ApaPrintMinterm
◆ Cudd_ApaSetToLiteral()
| void Cudd_ApaSetToLiteral | ( | int | digits, |
| DdApaNumber | number, | ||
| DdApaDigit | literal | ||
| ) |
Sets an arbitrary precision integer to a one-digit literal.
- Side effects The result is returned in parameter number.
◆ Cudd_ApaShiftRight()
| void Cudd_ApaShiftRight | ( | int | digits, |
| DdApaDigit | in, | ||
| DdConstApaNumber | a, | ||
| DdApaNumber | b | ||
| ) |
Shifts right an arbitrary precision integer by one binary place.
The most significant binary digit of the result is taken from parameter in.
- Side effects The result is returned in parameter b.
◆ Cudd_ApaShortDivision()
| DdApaDigit Cudd_ApaShortDivision | ( | int | digits, |
| DdConstApaNumber | dividend, | ||
| DdApaDigit | divisor, | ||
| DdApaNumber | quotient | ||
| ) |
Divides an arbitrary precision integer by a digit.
- Returns
- the remainder digit.
- Side effects The quotient is returned in parameter quotient.
◆ Cudd_ApaStringDecimal()
| char* Cudd_ApaStringDecimal | ( | int | digits, |
| DdConstApaNumber | number | ||
| ) |
converts an arbitrary precision integer to a string in decimal format.
- Returns
- the string if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_ApaPrintDecimal
◆ Cudd_ApaSubtract()
| DdApaDigit Cudd_ApaSubtract | ( | int | digits, |
| DdConstApaNumber | a, | ||
| DdConstApaNumber | b, | ||
| DdApaNumber | diff | ||
| ) |
Subtracts two arbitrary precision integers.
- Returns
- the borrow out of the most significant digit.
- Side effects The result of the subtraction is stored in parameter
diff.
◆ Cudd_AutodynDisable()
| void Cudd_AutodynDisable | ( | DdManager * | unique | ) |
Disables automatic dynamic reordering.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_AutodynDisableZdd()
| void Cudd_AutodynDisableZdd | ( | DdManager * | unique | ) |
Disables automatic dynamic reordering of ZDDs.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_AutodynEnable()
| void Cudd_AutodynEnable | ( | DdManager * | unique, |
| Cudd_ReorderingType | method | ||
| ) |
Enables automatic dynamic reordering of BDDs and ADDs.
Parameter method is used to determine the method used for reordering. If CUDD_REORDER_SAME is passed, the method is unchanged.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_AutodynEnableZdd()
| void Cudd_AutodynEnableZdd | ( | DdManager * | unique, |
| Cudd_ReorderingType | method | ||
| ) |
Enables automatic dynamic reordering of ZDDs.
Parameter method is used to determine the method used for reordering ZDDs. If CUDD_REORDER_SAME is passed, the method is unchanged.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_AverageDistance()
| double Cudd_AverageDistance | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Computes the average distance between adjacent nodes in the manager.
Adjacent nodes are node pairs such that the second node is the then child, else child, or next node in the collision list.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_bddAdjPermuteX()
Rearranges a set of variables in the BDD B.
The size of the set is given by n. This procedure is intended for the ‘randomization’ of the priority functions.
- Returns
- a pointer to the BDD if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_bddAnd()
Computes the conjunction of two BDDs f and g.
- Returns
- a pointer to the resulting BDD if successful; NULL if the intermediate result blows up.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_bddIte Cudd_addApply Cudd_bddAndAbstract Cudd_bddIntersect Cudd_bddOr Cudd_bddNand Cudd_bddNor Cudd_bddXor Cudd_bddXnor
- Parameters
-
dd manager f first operand g second operand
◆ Cudd_bddAndAbstract()
Takes the AND of two BDDs and simultaneously abstracts the variables in cube.
The variables are existentially abstracted. Cudd_bddAndAbstract implements the semiring matrix multiplication algorithm for the boolean semiring.
- Returns
- a pointer to the result is successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_bddAndAbstractLimit()
| DdNode* Cudd_bddAndAbstractLimit | ( | DdManager * | manager, |
| DdNode * | f, | ||
| DdNode * | g, | ||
| DdNode * | cube, | ||
| unsigned int | limit | ||
| ) |
Takes the AND of two BDDs and simultaneously abstracts variables unless too many nodes are needed.
The variables in cube are existentially abstracted.
- Returns
- a pointer to the result is successful; NULL otherwise. In particular, if the number of new nodes created exceeds
limit, this function returns NULL.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_bddAndAbstract
◆ Cudd_bddAndLimit()
Computes the conjunction of two BDDs f and g unless too many nodes are required.
- Returns
- a pointer to the resulting BDD if successful; NULL if the intermediate result blows up or more new nodes than
limitare required.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_bddAnd
- Parameters
-
dd manager f first operand g second operand limit maximum number of new nodes
◆ Cudd_bddApproxConjDecomp()
Performs two-way conjunctive decomposition of a BDD.
This procedure owes its name to the use of supersetting to obtain an initial factor of the given function. The conjuncts produced by this procedure tend to be imbalanced.
- Returns
- the number of conjuncts produced, that is, 2 if successful; 1 if no meaningful decomposition was found; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects The factors are returned in an array as side effects.
- The array is allocated by this function. It is the caller's responsibility to free it. On successful completion, the conjuncts are already referenced. If the function returns 0, the array for the conjuncts is not allocated. If the function returns 1, the only factor equals the function to be decomposed.
- See also
- Cudd_bddApproxDisjDecomp Cudd_bddIterConjDecomp Cudd_bddGenConjDecomp Cudd_bddVarConjDecomp Cudd_RemapOverApprox Cudd_bddSqueeze Cudd_bddLICompaction
- Parameters
-
dd manager f function to be decomposed conjuncts address of the first factor
◆ Cudd_bddApproxDisjDecomp()
Performs two-way disjunctive decomposition of a BDD.
The disjuncts produced by this procedure tend to be imbalanced.
- Returns
- the number of disjuncts produced, that is, 2 if successful; 1 if no meaningful decomposition was found; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects The two disjuncts are returned in an array as side effects.
- The array is allocated by this function. It is the caller's responsibility to free it. On successful completion, the disjuncts are already referenced. If the function returns 0, the array for the disjuncts is not allocated. If the function returns 1, the only factor equals the function to be decomposed.
- Parameters
-
dd manager f function to be decomposed disjuncts address of the array of the disjuncts
◆ Cudd_bddBindVar()
| int Cudd_bddBindVar | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| int | index | ||
| ) |
Prevents sifting of a variable.
This function sets a flag to prevent sifting of a variable.
- Returns
- 1 if successful; 0 otherwise (i.e., invalid variable index).
- Side effects Changes the "bindVar" flag in DdSubtable.
- See also
- Cudd_bddUnbindVar
- Parameters
-
dd manager index variable index
◆ Cudd_bddBooleanDiff()
Computes the boolean difference of f with respect to x.
Computes the boolean difference of f with respect to the variable with index x.
- Returns
- the BDD of the boolean difference if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_bddCharToVect()
Computes a vector of BDDs whose image equals a non-zero function.
The result depends on the variable order. The i-th component of the vector depends only on the first i variables in the order. Each BDD in the vector is not larger than the BDD of the given characteristic function. This function is based on the description of char-to-vect in "Verification of Sequential Machines Using Boolean Functional Vectors" by O. Coudert, C. Berthet and J. C. Madre.
- Returns
- a pointer to an array containing the result if successful; NULL otherwise. The size of the array equals the number of variables in the manager. The components of the solution have their reference counts already incremented (unlike the results of most other functions in the package).
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_bddConstrain
◆ Cudd_bddClippingAnd()
Approximates the conjunction of two BDDs f and g.
- Returns
- a pointer to the resulting BDD if successful; NULL if the intermediate result blows up.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_bddAnd
- Parameters
-
dd manager f first conjunct g second conjunct maxDepth maximum recursion depth direction under (0) or over (1) approximation
◆ Cudd_bddClippingAndAbstract()
| DdNode* Cudd_bddClippingAndAbstract | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| DdNode * | f, | ||
| DdNode * | g, | ||
| DdNode * | cube, | ||
| int | maxDepth, | ||
| int | direction | ||
| ) |
Approximates the conjunction of two BDDs f and g and simultaneously abstracts the variables in cube.
The variables are existentially abstracted.
- Returns
- a pointer to the resulting BDD if successful; NULL if the intermediate result blows up.
- Side effects None
- Parameters
-
dd manager f first conjunct g second conjunct cube cube of variables to be abstracted maxDepth maximum recursion depth direction under (0) or over (1) approximation
◆ Cudd_bddClosestCube()
Finds a cube of f at minimum Hamming distance from the minterms of g.
All the minterms of the cube are at the minimum distance. If the distance is 0, the cube belongs to the intersection of f and g.
- Returns
- the cube if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects The distance is returned as a side effect.
- See also
- Cudd_MinHammingDist
◆ Cudd_bddCompose()
Substitutes g for x_v in the BDD for f.
v is the index of the variable to be substituted. Cudd_bddCompose passes the corresponding projection function to the recursive procedure, so that the cache may be used.
- Returns
- the composed BDD if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_addCompose
◆ Cudd_bddComputeCube()
Computes the cube of an array of BDD variables.
If non-null, the phase argument indicates which literal of each variable should appear in the cube. If phase[i] is nonzero, then the positive literal is used. If phase is NULL, the cube is positive unate.
- Returns
- a pointer to the result if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_bddConstrain()
Computes f constrain c.
Computes f constrain c (f @ c). Uses a canonical form: (f' @ c) = (f @ c)'. (Note: this is not true for c.) List of special cases:
- f @ 0 = 0
- f @ 1 = f
- 0 @ c = 0
- 1 @ c = 1
- f @ f = 1
- f @ f'= 0
Note that if F=(f1,...,fn) and reordering takes place while computing F @ c, then the image restriction property (Img(F,c) = Img(F @ c)) is lost.
- Returns
- a pointer to the result if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_bddRestrict Cudd_addConstrain
◆ Cudd_bddConstrainDecomp()
BDD conjunctive decomposition as in McMillan's CAV96 paper.
The decomposition is canonical only for a given variable order. If canonicity is required, variable ordering must be disabled after the decomposition has been computed. The components of the solution have their reference counts already incremented (unlike the results of most other functions in the package).
- Returns
- an array with one entry for each BDD variable in the manager if successful; otherwise NULL.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_bddCorrelation()
Computes the correlation of f and g.
If f == g, their correlation is 1. If f == g', their correlation is 0.
- Returns
- the fraction of minterms in the ON-set of the EXNOR of f and g. If it runs out of memory, returns (double)CUDD_OUT_OF_MEM.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_bddCorrelationWeights
◆ Cudd_bddCorrelationWeights()
Computes the correlation of f and g for given input probabilities.
On input, prob[i] is supposed to contain the probability of the i-th input variable to be 1. If f == g, their correlation is
- If f == g', their correlation is 0. The correlation of f and the constant one gives the probability of f.
- Returns
- the probability that f and g have the same value. If it runs out of memory, returns (double)CUDD_OUT_OF_MEM.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_bddCorrelation
◆ Cudd_bddExistAbstract()
Existentially abstracts all the variables in cube from f.
- Returns
- the abstracted BDD if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_bddExistAbstractLimit()
| DdNode* Cudd_bddExistAbstractLimit | ( | DdManager * | manager, |
| DdNode * | f, | ||
| DdNode * | cube, | ||
| unsigned int | limit | ||
| ) |
Existentially abstracts all the variables in cube from f.
- Returns
- the abstracted BDD if successful; NULL if the intermediate result blows up or more new nodes than
limitare required.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_bddExistAbstract
◆ Cudd_bddGenConjDecomp()
Performs two-way conjunctive decomposition of a BDD.
This procedure owes its name to the fact tht it generalizes the decomposition based on the cofactors with respect to one variable. The conjuncts produced by this procedure tend to be balanced.
- Returns
- the number of conjuncts produced, that is, 2 if successful; 1 if no meaningful decomposition was found; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects The two factors are returned in an array as side effects.
- The array is allocated by this function. It is the caller's responsibility to free it. On successful completion, the conjuncts are already referenced. If the function returns 0, the array for the conjuncts is not allocated. If the function returns 1, the only factor equals the function to be decomposed.
- Parameters
-
dd manager f function to be decomposed conjuncts address of the array of conjuncts
◆ Cudd_bddGenDisjDecomp()
Performs two-way disjunctive decomposition of a BDD.
The disjuncts produced by this procedure tend to be balanced.
- Returns
- the number of disjuncts produced, that is, 2 if successful; 1 if no meaningful decomposition was found; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects The two disjuncts are returned in an array as side effects.
- The array is allocated by this function. It is the caller's responsibility to free it. On successful completion, the disjuncts are already referenced. If the function returns 0, the array for the disjuncts is not allocated. If the function returns 1, the only factor equals the function to be decomposed.
- Parameters
-
dd manager f function to be decomposed disjuncts address of the array of the disjuncts
◆ Cudd_bddInterpolate()
Finds an interpolant of two functions.
Given BDDs l and u, representing the lower bound and upper bound of a function interval, Cudd_bddInterpolate produces the BDD of a function within the interval that only depends on the variables common to l and u.
The approach is based on quantification as in Cudd_bddRestrict(). The function assumes that l implies u, but does not check whether that's true.
- Returns
- a pointer to the result if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_bddRestrict Cudd_bddSqueeze
- Parameters
-
dd manager l lower bound u upper bound
◆ Cudd_bddIntersect()
Returns a function included in the intersection of f and g.
The function computed (if not zero) is a witness that the intersection is not empty. Cudd_bddIntersect tries to build as few new nodes as possible. If the only result of interest is whether f and g intersect, Cudd_bddLeq should be used instead.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_bddLeq Cudd_bddIteConstant
- Parameters
-
dd manager f first operand g second operand
◆ Cudd_bddInterval()
| DdNode* Cudd_bddInterval | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| int | N, | ||
| DdNode ** | x, | ||
| unsigned int | lowerB, | ||
| unsigned int | upperB | ||
| ) |
Generates a BDD for the function lowerB ≤ x ≤ upperB.
This function generates a BDD for the function lowerB ≤ x ≤ upperB, where x is an N-bit number, x[0] x[1] ... x[N-1], with 0 the most significant bit (important!). The number of variables N should be sufficient to represent the bounds; otherwise, the bounds are truncated to their N least significant bits. Two BDDs are built bottom-up for lowerB ≤ x and x ≤ upperB, and they are finally conjoined.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_Xgty
- Parameters
-
dd DD manager N number of x variables x array of x variables lowerB lower bound upperB upper bound
◆ Cudd_bddIsNsVar()
| int Cudd_bddIsNsVar | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| int | index | ||
| ) |
Checks whether a variable is next state.
- Returns
- 1 if the variable's type is present state; 0 if the variable exists but is not a present state; -1 if the variable does not exist.
- Side effects none
◆ Cudd_bddIsop()
Computes a BDD in the interval between L and U with a simple sum-of-product cover.
This procedure is similar to Cudd_zddIsop, but it does not return the ZDD for the cover.
- Returns
- a pointer to the BDD if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_zddIsop
◆ Cudd_bddIsPiVar()
| int Cudd_bddIsPiVar | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| int | index | ||
| ) |
Checks whether a variable is primary input.
- Returns
- 1 if the variable's type is primary input; 0 if the variable exists but is not a primary input; -1 if the variable does not exist.
- Side effects none
- Parameters
-
dd manager index variable index
◆ Cudd_bddIsPsVar()
| int Cudd_bddIsPsVar | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| int | index | ||
| ) |
Checks whether a variable is present state.
- Returns
- 1 if the variable's type is present state; 0 if the variable exists but is not a present state; -1 if the variable does not exist.
- Side effects none
◆ Cudd_bddIsVar()
Returns 1 if the given node is a BDD variable; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_bddIsVarEssential()
Determines whether a given variable is essential with a given phase in a BDD.
Uses Cudd_bddIteConstant. Returns 1 if phase == 1 and f–>x_id, or if phase == 0 and f–>x_id'.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_FindEssential
◆ Cudd_bddIsVarHardGroup()
| int Cudd_bddIsVarHardGroup | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| int | index | ||
| ) |
Checks whether a variable is set to be in a hard group.
This function is used for lazy sifting.
- Returns
- 1 if the variable is marked to be in a hard group; 0 if the variable exists, but it is not marked to be in a hard group; -1 if the variable does not exist.
- Side effects none
- See also
- Cudd_bddSetVarHardGroup
◆ Cudd_bddIsVarToBeGrouped()
| int Cudd_bddIsVarToBeGrouped | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| int | index | ||
| ) |
Checks whether a variable is set to be grouped.
This function is used for lazy sifting.
- Side effects none
◆ Cudd_bddIsVarToBeUngrouped()
| int Cudd_bddIsVarToBeUngrouped | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| int | index | ||
| ) |
Checks whether a variable is set to be ungrouped.
This function is used for lazy sifting.
- Returns
- 1 if the variable is marked to be ungrouped; 0 if the variable exists, but it is not marked to be ungrouped; -1 if the variable does not exist.
- Side effects none
- See also
- Cudd_bddSetVarToBeUngrouped
◆ Cudd_bddIte()
Implements ITE(f,g,h).
- Returns
- a pointer to the resulting BDD if successful; NULL if the intermediate result blows up.
- Side effects None
- Parameters
-
dd manager f first operand g second operand h third operand
◆ Cudd_bddIteConstant()
Implements ITEconstant(f,g,h).
- Returns
- a pointer to the resulting BDD (which may or may not be constant) or DD_NON_CONSTANT.
No new nodes are created.
- Side effects None
- Parameters
-
dd manager f first operand g second operand h thord operand
◆ Cudd_bddIteLimit()
Implements ITE(f,g,h) unless too many nodes are required.
- Returns
- a pointer to the resulting BDD if successful; NULL if the intermediate result blows up or more new nodes than
limitare required.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_bddIte
- Parameters
-
dd manager f first operand g second operand h third operand limit maximum number of new nodes
◆ Cudd_bddIterConjDecomp()
Performs two-way conjunctive decomposition of a BDD.
This procedure owes its name to the iterated use of supersetting to obtain a factor of the given function. The conjuncts produced by this procedure tend to be imbalanced.
- Returns
- the number of conjuncts produced, that is, 2 if successful; 1 if no meaningful decomposition was found; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects The factors are returned in an array as side effects.
- The array is allocated by this function. It is the caller's responsibility to free it. On successful completion, the conjuncts are already referenced. If the function returns 0, the array for the conjuncts is not allocated. If the function returns 1, the only factor equals the function to be decomposed.
- See also
- Cudd_bddIterDisjDecomp Cudd_bddApproxConjDecomp Cudd_bddGenConjDecomp Cudd_bddVarConjDecomp Cudd_RemapOverApprox Cudd_bddSqueeze Cudd_bddLICompaction
- Parameters
-
dd manager f function to be decomposed conjuncts address of the array of conjuncts
◆ Cudd_bddIterDisjDecomp()
Performs two-way disjunctive decomposition of a BDD.
The disjuncts produced by this procedure tend to be imbalanced.
- Returns
- the number of disjuncts produced, that is, 2 if successful; 1 if no meaningful decomposition was found; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects The two disjuncts are returned in an array as side effects.
- The array is allocated by this function. It is the caller's responsibility to free it. On successful completion, the disjuncts are already referenced. If the function returns 0, the array for the disjuncts is not allocated. If the function returns 1, the only factor equals the function to be decomposed.
- Parameters
-
dd manager f function to be decomposed disjuncts address of the array of the disjuncts
◆ Cudd_bddIthVar()
Returns the BDD variable with index i.
Retrieves the BDD variable with index i if it already exists, or creates a new BDD variable.
- Returns
- a pointer to the variable if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_bddLargestPrimeUnate()
Find a largest prime implicant of a unate function.
The behavior is undefined if f is not unate. The third argument is used to determine whether f is unate positive (increasing) or negative (decreasing) in each of the variables in its support.
- Returns
- the BDD for the prime if succesful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_bddMaximallyExpand
- Parameters
-
dd manager f unate function phaseBdd cube of the phases
◆ Cudd_bddLeq()
Checks whether f is less than or equal to g.
- Returns
- 1 if f is less than or equal to g; 0 otherwise.
No new nodes are created.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_bddIteConstant Cudd_addEvalConst
- Parameters
-
dd manager f first operand g second operand
◆ Cudd_bddLeqUnless()
Tells whether f is less than of equal to G unless D is 1.
f, g, and D are BDDs. No new nodes are created.
- Returns
- 1 if f is less than of equal to G, and 0 otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_bddLICompaction()
Performs safe minimization of a BDD.
Given the BDD f of a function to be minimized and a BDD c representing the care set, Cudd_bddLICompaction produces the BDD of a function that agrees with f wherever c is 1. Safe minimization means that the size of the result is guaranteed not to exceed the size of f. This function is based on the DAC97 paper by Hong et al..
- Returns
- a pointer to the result if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_bddRestrict
- Parameters
-
dd manager f function to be minimized c constraint (care set)
◆ Cudd_bddLiteralSetIntersection()
Computes the intesection of two sets of literals represented as BDDs.
Each set is represented as a cube of the literals in the set. The empty set is represented by the constant 1. No variable can be simultaneously present in both phases in a set.
- Returns
- a pointer to the BDD representing the intersected sets, if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_bddMakePrime()
Expands cube to a prime implicant of f.
- Returns
- the prime if successful; NULL otherwise. In particular, NULL is returned if cube is not a real cube or is not an implicant of f.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_bddMaximallyExpand
- Parameters
-
dd manager cube cube to be expanded f function of which the cube is to be made a prime
◆ Cudd_bddMaximallyExpand()
Expands lb to prime implicants of (f and ub).
Expands lb to all prime implicants of (f and ub) that contain lb. Assumes that lb is contained in ub.
- Returns
- the disjunction of the primes if lb is contained in f; returns the zero BDD if lb is not contained in f; returns NULL in case of failure. In particular, NULL is returned if cube is not a real cube or is not an implicant of f. Returning the disjunction of all prime implicants works because the resulting function is unate.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_bddMakePrime
- Parameters
-
dd manager lb cube to be expanded ub upper bound cube f function against which to expand
◆ Cudd_bddMinimize()
Finds a small BDD that agrees with f over c.
- Returns
- a pointer to the result if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_bddNand()
Computes the NAND of two BDDs f and g.
- Returns
- a pointer to the resulting BDD if successful; NULL if the intermediate result blows up.
- Side effects None
- Parameters
-
dd manager f first operand g second operand
◆ Cudd_bddNewVar()
Returns a new BDD variable.
The new variable has an index equal to the largest previous index plus 1.
- Returns
- a pointer to the new variable if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_bddNewVarAtLevel()
Returns a new BDD variable at a specified level.
The new variable has an index equal to the largest previous index plus 1 and is positioned at the specified level in the order.
- Returns
- a pointer to the new variable if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_bddNor()
Computes the NOR of two BDDs f and g.
- Returns
- a pointer to the resulting BDD if successful; NULL if the intermediate result blows up.
- Side effects None
- Parameters
-
dd manager f first operand g second operand
◆ Cudd_bddNPAnd()
Computes f non-polluting-and g.
The non-polluting AND of f and g is a hybrid of AND and Restrict. From Restrict, this operation takes the idea of existentially quantifying the top variable of the second operand if it does not appear in the first. Therefore, the variables that appear in the result also appear in f. For the rest, the function behaves like AND. Since the two operands play different roles, non-polluting AND is not commutative.
- Returns
- a pointer to the result if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_bddConstrain Cudd_bddRestrict
◆ Cudd_bddOr()
Computes the disjunction of two BDDs f and g.
- Returns
- a pointer to the resulting BDD if successful; NULL if the intermediate result blows up.
- Side effects None
- Parameters
-
dd manager f first operand g second operand
◆ Cudd_bddOrLimit()
Computes the disjunction of two BDDs f and g unless too many nodes are required.
- Returns
- a pointer to the resulting BDD if successful; NULL if the intermediate result blows up or more new nodes than
limitare required.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_bddOr
- Parameters
-
dd manager f first operand g second operand limit maximum number of new nodes
◆ Cudd_bddPermute()
Permutes the variables of a BDD.
Given a permutation in array permut, creates a new BDD with permuted variables. There should be an entry in array permut for each variable in the manager. The i-th entry of permut holds the index of the variable that is to substitute the i-th variable.
- Returns
- a pointer to the resulting BDD if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_addPermute Cudd_bddSwapVariables
◆ Cudd_bddPickArbitraryMinterms()
Picks k on-set minterms evenly distributed from given DD.
The minterms are in terms of vars. The array vars should contain at least all variables in the support of f; if this condition is not met the minterms built by this procedure may not be contained in f.
- Returns
- an array of BDDs for the minterms if successful; NULL otherwise. There are three reasons why the procedure may fail:
- It may run out of memory;
-
the function
fmay be the constant 0; -
the minterms may not be contained in
f.
- Side effects None
- Parameters
-
dd manager f function from which to pick k minterms vars array of variables n size of varsk number of minterms to find
◆ Cudd_bddPickOneCube()
Picks one on-set cube randomly from the given DD.
The cube is written into an array of characters. The array must have at least as many entries as there are variables.
- Returns
- 1 if successful; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_bddPickOneMinterm
◆ Cudd_bddPickOneMinterm()
Picks one on-set minterm randomly from the given DD.
The minterm is in terms of vars. The array vars should contain at least all variables in the support of f; if this condition is not met the minterm built by this procedure may not be contained in f.
- Returns
- a pointer to the BDD for the minterm if successful; NULL otherwise. There are three reasons why the procedure may fail:
- It may run out of memory;
-
the function
fmay be the constant 0; -
the minterm may not be contained in
f.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_bddPickOneCube
- Parameters
-
dd manager f function from which to pick one minterm vars array of variables n size of vars
◆ Cudd_bddPrintCover()
Prints a sum of prime implicants of a BDD.
Prints a sum of product cover for an incompletely specified function given by a lower bound and an upper bound. Each product is a prime implicant obtained by expanding the product corresponding to a path from node to the constant one. Uses the package default output file.
- Returns
- 1 if successful; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_PrintMinterm
◆ Cudd_bddRead()
| int Cudd_bddRead | ( | FILE * | fp, |
| DdManager * | dd, | ||
| DdNode ** | E, | ||
| DdNode *** | x, | ||
| DdNode *** | y, | ||
| int * | nx, | ||
| int * | ny, | ||
| int * | m, | ||
| int * | n, | ||
| int | bx, | ||
| int | sx, | ||
| int | by, | ||
| int | sy | ||
| ) |
Reads in a graph (without labels) given as a list of arcs.
Reads in a graph (without labels) given as an adjacency matrix. The first line of the input contains the numbers of rows and columns of the adjacency matrix. The remaining lines contain the arcs of the graph, one per line. Each arc is described by two integers, i.e., the row and column number, or the indices of the two endpoints. Cudd_bddRead produces a BDD that depends on two sets of variables: x and y. The x variables (x[0] ... x[nx-1]) encode the row index and the y variables (y[0] ... y[ny-1]) encode the column index. x[0] and y[0] are the most significant bits in the indices. The variables may already exist or may be created by the function. The index of x[i] is bx+i*sx, and the index of y[i] is by+i*sy.
On input, nx and ny hold the numbers of row and column variables already in existence. On output, they hold the numbers of row and column variables actually used by the matrix. When Cudd_bddRead creates the variable arrays, the index of x[i] is bx+i*sx, and the index of y[i] is by+i*sy. When some variables already exist, Cudd_bddRead expects the indices of the existing x variables to be bx+i*sx, and the indices of the existing y variables to be by+i*sy.
m and n are set to the numbers of rows and columns of the matrix. Their values on input are immaterial. The BDD for the graph is returned in E, and its reference count is > 0.
- Returns
- 1 in case of success; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects nx and ny are set to the numbers of row and column
- variables. m and n are set to the numbers of rows and columns. x and y are possibly extended to represent the array of row and column variables.
- See also
- Cudd_addHarwell Cudd_addRead
- Parameters
-
fp input file pointer dd DD manager E characteristic function of the graph x array of row variables y array of column variables nx number or row variables ny number or column variables m number of rows n number of columns bx first index of row variables sx step of row variables by first index of column variables sy step of column variables
◆ Cudd_bddReadPairIndex()
| int Cudd_bddReadPairIndex | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| int | index | ||
| ) |
Reads a corresponding pair index for a given index.
These pair indices are present and next state variable.
- Returns
- the corresponding variable index if the variable exists; -1 otherwise.
- Side effects modifies the manager
- See also
- Cudd_bddSetPairIndex
◆ Cudd_bddRealignDisable()
| void Cudd_bddRealignDisable | ( | DdManager * | unique | ) |
Disables realignment of ZDD order to BDD order.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_bddRealignEnable()
| void Cudd_bddRealignEnable | ( | DdManager * | unique | ) |
Enables realignment of BDD order to ZDD order.
Enables realignment of the BDD variable order to the ZDD variable order after the ZDDs have been reordered. The number of ZDD variables must be a multiple of the number of BDD variables for realignment to make sense. If this condition is not met, Cudd_zddReduceHeap will return 0. Let M be the ratio of the two numbers. For the purpose of realignment, the ZDD variables from M*i to (M+1)*i-1 are reagarded as corresponding to BDD variable i. Realignment is initially disabled.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_bddRealignmentEnabled()
| int Cudd_bddRealignmentEnabled | ( | DdManager * | unique | ) |
Tells whether the realignment of BDD order to ZDD order is enabled.
- Returns
- 1 if the realignment of BDD order to ZDD order is enabled; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_bddResetVarToBeGrouped()
| int Cudd_bddResetVarToBeGrouped | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| int | index | ||
| ) |
Resets a variable not to be grouped.
This function is used for lazy sifting.
- Returns
- 1 if successful; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects modifies the manager
◆ Cudd_bddRestrict()
BDD restrict according to Coudert and Madre's algorithm (ICCAD90).
If application of restrict results in a BDD larger than the input BDD, the input BDD is returned.
- Returns
- the restricted BDD if successful; otherwise NULL.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_bddConstrain Cudd_addRestrict
◆ Cudd_bddSetNsVar()
| int Cudd_bddSetNsVar | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| int | index | ||
| ) |
Sets a variable type to next state.
The variable type is used by lazy sifting.
- Returns
- 1 if successful; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects modifies the manager
- Parameters
-
dd manager index variable index
◆ Cudd_bddSetPairIndex()
| int Cudd_bddSetPairIndex | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| int | index, | ||
| int | pairIndex | ||
| ) |
Sets a corresponding pair index for a given index.
These pair indices are present and next state variable.
- Returns
- 1 if successful; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects modifies the manager
- See also
- Cudd_bddReadPairIndex
- Parameters
-
dd manager index variable index pairIndex corresponding variable index
◆ Cudd_bddSetPiVar()
| int Cudd_bddSetPiVar | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| int | index | ||
| ) |
Sets a variable type to primary input.
The variable type is used by lazy sifting.
- Returns
- 1 if successful; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects modifies the manager
- Parameters
-
dd manager index variable index
◆ Cudd_bddSetPsVar()
| int Cudd_bddSetPsVar | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| int | index | ||
| ) |
Sets a variable type to present state.
The variable type is used by lazy sifting.
- Returns
- 1 if successful; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects modifies the manager
- Parameters
-
dd manager index variable index
◆ Cudd_bddSetVarHardGroup()
| int Cudd_bddSetVarHardGroup | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| int | index | ||
| ) |
Sets a variable to be a hard group.
This function is used for lazy sifting.
- Returns
- 1 if successful; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects modifies the manager
◆ Cudd_bddSetVarToBeGrouped()
| int Cudd_bddSetVarToBeGrouped | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| int | index | ||
| ) |
Sets a variable to be grouped.
This function is used for lazy sifting.
- Returns
- 1 if successful; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects modifies the manager
◆ Cudd_bddSetVarToBeUngrouped()
| int Cudd_bddSetVarToBeUngrouped | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| int | index | ||
| ) |
Sets a variable to be ungrouped.
This function is used for lazy sifting.
- Returns
- 1 if successful; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects modifies the manager
- See also
- Cudd_bddIsVarToBeUngrouped
◆ Cudd_bddSqueeze()
Finds a small BDD in a function interval.
Given BDDs l and u, representing the lower bound and upper bound of a function interval, Cudd_bddSqueeze produces the BDD of a function within the interval with a small BDD.
- Returns
- a pointer to the result if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_bddRestrict Cudd_bddLICompaction
- Parameters
-
dd manager l lower bound u upper bound
◆ Cudd_bddSwapVariables()
Swaps two sets of variables of the same size (x and y) in the BDD f.
The size is given by n. The two sets of variables are assumed to be disjoint.
- Returns
- a pointer to the resulting BDD if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_bddPermute Cudd_addSwapVariables
◆ Cudd_BddToAdd()
Converts a BDD to a 0-1 ADD.
- Returns
- a pointer to the resulting ADD if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_BddToCubeArray()
Builds a positional array from the BDD of a cube.
Array must have one entry for each BDD variable. The positional array has 1 in i-th position if the variable of index i appears in true form in the cube; it has 0 in i-th position if the variable of index i appears in complemented form in the cube; finally, it has 2 in i-th position if the variable of index i does not appear in the cube.
- Returns
- 1 if successful (the BDD is indeed a cube); 0 otherwise.
- Side effects The result is in the array passed by reference.
- See also
- Cudd_CubeArrayToBdd
◆ Cudd_bddTransfer()
Convert a BDD from a manager to another one.
The orders of the variables in the two managers may be different.
- Returns
- a pointer to the BDD in the destination manager if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_bddUnbindVar()
| int Cudd_bddUnbindVar | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| int | index | ||
| ) |
Allows the sifting of a variable.
This function resets the flag that prevents the sifting of a variable. In successive variable reorderings, the variable will NOT be skipped, that is, sifted. Initially all variables can be sifted. It is necessary to call this function only to re-enable sifting after a call to Cudd_bddBindVar.
- Returns
- 1 if successful; 0 otherwise (i.e., invalid variable index).
- Side effects Changes the "bindVar" flag in DdSubtable.
- See also
- Cudd_bddBindVar
- Parameters
-
dd manager index variable index
◆ Cudd_bddUnivAbstract()
Universally abstracts all the variables in cube from f.
- Returns
- the abstracted BDD if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_bddVarConjDecomp()
Performs two-way conjunctive decomposition of a BDD.
Conjunctively decomposes one BDD according to a variable. If f is the function of the BDD and x is the variable, the decomposition is (f+x)(f+x'). The variable is chosen so as to balance the sizes of the two conjuncts and to keep them small.
- Returns
- the number of conjuncts produced, that is, 2 if successful; 1 if no meaningful decomposition was found; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects The two factors are returned in an array as side effects.
- The array is allocated by this function. It is the caller's responsibility to free it. On successful completion, the conjuncts are already referenced. If the function returns 0, the array for the conjuncts is not allocated. If the function returns 1, the only factor equals the function to be decomposed.
- Parameters
-
dd manager f function to be decomposed conjuncts address of the array of conjuncts
◆ Cudd_bddVarDisjDecomp()
Performs two-way disjunctive decomposition of a BDD.
Performs two-way disjunctive decomposition of a BDD according to a variable. If f is the function of the BDD and x is the variable, the decomposition is f*x + f*x'. The variable is chosen so as to balance the sizes of the two disjuncts and to keep them small.
- Returns
- the number of disjuncts produced, that is, 2 if successful; 1 if no meaningful decomposition was found; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects The two disjuncts are returned in an array as side effects.
- The array is allocated by this function. It is the caller's responsibility to free it. On successful completion, the disjuncts are already referenced. If the function returns 0, the array for the disjuncts is not allocated. If the function returns 1, the only factor equals the function to be decomposed.
- Parameters
-
dd manager f function to be decomposed disjuncts address of the array of the disjuncts
◆ Cudd_bddVarIsBound()
| int Cudd_bddVarIsBound | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| int | index | ||
| ) |
Tells whether a variable can be sifted.
This function returns 1 if a variable is enabled for sifting. Initially all variables can be sifted. This function returns 0 if there has been a previous call to Cudd_bddBindVar for that variable not followed by a call to Cudd_bddUnbindVar. The function returns 0 also in the case in which the index of the variable is out of bounds.
- Side effects none
- See also
- Cudd_bddBindVar Cudd_bddUnbindVar
- Parameters
-
dd manager index variable index
◆ Cudd_bddVarIsDependent()
Checks whether a variable is dependent on others in a function.
No new nodes are created.
- Returns
- 1 if the variable is dependent; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects None
- Parameters
-
dd manager f function var variable
◆ Cudd_bddVarMap()
Remaps the variables of a BDD using the default variable map.
A typical use of this function is to swap two sets of variables. The variable map must be registered with Cudd_SetVarMap.
- Returns
- a pointer to the resulting BDD if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- Parameters
-
manager DD manager f function in which to remap variables
◆ Cudd_bddVectorCompose()
Composes a BDD with a vector of BDDs.
Given a vector of BDDs, creates a new BDD by substituting the BDDs for the variables of the BDD f. There should be an entry in vector for each variable in the manager. If no substitution is sought for a given variable, the corresponding projection function should be specified in the vector. This function implements simultaneous composition.
- Returns
- a pointer to the resulting BDD if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_bddXnor()
Computes the exclusive NOR of two BDDs f and g.
- Returns
- a pointer to the resulting BDD if successful; NULL if the intermediate result blows up.
- Side effects None
- Parameters
-
dd manager f first operand g second operand
◆ Cudd_bddXnorLimit()
Computes the exclusive NOR of two BDDs f and g unless too many nodes are required.
- Returns
- a pointer to the resulting BDD if successful; NULL if the intermediate result blows up or more new nodes than
limitare required.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_bddXnor
- Parameters
-
dd manager f first operand g second operand limit maximum number of new nodes
◆ Cudd_bddXor()
Computes the exclusive OR of two BDDs f and g.
- Returns
- a pointer to the resulting BDD if successful; NULL if the intermediate result blows up.
- Side effects None
- Parameters
-
dd manager f first operand g second operand
◆ Cudd_bddXorExistAbstract()
Takes the exclusive OR of two BDDs and simultaneously abstracts the variables in cube.
The variables are existentially abstracted.
- Returns
- a pointer to the result is successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_BiasedOverApprox()
| DdNode* Cudd_BiasedOverApprox | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| DdNode * | f, | ||
| DdNode * | b, | ||
| int | numVars, | ||
| int | threshold, | ||
| double | quality1, | ||
| double | quality0 | ||
| ) |
Extracts a dense superset from a BDD with the biased underapproximation method.
The procedure is identical to the underapproximation procedure except for the fact that it works on the complement of the given function. Extracting the subset of the complement function is equivalent to extracting the superset of the function. The parameter numVars is the maximum number of variables to be used in minterm calculation. The optimal number should be as close as possible to the size of the support of f. However, it is safe to pass the value returned by Cudd_ReadSize for numVars when the number of variables is under 1023. If numVars is larger than 1023, it will overflow. If a 0 parameter is passed then the procedure will compute a value which will avoid overflow but will cause underflow with 2046 variables or more.
- Returns
- a pointer to the BDD of the superset if successful. NULL if intermediate result causes the procedure to run out of memory.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_SupersetHeavyBranch Cudd_SupersetShortPaths Cudd_RemapOverApprox Cudd_BiasedUnderApprox Cudd_ReadSize
- Parameters
-
dd manager f function to be superset b bias function numVars number of variables in the support of f threshold when to stop approximation quality1 minimum improvement for accepted changes when b=1 quality0 minimum improvement for accepted changes when b=0
◆ Cudd_BiasedUnderApprox()
| DdNode* Cudd_BiasedUnderApprox | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| DdNode * | f, | ||
| DdNode * | b, | ||
| int | numVars, | ||
| int | threshold, | ||
| double | quality1, | ||
| double | quality0 | ||
| ) |
Extracts a dense subset from a BDD with the biased underapproximation method.
This procedure uses a biased remapping technique and density as the cost function. The bias is a function. This procedure tries to approximate where the bias is 0 and preserve the given function where the bias is 1. The parameter numVars is the maximum number of variables to be used in minterm calculation. The optimal number should be as close as possible to the size of the support of f. However, it is safe to pass the value returned by Cudd_ReadSize for numVars when the number of variables is under 1023. If numVars is larger than 1023, it will cause overflow. If a 0 parameter is passed then the procedure will compute a value which will avoid overflow but will cause underflow with 2046 variables or more.
- Returns
- a pointer to the BDD of the subset if successful. NULL if the procedure runs out of memory.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_SubsetShortPaths Cudd_SubsetHeavyBranch Cudd_UnderApprox Cudd_RemapUnderApprox Cudd_ReadSize
- Parameters
-
dd manager f function to be subset b bias function numVars number of variables in the support of f threshold when to stop approximation quality1 minimum improvement for accepted changes when b=1 quality0 minimum improvement for accepted changes when b=0
◆ Cudd_CheckCube()
Checks whether g is the BDD of a cube.
The constant 1 is a valid cube, but all other constant functions cause cuddCheckCube to return 0.
- Returns
- 1 in case of success; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_CheckKeys()
| int Cudd_CheckKeys | ( | DdManager * | table | ) |
Checks for several conditions that should not occur.
Checks for the following conditions:
- Wrong sizes of subtables.
- Wrong number of keys found in unique subtable.
- Wrong number of dead found in unique subtable.
- Wrong number of keys found in the constant table
- Wrong number of dead found in the constant table
- Wrong number of total slots found
- Wrong number of maximum keys found
- Wrong number of total dead found
Reports the average length of non-empty lists.
- Returns
- the number of subtables for which the number of keys is wrong.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_DebugCheck
◆ Cudd_CheckZeroRef()
| int Cudd_CheckZeroRef | ( | DdManager * | manager | ) |
Checks the unique table for nodes with non-zero reference counts.
It is normally called before Cudd_Quit to make sure that there are no memory leaks due to missing Cudd_RecursiveDeref's. Takes into account that reference counts may saturate and that the basic constants and the projection functions are referenced by the manager.
- Returns
- the number of nodes with non-zero reference count. (Except for the cases mentioned above.)
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_ClassifySupport()
| int Cudd_ClassifySupport | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| DdNode * | f, | ||
| DdNode * | g, | ||
| DdNode ** | common, | ||
| DdNode ** | onlyF, | ||
| DdNode ** | onlyG | ||
| ) |
Classifies the variables in the support of two DDs.
Classifies the variables in the support of two DDs f and g, depending on whether they appear in both DDs, only in f, or only in g.
- Returns
- 1 if successful; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects The cubes of the three classes of variables are
- returned as side effects.
- See also
- Cudd_Support Cudd_VectorSupport
- Parameters
-
dd manager f first DD g second DD common cube of shared variables onlyF cube of variables only in f onlyG cube of variables only in g
◆ Cudd_ClearErrorCode()
| void Cudd_ClearErrorCode | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
◆ Cudd_Cofactor()
Computes the cofactor of f with respect to g.
g must be the BDD or the ADD of a cube.
- Returns
- a pointer to the cofactor if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_bddConstrain Cudd_bddRestrict
◆ Cudd_CofMinterm()
Computes the fraction of minterms in the on-set of all the positive cofactors of a BDD or ADD.
The array has as many positions as there are BDD variables in the manager plus one. The last position of the array contains the fraction of the minterms in the ON-set of the function represented by the BDD or ADD. The other positions of the array hold the variable signatures.
- Returns
- the pointer to an array of doubles if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_CountLeaves()
| int Cudd_CountLeaves | ( | DdNode * | node | ) |
Counts the number of leaves in a DD.
- Returns
- the number of leaves in the DD rooted at node if successful; CUDD_OUT_OF_MEM otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_PrintDebug
◆ Cudd_CountMinterm()
Counts the minterms of an ADD or BDD.
The function is assumed to depend on nvars variables. The minterm count is represented as a double; hence overflow is possible. For functions with many variables (more than 1023 if floating point conforms to IEEE 754), one should consider Cudd_ApaCountMinterm() or Cudd_EpdCountMinterm().
- Returns
- the number of minterms of the function rooted at node if successful; +infinity if the number of minterms is known to be larger than the maximum value representable as a double;
(double) CUDD_OUT_OF_MEMotherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_CountPath()
| double Cudd_CountPath | ( | DdNode * | node | ) |
Counts the paths of a DD.
Paths to all terminal nodes are counted. The path count is represented as a double; hence overflow is possible.
- Returns
- the number of paths of the function rooted at node if successful;
(double) CUDD_OUT_OF_MEMotherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_CountMinterm
◆ Cudd_CountPathsToNonZero()
| double Cudd_CountPathsToNonZero | ( | DdNode * | node | ) |
Counts the paths to a non-zero terminal of a DD.
The path count is represented as a double; hence overflow is possible.
- Returns
- the number of paths of the function rooted at node.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_CountMinterm Cudd_CountPath
◆ Cudd_CProjection()
Computes the compatible projection of R w.r.t. cube Y.
Computes the compatible projection of relation R with respect to cube Y. For a comparison between Cudd_CProjection and Cudd_PrioritySelect, see the documentation of the latter.
- Returns
- a pointer to the c-projection if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_PrioritySelect
◆ Cudd_CubeArrayToBdd()
Builds the BDD of a cube from a positional array.
The array must have one integer entry for each BDD variable. If the i-th entry is 1, the variable of index i appears in true form in the cube; If the i-th entry is 0, the variable of index i appears complemented in the cube; otherwise the variable does not appear in the cube.
- Returns
- a pointer to the BDD for the cube if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_DagSize()
| int Cudd_DagSize | ( | DdNode * | node | ) |
Counts the number of nodes in a DD.
- Returns
- the number of nodes in the graph rooted at node.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_SharingSize Cudd_PrintDebug
◆ Cudd_DeadAreCounted()
| int Cudd_DeadAreCounted | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Tells whether dead nodes are counted towards triggering reordering.
- Returns
- 1 if dead nodes are counted; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_DebugCheck()
| int Cudd_DebugCheck | ( | DdManager * | table | ) |
Checks for inconsistencies in the DD heap.
The following inconsistencies are checked:
- node has illegal index
- live node has dead children
- node has illegal Then or Else pointers
- BDD/ADD node has identical children
- ZDD node has zero then child
- wrong number of total nodes
- wrong number of dead nodes
- ref count error at node
- Returns
- 0 if no inconsistencies are found; DD_OUT_OF_MEM if there is not enough memory; 1 otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_CheckKeys
◆ Cudd_Decreasing()
Checks whether a BDD is negative unate in a variable.
Determines whether the function represented by BDD f is negative unate (monotonic decreasing) in variable i. This function does not generate any new nodes.
- Returns
- the constant one is f is unate and the (logical) constant zero if it is not.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_Increasing
◆ Cudd_DelayedDerefBdd()
Decreases the reference count of BDD node n.
Enqueues node n for later dereferencing. If the queue is full decreases the reference count of the oldest node N to make room for n. If N dies, recursively decreases the reference counts of its children. It is used to dispose of a BDD that is currently not needed, but may be useful again in the near future. The dereferencing proper is done as in Cudd_IterDerefBdd.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_RecursiveDeref Cudd_IterDerefBdd
◆ Cudd_Density()
Computes the density of a BDD or ADD.
The density is the ratio of the number of minterms to the number of nodes. If 0 is passed as number of variables, the number of variables existing in the manager is used.
- Returns
- the density if successful; (double) CUDD_OUT_OF_MEM otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_CountMinterm Cudd_DagSize
- Parameters
-
dd manager f function whose density is sought nvars size of the support of f
◆ Cudd_Deref()
| void Cudd_Deref | ( | DdNode * | node | ) |
Decreases the reference count of node.
It is primarily used in recursive procedures to decrease the ref count of a result node before returning it. This accomplishes the goal of removing the protection applied by a previous Cudd_Ref.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_DisableGarbageCollection()
| void Cudd_DisableGarbageCollection | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Disables garbage collection.
Garbage collection is initially enabled. This function may be called to disable it. However, garbage collection will still occur when a new node must be created and no memory is left, or when garbage collection is required for correctness. (E.g., before reordering.)
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_DisableOrderingMonitoring()
| int Cudd_DisableOrderingMonitoring | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Disables monitoring of ordering.
- Returns
- 1 if successful; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects Removes functions from the pre-reordering and post-reordering
- hooks.
- See also
- Cudd_EnableOrderingMonitoring
◆ Cudd_DisableReorderingReporting()
| int Cudd_DisableReorderingReporting | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Disables reporting of reordering stats.
- Returns
- 1 if successful; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects Removes functions from the pre-reordering and post-reordering
- hooks.
◆ Cudd_Disequality()
Generates a BDD for the function x - y != c.
This function generates a BDD for the function x -y != c. Both x and y are N-bit numbers, x[0] x[1] ... x[N-1] and y[0] y[1] ... y[N-1], with 0 the most significant bit. The BDD is built bottom-up. It has a linear number of nodes if the variables are ordered as follows: x[0] y[0] x[1] y[1] ... x[N-1] y[N-1].
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_Xgty
- Parameters
-
dd DD manager N number of x and y variables c right-hand side constant x array of x variables y array of y variables
◆ Cudd_DumpBlif()
| int Cudd_DumpBlif | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| int | n, | ||
| DdNode ** | f, | ||
| char const *const * | inames, | ||
| char const *const * | onames, | ||
| char * | mname, | ||
| FILE * | fp, | ||
| int | mv | ||
| ) |
Writes a blif file representing the argument BDDs.
Each BDD is written as a network of multiplexers. Cudd_DumpBlif does not close the file: This is the caller responsibility. Cudd_DumpBlif uses a minimal unique subset of the hexadecimal address of a node as name for it. If the argument inames is non-null, it is assumed to hold the pointers to the names of the inputs. Similarly for onames.
- Returns
- 1 in case of success; 0 otherwise (e.g., out-of-memory, file system full, or an ADD with constants different from 0 and 1).
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_DumpBlifBody Cudd_DumpDot Cudd_PrintDebug Cudd_DumpDDcal Cudd_DumpDaVinci Cudd_DumpFactoredForm
- Parameters
-
dd manager n number of output nodes to be dumped f array of output nodes to be dumped inames array of input names (or NULL) onames array of output names (or NULL) mname model name (or NULL) fp pointer to the dump file mv 0: blif, 1: blif-MV
◆ Cudd_DumpBlifBody()
| int Cudd_DumpBlifBody | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| int | n, | ||
| DdNode ** | f, | ||
| char const *const * | inames, | ||
| char const *const * | onames, | ||
| FILE * | fp, | ||
| int | mv | ||
| ) |
Writes a blif body representing the argument BDDs.
Each BDD is written as a network of multiplexers. No header (.model, .inputs, and .outputs) and footer (.end) are produced by this function. One multiplexer is written for each BDD node. Cudd_DumpBlifBody does not close the file: This is the caller responsibility. Cudd_DumpBlifBody uses a minimal unique subset of the hexadecimal address of a node as name for it. If the argument inames is non-null, it is assumed to hold the pointers to the names of the inputs. Similarly for onames. This function prints out only .names part.
- Returns
- 1 in case of success; 0 otherwise (e.g., out-of-memory, file system full, or an ADD with constants different from 0 and 1).
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_DumpBlif Cudd_DumpDot Cudd_PrintDebug Cudd_DumpDDcal Cudd_DumpDaVinci Cudd_DumpFactoredForm
- Parameters
-
dd manager n number of output nodes to be dumped f array of output nodes to be dumped inames array of input names (or NULL) onames array of output names (or NULL) fp pointer to the dump file mv 0: blif, 1: blif-MV
◆ Cudd_DumpDaVinci()
| int Cudd_DumpDaVinci | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| int | n, | ||
| DdNode ** | f, | ||
| char const *const * | inames, | ||
| char const *const * | onames, | ||
| FILE * | fp | ||
| ) |
Writes a daVinci file representing the argument BDDs.
Writes a daVinci file representing the argument BDDs. Cudd_DumpDaVinci does not close the file: This is the caller responsibility. Cudd_DumpDaVinci uses a minimal unique subset of the hexadecimal address of a node as name for it. If the argument inames is non-null, it is assumed to hold the pointers to the names of the inputs. Similarly for onames.
- Returns
- 1 in case of success; 0 otherwise (e.g., out-of-memory or file system full).
- Side effects None
- Parameters
-
dd manager n number of output nodes to be dumped f array of output nodes to be dumped inames array of input names (or NULL) onames array of output names (or NULL) fp pointer to the dump file
◆ Cudd_DumpDDcal()
| int Cudd_DumpDDcal | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| int | n, | ||
| DdNode ** | f, | ||
| char const *const * | inames, | ||
| char const *const * | onames, | ||
| FILE * | fp | ||
| ) |
Writes a DDcal file representing the argument BDDs.
Writes a DDcal file representing the argument BDDs. Cudd_DumpDDcal does not close the file: This is the caller responsibility. Cudd_DumpDDcal uses a minimal unique subset of the hexadecimal address of a node as name for it. If the argument inames is non-null, it is assumed to hold the pointers to the names of the inputs. Similarly for onames.
- Returns
- 1 in case of success; 0 otherwise (e.g., out-of-memory or file system full).
- Side effects None
- Parameters
-
dd manager n number of output nodes to be dumped f array of output nodes to be dumped inames array of input names (or NULL) onames array of output names (or NULL) fp pointer to the dump file
◆ Cudd_DumpDot()
| int Cudd_DumpDot | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| int | n, | ||
| DdNode ** | f, | ||
| char const *const * | inames, | ||
| char const *const * | onames, | ||
| FILE * | fp | ||
| ) |
Writes a dot file representing the argument DDs.
Writes a file representing the argument DDs in a format suitable for the graph drawing program dot. Cudd_DumpDot does not close the file: This is the caller responsibility. Cudd_DumpDot uses a minimal unique subset of the hexadecimal address of a node as name for it. If the argument inames is non-null, it is assumed to hold the pointers to the names of the inputs. Similarly for onames. Cudd_DumpDot uses the following convention to draw arcs:
- solid line: THEN arcs;
- dotted line: complement arcs;
- dashed line: regular ELSE arcs.
The dot options are chosen so that the drawing fits on a letter-size sheet.
- Returns
- 1 in case of success; 0 otherwise (e.g., out-of-memory, file system full).
- Side effects None
- Parameters
-
dd manager n number of output nodes to be dumped f array of output nodes to be dumped inames array of input names (or NULL) onames array of output names (or NULL) fp pointer to the dump file
◆ Cudd_DumpFactoredForm()
| int Cudd_DumpFactoredForm | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| int | n, | ||
| DdNode ** | f, | ||
| char const *const * | inames, | ||
| char const *const * | onames, | ||
| FILE * | fp | ||
| ) |
Writes factored forms representing the argument BDDs.
Writes factored forms representing the argument BDDs. The format of the factored form is the one used in the genlib files for technology mapping in sis. Cudd_DumpFactoredForm does not close the file: This is the caller responsibility. Caution must be exercised because a factored form may be exponentially larger than the argument BDD. If the argument inames is non-null, it is assumed to hold the pointers to the names of the inputs. Similarly for onames. If the number of output nodes is 0, it is interpreted as 1, but no output name followed by equal sign is printed before the factored form.
- Returns
- 1 in case of success; 0 otherwise (e.g., file system full).
- Side effects None
- Parameters
-
dd manager n number of output nodes to be dumped f array of output nodes to be dumped inames array of input names (or NULL) onames array of output names (or NULL) fp pointer to the dump file
◆ Cudd_Dxygtdxz()
Generates a BDD for the function d(x,y) > d(x,z).
This function generates a BDD for the function d(x,y) > d(x,z); x, y, and z are N-bit numbers, x[0] x[1] ... x[N-1], y[0] y[1] ... y[N-1], and z[0] z[1] ... z[N-1], with 0 the most significant bit. The distance d(x,y) is defined as: 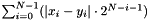 . The BDD is built bottom-up. It has 7*N-3 internal nodes, if the variables are ordered as follows: x[0] y[0] z[0] x[1] y[1] z[1] ... x[N-1] y[N-1] z[N-1].
. The BDD is built bottom-up. It has 7*N-3 internal nodes, if the variables are ordered as follows: x[0] y[0] z[0] x[1] y[1] z[1] ... x[N-1] y[N-1] z[N-1].
- Side effects None
- Parameters
-
dd DD manager N number of x, y, and z variables x array of x variables y array of y variables z array of z variables
◆ Cudd_Dxygtdyz()
Generates a BDD for the function d(x,y) > d(y,z).
This function generates a BDD for the function d(x,y) > d(y,z); x, y, and z are N-bit numbers, x[0] x[1] ... x[N-1], y[0] y[1] ... y[N-1], and z[0] z[1] ... z[N-1], with 0 the most significant bit. The distance d(x,y) is defined as: 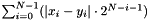 . The BDD is built bottom-up. It has 7*N-3 internal nodes, if the variables are ordered as follows: x[0] y[0] z[0] x[1] y[1] z[1] ... x[N-1] y[N-1] z[N-1].
. The BDD is built bottom-up. It has 7*N-3 internal nodes, if the variables are ordered as follows: x[0] y[0] z[0] x[1] y[1] z[1] ... x[N-1] y[N-1] z[N-1].
- Side effects None
- Parameters
-
dd DD manager N number of x, y, and z variables x array of x variables y array of y variables z array of z variables
◆ Cudd_E()
◆ Cudd_EnableGarbageCollection()
| void Cudd_EnableGarbageCollection | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Enables garbage collection.
Garbage collection is initially enabled. Therefore it is necessary to call this function only if garbage collection has been explicitly disabled.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_EnableOrderingMonitoring()
| int Cudd_EnableOrderingMonitoring | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Enables monitoring of ordering.
- Returns
- 1 if successful; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects Installs functions in the pre-reordering and post-reordering
- hooks.
- See also
- Cudd_EnableReorderingReporting
◆ Cudd_EnableReorderingReporting()
| int Cudd_EnableReorderingReporting | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Enables reporting of reordering stats.
- Returns
- 1 if successful; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects Installs functions in the pre-reordering and post-reordering
- hooks.
◆ Cudd_EpdPrintMinterm()
Prints the number of minterms of an ADD or BDD with extended range.
- Returns
- 1 if successful; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_EqualSupNorm()
| int Cudd_EqualSupNorm | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| DdNode * | f, | ||
| DdNode * | g, | ||
| CUDD_VALUE_TYPE | tolerance, | ||
| int | pr | ||
| ) |
Compares two ADDs for equality within tolerance.
Two ADDs are reported to be equal if the maximum difference between them (the sup norm of their difference) is less than or equal to the tolerance parameter. If parameter pr is positive the first failure is reported to the standard output.
- Returns
- 1 if the two ADDs are equal (within tolerance); 0 otherwise.
- Side effects None
- Parameters
-
dd manager f first ADD g second ADD tolerance maximum allowed difference pr verbosity level
◆ Cudd_EquivDC()
Tells whether F and G are identical wherever D is 0.
F and G are either two ADDs or two BDDs. D is either a 0-1 ADD or a BDD. No new nodes are created.
- Returns
- 1 if F and G are equivalent, and 0 otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_bddLeqUnless
◆ Cudd_EstimateCofactor()
Estimates the number of nodes in a cofactor of a DD.
This function uses a refinement of the algorithm of Cabodi et al. (ICCAD96). The refinement allows the procedure to account for part of the recombination that may occur in the part of the cofactor above the cofactoring variable. This procedure does not create any new node. It does keep a small table of results; therefore it may run out of memory. If this is a concern, one should use Cudd_EstimateCofactorSimple, which is faster, does not allocate any memory, but is less accurate.
- Returns
- an estimate of the number of nodes in a cofactor of the graph rooted at node with respect to the variable whose index is i. In case of failure, returns CUDD_OUT_OF_MEM.
- Side effects None
- Parameters
-
dd manager f function i index of variable phase 1: positive; 0: negative
◆ Cudd_EstimateCofactorSimple()
| int Cudd_EstimateCofactorSimple | ( | DdNode * | node, |
| int | i | ||
| ) |
Estimates the number of nodes in a cofactor of a DD.
Returns an estimate of the number of nodes in the positive cofactor of the graph rooted at node with respect to the variable whose index is i. This procedure implements with minor changes the algorithm of Cabodi et al. (ICCAD96). It does not allocate any memory, it does not change the state of the manager, and it is fast. However, it has been observed to overestimate the size of the cofactor by as much as a factor of 2.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_DagSize
◆ Cudd_Eval()
Returns the value of a DD for a given variable assignment.
The variable assignment is passed in an array of int's, that should specify a zero or a one for each variable in the support of the function.
- Returns
- a pointer to a constant node. No new nodes are produced.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_bddLeq Cudd_addEvalConst
◆ Cudd_ExpectedUsedSlots()
| double Cudd_ExpectedUsedSlots | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Computes the expected fraction of used slots in the unique table.
This expected value is based on the assumption that the hash function distributes the keys randomly; it can be compared with the result of Cudd_ReadUsedSlots to monitor the performance of the unique table hash function.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_ReadSlots Cudd_ReadUsedSlots
◆ Cudd_FactoredFormString()
Returns a string with the factored form of the argument BDDs.
The factored form uses & for conjunction, | for disjunction and ! for negation. Caution must be exercised because a factored form may be exponentially larger than the argument BDD. If the argument inames is non-null, it is assumed to hold the pointers to the names of the inputs.
- Returns
- a string in case of success; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_FindEssential()
Finds the essential variables of a DD.
Returns the cube of the essential variables. A positive literal means that the variable must be set to 1 for the function to be
- A negative literal means that the variable must be set to 0 for the function to be 1.
- Returns
- a pointer to the cube BDD if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_bddIsVarEssential
◆ Cudd_FindTwoLiteralClauses()
Finds the two literal clauses of a DD.
Returns the one- and two-literal clauses of a DD. For a constant DD, the empty set of clauses is returned. This is obviously correct for a non-zero constant. For the constant zero, it is based on the assumption that only those clauses containing variables in the support of the function are considered. Since the support of a constant function is empty, no clauses are returned.
- Returns
- a pointer to the structure holding the clauses if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_FindEssential
◆ Cudd_FirstCube()
| DdGen* Cudd_FirstCube | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| DdNode * | f, | ||
| int ** | cube, | ||
| CUDD_VALUE_TYPE * | value | ||
| ) |
Finds the first cube of a decision diagram.
Defines an iterator on the onset of a decision diagram and finds its first cube.
A cube is represented as an array of literals, which are integers in {0, 1, 2}; 0 represents a complemented literal, 1 represents an uncomplemented literal, and 2 stands for don't care. The enumeration produces a disjoint cover of the function associated with the diagram. The size of the array equals the number of variables in the manager at the time Cudd_FirstCube is called.
For each cube, a value is also returned. This value is always 1 for a BDD, while it may be different from 1 for an ADD. For BDDs, the offset is the set of cubes whose value is the logical zero. For ADDs, the offset is the set of cubes whose value is the background value. The cubes of the offset are not enumerated.
- Returns
- a generator that contains the information necessary to continue the enumeration if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects The first cube and its value are returned as side effects.
◆ Cudd_FirstNode()
Finds the first node of a decision diagram.
Defines an iterator on the nodes of a decision diagram and finds its first node. The nodes are enumerated in a reverse topological order, so that a node is always preceded in the enumeration by its descendants.
- Returns
- a generator that contains the information necessary to continue the enumeration if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects The first node is returned as a side effect.
◆ Cudd_FirstPrime()
Finds the first prime of a Boolean function.
Defines an iterator on a pair of BDDs describing a (possibly incompletely specified) Boolean functions and finds the first cube of a cover of the function.
The two argument BDDs are the lower and upper bounds of an interval. It is a mistake to call this function with a lower bound that is not less than or equal to the upper bound.
A cube is represented as an array of literals, which are integers in {0, 1, 2}; 0 represents a complemented literal, 1 represents an uncomplemented literal, and 2 stands for don't care. The enumeration produces a prime and irredundant cover of the function associated with the two BDDs. The size of the array equals the number of variables in the manager at the time Cudd_FirstCube is called.
This iterator can only be used on BDDs.
- Returns
- a generator that contains the information necessary to continue the enumeration if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects The first cube is returned as side effect.
◆ Cudd_FreeApaNumber()
| void Cudd_FreeApaNumber | ( | DdApaNumber | number | ) |
◆ Cudd_GarbageCollectionEnabled()
| int Cudd_GarbageCollectionEnabled | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Tells whether garbage collection is enabled.
- Returns
- 1 if garbage collection is enabled; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_GenFree()
| int Cudd_GenFree | ( | DdGen * | gen | ) |
Frees a CUDD generator.
- Returns
- always 0.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_IncreaseTimeLimit()
| void Cudd_IncreaseTimeLimit | ( | DdManager * | unique, |
| unsigned long | increase | ||
| ) |
Increases the time limit for the manager.
The time increase must be expressed in milliseconds.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_Increasing()
Checks whether a BDD is positive unate in a variable.
Determines whether the function represented by BDD f is positive unate (monotonic increasing) in variable i. It is based on Cudd_Decreasing and the fact that f is monotonic increasing in i if and only if its complement is monotonic decreasing in i.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_Decreasing
◆ Cudd_IndicesToCube()
Builds a cube of BDD variables from an array of indices.
- Returns
- a pointer to the result if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_Inequality()
Generates a BDD for the function x - y ≥ c.
This function generates a BDD for the function x -y ≥ c. Both x and y are N-bit numbers, x[0] x[1] ... x[N-1] and y[0] y[1] ... y[N-1], with 0 the most significant bit. The BDD is built bottom-up. It has a linear number of nodes if the variables are ordered as follows: x[0] y[0] x[1] y[1] ... x[N-1] y[N-1].
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_Xgty
- Parameters
-
dd DD manager N number of x and y variables c right-hand side constant x array of x variables y array of y variables
◆ Cudd_Init()
| DdManager* Cudd_Init | ( | unsigned int | numVars, |
| unsigned int | numVarsZ, | ||
| unsigned int | numSlots, | ||
| unsigned int | cacheSize, | ||
| size_t | maxMemory | ||
| ) |
Creates a new DD manager.
Initializes the table, the basic constants and the projection functions. If maxMemory is 0, Cudd_Init decides suitable values for the maximum size of the cache and for the limit for fast unique table growth based on the available memory.
- Returns
- a pointer to the manager if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_Quit
- Parameters
-
numVars initial number of BDD variables (i.e., subtables) numVarsZ initial number of ZDD variables (i.e., subtables) numSlots initial size of the unique tables cacheSize initial size of the cache maxMemory target maximum memory occupation
◆ Cudd_InstallOutOfMemoryHandler()
Installs a handler for failed memory allocations.
Changing the handler only has an effect if the wrappers in safe_mem.c are in use.
- Returns
- the current handler.
◆ Cudd_IsConstant()
| int Cudd_IsConstant | ( | DdNode * | node | ) |
Returns 1 if the node is a constant node.
A constant node is not an internal node. The pointer passed to Cudd_IsConstant may be either regular or complemented.
- Side effects none
◆ Cudd_IsGenEmpty()
| int Cudd_IsGenEmpty | ( | DdGen * | gen | ) |
Queries the status of a generator.
- Returns
- 1 if the generator is empty or NULL; 0 otherswise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_IsInHook()
| int Cudd_IsInHook | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| DD_HFP | f, | ||
| Cudd_HookType | where | ||
| ) |
Checks whether a function is in a hook.
A hook is a list of application-provided functions called on certain occasions by the package.
- Returns
- 1 if the function is found; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_AddHook Cudd_RemoveHook
◆ Cudd_IsNonConstant()
| int Cudd_IsNonConstant | ( | DdNode * | f | ) |
Returns 1 if a DD node is not constant.
This function is useful to test the results of Cudd_bddIteConstant, Cudd_addIteConstant, Cudd_addEvalConst. These results may be a special value signifying non-constant. In the other cases Cudd_IsConstant can be used.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_IterDerefBdd()
Decreases the reference count of BDD node n.
If n dies, recursively decreases the reference counts of its children. It is used to dispose of a BDD that is no longer needed. It is more efficient than Cudd_RecursiveDeref, but it cannot be used on ADDs. The greater efficiency comes from being able to assume that no constant node will ever die as a result of a call to this procedure.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_LargestCube()
Finds a largest cube in a DD.
f is the DD we want to get the largest cube for. The problem is translated into the one of finding a shortest path in f, when both THEN and ELSE arcs are assumed to have unit length. This yields a largest cube in the disjoint cover corresponding to the DD. Therefore, it is not necessarily the largest implicant of f.
- Returns
- the largest cube as a BDD.
- Side effects The number of literals of the cube is returned in the location
- pointed by length if it is non-null.
- See also
- Cudd_ShortestPath
◆ Cudd_LdblCountMinterm()
Returns the number of minterms of aa ADD or BDD as a long double.
On systems where double and long double are the same type, Cudd_CountMinterm() is preferable. On systems where long double values have 15-bit exponents, this function avoids overflow for up to 16383 variables. It applies scaling to try to avoid overflow when the number of variables is larger than 16383, but smaller than 32764.
- Returns
- The nimterm count if successful; +infinity if the number is known to be too large for representation as a long double;
(long double)CUDD_OUT_OF_MEMotherwise.
◆ Cudd_MakeBddFromZddCover()
Converts a ZDD cover to a BDD.
Converts a ZDD cover to a BDD for the function represented by the cover.
- Returns
- a BDD node if successful; otherwise it returns NULL.
- See also
- Cudd_zddIsop
◆ Cudd_MinHammingDist()
Returns the minimum Hamming distance between f and minterm.
Returns the minimum Hamming distance between the minterms of a function f and a reference minterm. The function is given as a BDD; the minterm is given as an array of integers, one for each variable in the manager.
- Returns
- the minimum distance if it is less than the upper bound; the upper bound if the minimum distance is at least as large; CUDD_OUT_OF_MEM in case of failure.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_addHamming Cudd_bddClosestCube
- Parameters
-
dd DD manager f function to examine minterm reference minterm upperBound distance above which an approximate answer is OK
◆ Cudd_NewApaNumber()
| DdApaNumber Cudd_NewApaNumber | ( | int | digits | ) |
Allocates memory for an arbitrary precision integer.
- Returns
- a pointer to the allocated memory if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_FreeApaNumber
◆ Cudd_NextCube()
| int Cudd_NextCube | ( | DdGen * | gen, |
| int ** | cube, | ||
| CUDD_VALUE_TYPE * | value | ||
| ) |
Generates the next cube of a decision diagram onset.
- Returns
- 0 if the enumeration is completed; 1 otherwise.
- Side effects The cube and its value are returned as side effects. The
- generator is modified.
◆ Cudd_NextNode()
Finds the next node of a decision diagram.
- Returns
- 0 if the enumeration is completed; 1 otherwise.
- Side effects The next node is returned as a side effect.
◆ Cudd_NextPrime()
| int Cudd_NextPrime | ( | DdGen * | gen, |
| int ** | cube | ||
| ) |
Generates the next prime of a Boolean function.
- Returns
- 0 if the enumeration is completed; 1 otherwise.
- Side effects The cube and is returned as side effects. The
- generator is modified.
◆ Cudd_NodeReadIndex()
| unsigned int Cudd_NodeReadIndex | ( | DdNode * | node | ) |
Returns the index of the node.
The node pointer can be either regular or complemented.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_ReadIndex
◆ Cudd_OrderingMonitoring()
| int Cudd_OrderingMonitoring | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Returns 1 if monitoring of ordering is enabled; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects none
◆ Cudd_OutOfMem()
| void Cudd_OutOfMem | ( | size_t | size | ) |
Warns that a memory allocation failed.
This function can be used as replacement of MMout_of_memory to prevent the safe_mem functions of the util package from exiting when malloc returns NULL. One possible use is in case of discretionary allocations; for instance, an allocation of memory to enlarge the computed table.
- Side effects None
- Parameters
-
size size of the allocation that failed
◆ Cudd_OutOfMemSilent()
| void Cudd_OutOfMemSilent | ( | size_t | size | ) |
Doesn not warn that a memory allocation failed.
This function can be used as replacement of MMout_of_memory to prevent the safe_mem functions of the util package from exiting when malloc returns NULL. One possible use is in case of discretionary allocations; for instance, an allocation of memory to enlarge the computed table.
- Side effects None
- Parameters
-
size size of the allocation that failed
◆ Cudd_OverApprox()
| DdNode* Cudd_OverApprox | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| DdNode * | f, | ||
| int | numVars, | ||
| int | threshold, | ||
| int | safe, | ||
| double | quality | ||
| ) |
Extracts a dense superset from a BDD with Shiple's underapproximation method.
The procedure is identical to the underapproximation procedure except for the fact that it works on the complement of the given function. Extracting the subset of the complement function is equivalent to extracting the superset of the function. The parameter numVars is the maximum number of variables to be used in minterm calculation. The optimal number should be as close as possible to the size of the support of f. However, it is safe to pass the value returned by Cudd_ReadSize for numVars when the number of variables is under 1023. If numVars is larger than 1023, it will overflow. If a 0 parameter is passed then the procedure will compute a value which will avoid overflow but will cause underflow with 2046 variables or more.
- Returns
- a pointer to the BDD of the superset if successful. NULL if intermediate result causes the procedure to run out of memory.
- Side effects None
- Parameters
-
dd manager f function to be superset numVars number of variables in the support of f threshold when to stop approximation safe enforce safe approximation quality minimum improvement for accepted changes
◆ Cudd_Prime()
| unsigned int Cudd_Prime | ( | unsigned int | p | ) |
Returns the next prime ≥ p.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_PrintDebug()
Prints to the manager standard output a DD and its statistics.
The statistics include the number of nodes, the number of leaves, and the number of minterms. (The number of minterms is the number of assignments to the variables that cause the function to be different from the logical zero (for BDDs) and from the background value (for ADDs.) The statistics are printed if pr > 0. Specifically:
- pr = 0 : prints nothing
- pr = 1 : prints counts of nodes and minterms
- pr = 2 : prints counts + disjoint sum of product
- pr = 3 : prints counts + list of nodes
- pr > 3 : prints counts + disjoint sum of product + list of nodes
For the purpose of counting the number of minterms, the function is supposed to depend on n variables.
- Returns
- 1 if successful; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_PrintGroupedOrder()
| int Cudd_PrintGroupedOrder | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| const char * | str, | ||
| void * | data | ||
| ) |
Hook function to print the current variable order.
It may be called before or after reordering. Prints on the manager's stdout a parenthesized list that describes the variable groups.
- Returns
- 1 if successful; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_StdPreReordHook
◆ Cudd_PrintInfo()
| int Cudd_PrintInfo | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| FILE * | fp | ||
| ) |
Prints out statistics and settings for a CUDD manager.
- Returns
- 1 if successful; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_PrintLinear()
| int Cudd_PrintLinear | ( | DdManager * | table | ) |
Prints the linear transform matrix.
- Returns
- 1 in case of success; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects none
◆ Cudd_PrintMinterm()
Prints a disjoint sum of products.
Prints a disjoint sum of product cover for the function rooted at node. Each product corresponds to a path from node to a leaf node different from the logical zero, and different from the background value. Uses the package default output file.
- Returns
- 1 if successful; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_PrintDebug Cudd_bddPrintCover
◆ Cudd_PrintSummary()
Prints a one-line summary of an ADD or BDD to the manager stdout.
The summary includes the number of nodes, the number of leaves, and the number of minterms. The number of minterms is computed with arbitrary precision unlike Cudd_PrintDebug(). For the purpose of counting minterms, the function f is supposed to depend on n variables.
- Returns
- 1 if successful; 0 otherwise.
- Parameters
-
dd manager f DD to be summarized n number of variables for minterm computation mode integer (0) or exponential (1) format
◆ Cudd_PrintTwoLiteralClauses()
Prints the one- and two-literal clauses of a DD.
The argument "names" can be NULL, in which case the variable indices are printed.
- Returns
- 1 if successful; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_FindTwoLiteralClauses
◆ Cudd_PrintVersion()
| void Cudd_PrintVersion | ( | FILE * | fp | ) |
Prints the package version number.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_PrioritySelect()
| DdNode* Cudd_PrioritySelect | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| DdNode * | R, | ||
| DdNode ** | x, | ||
| DdNode ** | y, | ||
| DdNode ** | z, | ||
| DdNode * | Pi, | ||
| int | n, | ||
| DD_PRFP | Pifunc | ||
| ) |
Selects pairs from R using a priority function.
Selects pairs from a relation R(x,y) (given as a BDD) in such a way that a given x appears in one pair only. Uses a priority function to determine which y should be paired to a given x. Three of the arguments–x, y, and z–are vectors of BDD variables. The first two are the variables on which R depends. The third vector is a vector of auxiliary variables, used during the computation. This vector is optional. If a NULL value is passed instead, Cudd_PrioritySelect will create the working variables on the fly. The sizes of x and y (and z if it is not NULL) should equal n. The priority function Pi can be passed as a BDD, or can be built by Cudd_PrioritySelect. If NULL is passed instead of a DdNode *, parameter Pifunc is used by Cudd_PrioritySelect to build a BDD for the priority function. (Pifunc is a pointer to a C function.) If Pi is not NULL, then Pifunc is ignored. Pifunc should have the same interface as the standard priority functions (e.g., Cudd_Dxygtdxz). Cudd_PrioritySelect and Cudd_CProjection can sometimes be used interchangeably. Specifically, calling Cudd_PrioritySelect with Cudd_Xgty as Pifunc produces the same result as calling Cudd_CProjection with the all-zero minterm as reference minterm. However, depending on the application, one or the other may be preferable:
- When extracting representatives from an equivalence relation, Cudd_CProjection has the advantage of nor requiring the auxiliary variables.
- When computing matchings in general bipartite graphs, Cudd_PrioritySelect normally obtains better results because it can use more powerful matching schemes (e.g., Cudd_Dxygtdxz).
- Returns
- a pointer to the selected function if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects If called with z == NULL, will create new variables in
- the manager.
- Parameters
-
dd manager R BDD of the relation x array of x variables y array of y variables z array of z variables (optional: may be NULL) Pi BDD of the priority function (optional: may be NULL) n size of x, y, and z Pifunc function used to build Pi if it is NULL
◆ Cudd_Quit()
| void Cudd_Quit | ( | DdManager * | unique | ) |
Deletes resources associated with a DD manager.
Calling Cudd_Quit with a null pointer has no effect.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_Init
- Parameters
-
unique pointer to manager
◆ Cudd_Random()
| int32_t Cudd_Random | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Portable random number generator.
Based on ran2 from "Numerical Recipes in C." It is a long period (> 2 * 10^18) random number generator of L'Ecuyer with Bays-Durham shuffle. The random generator can be explicitly initialized by calling Cudd_Srandom. If no explicit initialization is performed, then the seed 1 is assumed.
- Returns
- a long integer uniformly distributed between 0 and 2147483561 (inclusive of the endpoint values).
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_Srandom
◆ Cudd_ReadApplicationHook()
| void* Cudd_ReadApplicationHook | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
◆ Cudd_ReadArcviolation()
| int Cudd_ReadArcviolation | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Returns the current value of the arcviolation parameter used in group sifting.
This parameter is used to decide how many arcs into y not coming from x are tolerable when checking for aggregation due to extended symmetry. The value should be between 0 and 100. A small value causes fewer variables to be aggregated. The default value is 0.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_SetArcviolation
◆ Cudd_ReadBackground()
Reads the background constant of the manager.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_ReadCacheHits()
| double Cudd_ReadCacheHits | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
◆ Cudd_ReadCacheLookUps()
| double Cudd_ReadCacheLookUps | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
◆ Cudd_ReadCacheSlots()
| unsigned int Cudd_ReadCacheSlots | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
◆ Cudd_ReadCacheUsedSlots()
| double Cudd_ReadCacheUsedSlots | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Reads the fraction of used slots in the cache.
The unused slots are those in which no valid data is stored. Garbage collection, variable reordering, and cache resizing may cause used slots to become unused.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_ReadCacheSlots
◆ Cudd_ReadDead()
| unsigned int Cudd_ReadDead | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
◆ Cudd_ReadElapsedTime()
| unsigned long Cudd_ReadElapsedTime | ( | DdManager * | unique | ) |
Returns the time elapsed since the start time of the manager.
The time is expressed in milliseconds.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_ReadStartTime Cudd_SetStartTime
◆ Cudd_ReadEpsilon()
| CUDD_VALUE_TYPE Cudd_ReadEpsilon | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Reads the epsilon parameter of the manager.
The epsilon parameter control the comparison between floating point numbers.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_SetEpsilon
◆ Cudd_ReadErrorCode()
| Cudd_ErrorType Cudd_ReadErrorCode | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Returns the code of the last error.
The error codes are defined in cudd.h.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_ClearErrorCode
◆ Cudd_ReadGarbageCollections()
| int Cudd_ReadGarbageCollections | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Returns the number of times garbage collection has occurred.
The number includes both the calls from reordering procedures and those caused by requests to create new nodes.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_ReadGarbageCollectionTime
◆ Cudd_ReadGarbageCollectionTime()
| long Cudd_ReadGarbageCollectionTime | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Returns the time spent in garbage collection.
Returns the number of milliseconds spent doing garbage collection since the manager was initialized.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_ReadGarbageCollections
◆ Cudd_ReadGroupcheck()
| Cudd_AggregationType Cudd_ReadGroupcheck | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Reads the groupcheck parameter of the manager.
The groupcheck parameter determines the aggregation criterion in group sifting.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_SetGroupcheck
◆ Cudd_ReadInvPerm()
| int Cudd_ReadInvPerm | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| int | i | ||
| ) |
Returns the index of the variable currently in the i-th position of the order.
If the index is CUDD_CONST_INDEX, returns CUDD_CONST_INDEX; otherwise, if the index is out of bounds returns -1.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_ReadPerm Cudd_ReadInvPermZdd
◆ Cudd_ReadInvPermZdd()
| int Cudd_ReadInvPermZdd | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| int | i | ||
| ) |
Returns the index of the ZDD variable currently in the i-th position of the order.
If the index is CUDD_CONST_INDEX, returns CUDD_CONST_INDEX; otherwise, if the index is out of bounds returns -1.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_ReadPerm Cudd_ReadInvPermZdd
◆ Cudd_ReadIthClause()
| int Cudd_ReadIthClause | ( | DdTlcInfo * | tlc, |
| int | i, | ||
| unsigned * | var1, | ||
| unsigned * | var2, | ||
| int * | phase1, | ||
| int * | phase2 | ||
| ) |
Accesses the i-th clause of a DD.
Accesses the i-th clause of a DD given the clause set which must be already computed.
- Returns
- 1 if successful; 0 if i is out of range, or in case of error.
- Side effects the four components of a clause are returned as side effects.
- See also
- Cudd_FindTwoLiteralClauses
◆ Cudd_ReadKeys()
| unsigned int Cudd_ReadKeys | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Returns the number of nodes in the unique table.
Returns the total number of nodes currently in the unique table, including the dead nodes.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_ReadDead
◆ Cudd_ReadLinear()
| int Cudd_ReadLinear | ( | DdManager * | table, |
| int | x, | ||
| int | y | ||
| ) |
Reads an entry of the linear transform matrix.
- Side effects none
- Parameters
-
table CUDD manager x row index y column index
◆ Cudd_ReadLogicZero()
Returns the logic zero constant of the manager.
The logic zero constant is the complement of the one constant, and is distinct from the arithmetic zero.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_ReadOne Cudd_ReadZero
◆ Cudd_ReadLooseUpTo()
| unsigned int Cudd_ReadLooseUpTo | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Reads the looseUpTo parameter of the manager.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_ReadMaxCache()
| unsigned int Cudd_ReadMaxCache | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
◆ Cudd_ReadMaxCacheHard()
| unsigned int Cudd_ReadMaxCacheHard | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Reads the maxCacheHard parameter of the manager.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_ReadMaxGrowth()
| double Cudd_ReadMaxGrowth | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Reads the maxGrowth parameter of the manager.
This parameter determines how much the number of nodes can grow during sifting of a variable. Overall, sifting never increases the size of the decision diagrams. This parameter only refers to intermediate results. A lower value will speed up sifting, possibly at the expense of quality.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_ReadMaxGrowthAlternate()
| double Cudd_ReadMaxGrowthAlternate | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Reads the maxGrowthAlt parameter of the manager.
This parameter is analogous to the maxGrowth paramter, and is used every given number of reorderings instead of maxGrowth. The number of reorderings is set with Cudd_SetReorderingCycle. If the number of reorderings is 0 (default) maxGrowthAlt is never used.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_ReadMaxIndex()
| unsigned int Cudd_ReadMaxIndex | ( | void | ) |
Returns the maximum possible index for a variable.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_ReadMaxLive()
| unsigned int Cudd_ReadMaxLive | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Reads the maximum allowed number of live nodes.
When this number is exceeded, the package returns NULL.
- Side effects none
- See also
- Cudd_SetMaxLive
◆ Cudd_ReadMaxMemory()
| size_t Cudd_ReadMaxMemory | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Reads the maximum allowed memory.
When this number is exceeded, the package returns NULL.
- Side effects none
- See also
- Cudd_SetMaxMemory
◆ Cudd_ReadMaxReorderings()
| unsigned int Cudd_ReadMaxReorderings | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Returns the maximum number of times reordering may be invoked.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_ReadMemoryInUse()
| size_t Cudd_ReadMemoryInUse | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Returns the memory in use by the manager measured in bytes.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_ReadMinDead()
| unsigned int Cudd_ReadMinDead | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Reads the minDead parameter of the manager.
The minDead parameter is used by the package to decide whether to collect garbage or resize a subtable of the unique table when the subtable becomes too full. The application can indirectly control the value of minDead by setting the looseUpTo parameter.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_ReadMinHit()
| unsigned int Cudd_ReadMinHit | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Reads the hit rate that causes resizinig of the computed table.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_SetMinHit
◆ Cudd_ReadMinusInfinity()
Reads the minus-infinity constant from the manager.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_ReadNextReordering()
| unsigned int Cudd_ReadNextReordering | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Returns the threshold for the next dynamic reordering.
The threshold is in terms of number of nodes and is in effect only if reordering is enabled. The count does not include the dead nodes, unless the countDead parameter of the manager has been changed from its default setting.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_SetNextReordering
◆ Cudd_ReadNodeCount()
| long Cudd_ReadNodeCount | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Reports the number of nodes in BDDs and ADDs.
This number does not include the isolated projection functions and the unused constants. These nodes that are not counted are not part of the DDs manipulated by the application.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_ReadNodesDropped()
| double Cudd_ReadNodesDropped | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Returns the number of nodes dropped.
Returns the number of nodes killed by dereferencing if the keeping of this statistic is enabled; -1 otherwise. This statistic is enabled only if the package is compiled with DD_STATS defined.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_ReadNodesFreed
◆ Cudd_ReadNodesFreed()
| double Cudd_ReadNodesFreed | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Returns the number of nodes freed.
Returns the number of nodes returned to the free list if the keeping of this statistic is enabled; -1 otherwise. This statistic is enabled only if the package is compiled with DD_STATS defined.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_ReadNodesDropped
◆ Cudd_ReadNumberXovers()
| int Cudd_ReadNumberXovers | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Reads the current number of crossovers used by the genetic algorithm for variable reordering.
A larger number of crossovers will cause the genetic algorithm to take more time, but will generally produce better results. The default value is 0, in which case the package uses three times the number of variables as number of crossovers, with a maximum of 60.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_SetNumberXovers
◆ Cudd_ReadOne()
Returns the one constant of the manager.
The one constant is common to ADDs and BDDs.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_ReadOrderRandomization()
| unsigned int Cudd_ReadOrderRandomization | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Returns the order randomization factor.
If non-zero this factor is used to determine a perturbation of the next reordering threshold. Larger factors cause larger perturbations.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_SetOrderRandomization
◆ Cudd_ReadPeakLiveNodeCount()
| int Cudd_ReadPeakLiveNodeCount | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Reports the peak number of live nodes.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_ReadPeakNodeCount()
| long Cudd_ReadPeakNodeCount | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Reports the peak number of nodes.
This number includes node on the free list. At the peak, the number of nodes on the free list is guaranteed to be less than DD_MEM_CHUNK.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_ReadNodeCount Cudd_PrintInfo
◆ Cudd_ReadPerm()
| int Cudd_ReadPerm | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| int | i | ||
| ) |
Returns the current position of the i-th variable in the order.
If the index is CUDD_CONST_INDEX, returns CUDD_CONST_INDEX; otherwise, if the index is out of bounds returns -1.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_ReadInvPerm Cudd_ReadPermZdd
◆ Cudd_ReadPermZdd()
| int Cudd_ReadPermZdd | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| int | i | ||
| ) |
Returns the current position of the i-th ZDD variable in the order.
If the index is CUDD_CONST_INDEX, returns CUDD_CONST_INDEX; otherwise, if the index is out of bounds returns -1.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_ReadInvPermZdd Cudd_ReadPerm
◆ Cudd_ReadPlusInfinity()
Reads the plus-infinity constant from the manager.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_ReadPopulationSize()
| int Cudd_ReadPopulationSize | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Reads the current size of the population used by the genetic algorithm for variable reordering.
A larger population size will cause the genetic algorithm to take more time, but will generally produce better results. The default value is 0, in which case the package uses three times the number of variables as population size, with a maximum of 120.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_SetPopulationSize
◆ Cudd_ReadRecomb()
| int Cudd_ReadRecomb | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Returns the current value of the recombination parameter used in group sifting.
A larger (positive) value makes the aggregation of variables due to the second difference criterion more likely. A smaller (negative) value makes aggregation less likely.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_SetRecomb
◆ Cudd_ReadRecursiveCalls()
| double Cudd_ReadRecursiveCalls | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Returns the number of recursive calls.
Returns the number of recursive calls if the package is compiled with DD_COUNT defined.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_ReadReorderingCycle()
| int Cudd_ReadReorderingCycle | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Reads the reordCycle parameter of the manager.
This parameter determines how often the alternate threshold on maximum growth is used in reordering.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_ReadReorderings()
| unsigned int Cudd_ReadReorderings | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Returns the number of times reordering has occurred.
The number includes both the calls to Cudd_ReduceHeap from the application program and those automatically performed by the package. However, calls that do not even initiate reordering are not counted. A call may not initiate reordering if there are fewer than minsize live nodes in the manager, or if CUDD_REORDER_NONE is specified as reordering method. The calls to Cudd_ShuffleHeap are not counted.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_ReadReorderingTime()
| long Cudd_ReadReorderingTime | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Returns the time spent in reordering.
Returns the number of milliseconds spent reordering variables since the manager was initialized. The time spent in collecting garbage before reordering is included.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_ReadReorderings
◆ Cudd_ReadSiftMaxSwap()
| int Cudd_ReadSiftMaxSwap | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Reads the siftMaxSwap parameter of the manager.
This parameter gives the maximum number of swaps that will be attempted for each invocation of sifting. The real number of swaps may exceed the set limit because the package will always complete the sifting of the variable that causes the limit to be reached.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_ReadSiftMaxVar()
| int Cudd_ReadSiftMaxVar | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Reads the siftMaxVar parameter of the manager.
This parameter gives the maximum number of variables that will be sifted for each invocation of sifting.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_ReadSize()
| int Cudd_ReadSize | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
◆ Cudd_ReadSlots()
| unsigned int Cudd_ReadSlots | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Returns the total number of slots of the unique table.
This number is mainly for diagnostic purposes.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_ReadStartTime()
| unsigned long Cudd_ReadStartTime | ( | DdManager * | unique | ) |
Returns the start time of the manager.
This is initially set to the number of milliseconds since the program started, but may be reset by the application.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_ReadStderr()
| FILE* Cudd_ReadStderr | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Reads the stderr of a manager.
This is the file pointer to which messages normally going to stderr are written. It is initialized to stderr. Cudd_SetStderr allows the application to redirect it.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_SetStderr Cudd_ReadStdout
◆ Cudd_ReadStdout()
| FILE* Cudd_ReadStdout | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Reads the stdout of a manager.
This is the file pointer to which messages normally going to stdout are written. It is initialized to stdout. Cudd_SetStdout allows the application to redirect it.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_SetStdout Cudd_ReadStderr
◆ Cudd_ReadSwapSteps()
| double Cudd_ReadSwapSteps | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Reads the number of elementary reordering steps.
- Side effects none
◆ Cudd_ReadSymmviolation()
| int Cudd_ReadSymmviolation | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Returns the current value of the symmviolation parameter used in group sifting.
This parameter is used in group sifting to decide how many violations to the symmetry conditions f10 = f01 or f11 = f00 are tolerable when checking for aggregation due to extended symmetry. The value should be between 0 and 100. A small value causes fewer variables to be aggregated. The default value is 0.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_SetSymmviolation
◆ Cudd_ReadTimeLimit()
| unsigned long Cudd_ReadTimeLimit | ( | DdManager * | unique | ) |
Returns the time limit for the manager.
This is initially set to a very large number, but may be reset by the application. The time is expressed in milliseconds.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_ReadTimeoutHandler()
Read the current timeout handler function.
- Side effects If argp is non-null, the second argument to
- the handler is written to the location it points to.
- See also
- Cudd_RegisterTimeoutHandler
◆ Cudd_ReadUniqueLinks()
| double Cudd_ReadUniqueLinks | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Returns the number of links followed in the unique table.
Returns the number of links followed during look-ups in the unique table if the keeping of this statistic is enabled; -1 otherwise. If an item is found in the first position of its collision list, the number of links followed is taken to be 0. If it is in second position, the number of links is 1, and so on. This statistic is enabled only if the package is compiled with DD_UNIQUE_PROFILE defined.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_ReadUniqueLookUps
◆ Cudd_ReadUniqueLookUps()
| double Cudd_ReadUniqueLookUps | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Returns the number of look-ups in the unique table.
Returns the number of look-ups in the unique table if the keeping of this statistic is enabled; -1 otherwise. This statistic is enabled only if the package is compiled with DD_UNIQUE_PROFILE defined.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_ReadUniqueLinks
◆ Cudd_ReadUsedSlots()
| double Cudd_ReadUsedSlots | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Reads the fraction of used slots in the unique table.
The unused slots are those in which no valid data is stored. Garbage collection, variable reordering, and subtable resizing may cause used slots to become unused.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_ReadSlots
◆ Cudd_ReadVars()
Returns the i-th element of the vars array.
Returns the i-th element of the vars array if it falls within the array bounds; NULL otherwise. If i is the index of an existing variable, this function produces the same result as Cudd_bddIthVar. However, if the i-th var does not exist yet, Cudd_bddIthVar will create it, whereas Cudd_ReadVars will not.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_bddIthVar
◆ Cudd_ReadZddOne()
Returns the ZDD for the constant 1 function.
The representation of the constant 1 function as a ZDD depends on how many variables it (nominally) depends on. The index of the topmost variable in the support is given as argument i.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_ReadOne
◆ Cudd_ReadZddSize()
| int Cudd_ReadZddSize | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
◆ Cudd_ReadZero()
Returns the zero constant of the manager.
The zero constant is the arithmetic zero, rather than the logic zero. The latter is the complement of the one constant.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_ReadOne Cudd_ReadLogicZero
◆ Cudd_RecursiveDeref()
Decreases the reference count of node n.
If n dies, recursively decreases the reference counts of its children. It is used to dispose of a DD that is no longer needed.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_Deref Cudd_Ref Cudd_RecursiveDerefZdd
◆ Cudd_RecursiveDerefZdd()
Decreases the reference count of ZDD node n.
If n dies, recursively decreases the reference counts of its children. It is used to dispose of a ZDD that is no longer needed.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_Deref Cudd_Ref Cudd_RecursiveDeref
◆ Cudd_ReduceHeap()
| int Cudd_ReduceHeap | ( | DdManager * | table, |
| Cudd_ReorderingType | heuristic, | ||
| int | minsize | ||
| ) |
Main dynamic reordering routine.
Calls one of the possible reordering procedures:
- Swapping
- Sifting
- Symmetric Sifting
- Group Sifting
- Window Permutation
- Simulated Annealing
- Genetic Algorithm
- Dynamic Programming (exact)
For sifting, symmetric sifting, group sifting, and window permutation it is possible to request reordering to convergence.
The core of all methods is the reordering procedure cuddSwapInPlace() which swaps two adjacent variables and is based on Rudell's paper.
- Returns
- 1 in case of success; 0 otherwise. In the case of symmetric sifting (with and without convergence) returns 1 plus the number of symmetric variables, in case of success.
- Side effects Changes the variable order for all diagrams and clears
- the cache.
- Parameters
-
table DD manager heuristic method used for reordering minsize bound below which no reordering occurs
◆ Cudd_Ref()
| void Cudd_Ref | ( | DdNode * | n | ) |
Increases the reference count of a node, if it is not saturated.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_RecursiveDeref Cudd_Deref
◆ Cudd_RegisterOutOfMemoryCallback()
Installs an out-of-memory callback.
Registers a callback function that is called when a discretionary memory allocation fails.
- Returns
- the old callback function.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_RegisterTerminationCallback()
Installs a termination callback.
Registers a callback function that is called from time to time to decide whether computation should be abandoned.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_RegisterTimeoutHandler()
Register a timeout handler function.
To unregister a handler, register a NULL pointer.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_ReadTimeoutHandler
◆ Cudd_RemapOverApprox()
| DdNode* Cudd_RemapOverApprox | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| DdNode * | f, | ||
| int | numVars, | ||
| int | threshold, | ||
| double | quality | ||
| ) |
Extracts a dense superset from a BDD with the remapping underapproximation method.
The procedure is identical to the underapproximation procedure except for the fact that it works on the complement of the given function. Extracting the subset of the complement function is equivalent to extracting the superset of the function. The parameter numVars is the maximum number of variables to be used in minterm calculation. The optimal number should be as close as possible to the size of the support of f. However, it is safe to pass the value returned by Cudd_ReadSize for numVars when the number of variables is under 1023. If numVars is larger than 1023, it will overflow. If a 0 parameter is passed then the procedure will compute a value which will avoid overflow but will cause underflow with 2046 variables or more.
- Returns
- a pointer to the BDD of the superset if successful. NULL if intermediate result causes the procedure to run out of memory.
- Side effects None
- Parameters
-
dd manager f function to be superset numVars number of variables in the support of f threshold when to stop approximation quality minimum improvement for accepted changes
◆ Cudd_RemapUnderApprox()
| DdNode* Cudd_RemapUnderApprox | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| DdNode * | f, | ||
| int | numVars, | ||
| int | threshold, | ||
| double | quality | ||
| ) |
Extracts a dense subset from a BDD with the remapping underapproximation method.
This procedure uses a remapping technique and density as the cost function. The parameter numVars is the maximum number of variables to be used in minterm calculation. The optimal number should be as close as possible to the size of the support of f. However, it is safe to pass the value returned by Cudd_ReadSize for numVars when the number of variables is under 1023. If numVars is larger than 1023, it will cause overflow. If a 0 parameter is passed then the procedure will compute a value which will avoid overflow but will cause underflow with 2046 variables or more.
- Returns
- a pointer to the BDD of the subset if successful. NULL if the procedure runs out of memory.
- Side effects None
- Parameters
-
dd manager f function to be subset numVars number of variables in the support of f threshold when to stop approximation quality minimum improvement for accepted changes
◆ Cudd_RemoveHook()
| int Cudd_RemoveHook | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| DD_HFP | f, | ||
| Cudd_HookType | where | ||
| ) |
Removes a function from a hook.
A hook is a list of application-provided functions called on certain occasions by the package.
- Returns
- 1 if successful; 0 the function was not in the list.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_AddHook
◆ Cudd_ReorderingReporting()
| int Cudd_ReorderingReporting | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Returns 1 if reporting of reordering stats is enabled; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects none
◆ Cudd_ReorderingStatus()
| int Cudd_ReorderingStatus | ( | DdManager * | unique, |
| Cudd_ReorderingType * | method | ||
| ) |
Reports the status of automatic dynamic reordering of BDDs and ADDs.
The location pointed by parameter method is set to the reordering method currently selected if method is non-null.
- Returns
- 1 if automatic reordering is enabled; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects The location pointed by parameter method is set to the
- reordering method currently selected if method is non-null.
◆ Cudd_ReorderingStatusZdd()
| int Cudd_ReorderingStatusZdd | ( | DdManager * | unique, |
| Cudd_ReorderingType * | method | ||
| ) |
Reports the status of automatic dynamic reordering of ZDDs.
Parameter method is set to the ZDD reordering method currently selected.
- Returns
- 1 if automatic reordering is enabled; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects Parameter method is set to the ZDD reordering method currently
- selected.
◆ Cudd_Reserve()
| int Cudd_Reserve | ( | DdManager * | manager, |
| int | amount | ||
| ) |
Expand manager without creating variables.
Expand a manager by a specified number of subtables without actually creating new variables. This function can be used to reduce the frequency of resizing when an estimate of the number of variables is available. One would call this function instead of passing the number of variables to Cudd_Init if variables should not be created right away of if the estimate on their number became available only after the manager has been created.
- Returns
- 1 if successful; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_Init
◆ Cudd_ResetStartTime()
| void Cudd_ResetStartTime | ( | DdManager * | unique | ) |
Resets the start time of the manager.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_SetApplicationHook()
| void Cudd_SetApplicationHook | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| void * | value | ||
| ) |
◆ Cudd_SetArcviolation()
| void Cudd_SetArcviolation | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| int | arcviolation | ||
| ) |
Sets the value of the arcviolation parameter used in group sifting.
This parameter is used to decide how many arcs into y not coming from x are tolerable when checking for aggregation due to extended symmetry. The value should be between 0 and 100. A small value causes fewer variables to be aggregated. The default value is 0.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_ReadArcviolation
◆ Cudd_SetBackground()
Sets the background constant of the manager.
It assumes that the DdNode pointer bck is already referenced.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_SetEpsilon()
| void Cudd_SetEpsilon | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| CUDD_VALUE_TYPE | ep | ||
| ) |
Sets the epsilon parameter of the manager to ep.
The epsilon parameter control the comparison between floating point numbers.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_ReadEpsilon
◆ Cudd_SetGroupcheck()
| void Cudd_SetGroupcheck | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| Cudd_AggregationType | gc | ||
| ) |
Sets the parameter groupcheck of the manager to gc.
The groupcheck parameter determines the aggregation criterion in group sifting.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_ReadGroupCheck
◆ Cudd_SetLooseUpTo()
| void Cudd_SetLooseUpTo | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| unsigned int | lut | ||
| ) |
Sets the looseUpTo parameter of the manager.
This parameter of the manager controls the threshold beyond which no fast growth of the unique table is allowed. The threshold is given as a number of slots. If the value passed to this function is 0, the function determines a suitable value based on the available memory.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_ReadLooseUpTo Cudd_SetMinHit
◆ Cudd_SetMaxCacheHard()
| void Cudd_SetMaxCacheHard | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| unsigned int | mc | ||
| ) |
Sets the maxCacheHard parameter of the manager.
The cache cannot grow larger than maxCacheHard entries. This parameter allows an application to control the trade-off of memory versus speed. If the value passed to this function is 0, the function determines a suitable maximum cache size based on the available memory.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_ReadMaxCacheHard Cudd_SetMaxCache
◆ Cudd_SetMaxGrowth()
| void Cudd_SetMaxGrowth | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| double | mg | ||
| ) |
Sets the maxGrowth parameter of the manager.
This parameter determines how much the number of nodes can grow during sifting of a variable. Overall, sifting never increases the size of the decision diagrams. This parameter only refers to intermediate results. A lower value will speed up sifting, possibly at the expense of quality.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_SetMaxGrowthAlternate()
| void Cudd_SetMaxGrowthAlternate | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| double | mg | ||
| ) |
Sets the maxGrowthAlt parameter of the manager.
This parameter is analogous to the maxGrowth paramter, and is used every given number of reorderings instead of maxGrowth. The number of reorderings is set with Cudd_SetReorderingCycle. If the number of reorderings is 0 (default) maxGrowthAlt is never used.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_SetMaxLive()
| void Cudd_SetMaxLive | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| unsigned int | maxLive | ||
| ) |
Sets the maximum allowed number of live nodes.
When this number is exceeded, the package returns NULL.
- Side effects none
- See also
- Cudd_ReadMaxLive
◆ Cudd_SetMaxMemory()
| size_t Cudd_SetMaxMemory | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| size_t | maxMemory | ||
| ) |
Sets the maximum allowed memory.
When this number is exceeded, the package returns NULL.
- Returns
- the previous limit.
- Side effects none
- See also
- Cudd_ReadMaxMemory
◆ Cudd_SetMaxReorderings()
| void Cudd_SetMaxReorderings | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| unsigned int | mr | ||
| ) |
Sets the maximum number of times reordering may be invoked.
The default value is (practically) infinite.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_SetMinHit()
| void Cudd_SetMinHit | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| unsigned int | hr | ||
| ) |
Sets the hit rate that causes resizinig of the computed table.
Sets the minHit parameter of the manager. This parameter controls the resizing of the computed table. If the hit rate is larger than the specified value, and the cache is not already too large, then its size is doubled.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_ReadMinHit
◆ Cudd_SetNextReordering()
| void Cudd_SetNextReordering | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| unsigned int | next | ||
| ) |
Sets the threshold for the next dynamic reordering.
The threshold is in terms of number of nodes and is in effect only if reordering is enabled. The count does not include the dead nodes, unless the countDead parameter of the manager has been changed from its default setting.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_ReadNextReordering
◆ Cudd_SetNumberXovers()
| void Cudd_SetNumberXovers | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| int | numberXovers | ||
| ) |
Sets the number of crossovers used by the genetic algorithm for variable reordering.
A larger number of crossovers will cause the genetic algorithm to take more time, but will generally produce better results. The default value is 0, in which case the package uses three times the number of variables as number of crossovers, with a maximum of 60.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_ReadNumberXovers
◆ Cudd_SetOrderRandomization()
| void Cudd_SetOrderRandomization | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| unsigned int | factor | ||
| ) |
◆ Cudd_SetPopulationSize()
| void Cudd_SetPopulationSize | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| int | populationSize | ||
| ) |
Sets the size of the population used by the genetic algorithm for variable reordering.
A larger population size will cause the genetic algorithm to take more time, but will generally produce better results. The default value is 0, in which case the package uses three times the number of variables as population size, with a maximum of 120.
- Side effects Changes the manager.
- See also
- Cudd_ReadPopulationSize
◆ Cudd_SetRecomb()
| void Cudd_SetRecomb | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| int | recomb | ||
| ) |
Sets the value of the recombination parameter used in group sifting.
A larger (positive) value makes the aggregation of variables due to the second difference criterion more likely. A smaller (negative) value makes aggregation less likely. The default value is 0.
- Side effects Changes the manager.
- See also
- Cudd_ReadRecomb
◆ Cudd_SetReorderingCycle()
| void Cudd_SetReorderingCycle | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| int | cycle | ||
| ) |
Sets the reordCycle parameter of the manager.
This parameter determines how often the alternate threshold on maximum growth is used in reordering.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_SetSiftMaxSwap()
| void Cudd_SetSiftMaxSwap | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| int | sms | ||
| ) |
Sets the siftMaxSwap parameter of the manager.
This parameter gives the maximum number of swaps that will be attempted for each invocation of sifting. The real number of swaps may exceed the set limit because the package will always complete the sifting of the variable that causes the limit to be reached.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_SetSiftMaxVar()
| void Cudd_SetSiftMaxVar | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| int | smv | ||
| ) |
Sets the siftMaxVar parameter of the manager.
This parameter gives the maximum number of variables that will be sifted for each invocation of sifting.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_SetStartTime()
| void Cudd_SetStartTime | ( | DdManager * | unique, |
| unsigned long | st | ||
| ) |
Sets the start time of the manager.
The time must be expressed in milliseconds.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_SetStderr()
| void Cudd_SetStderr | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| FILE * | fp | ||
| ) |
◆ Cudd_SetStdout()
| void Cudd_SetStdout | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| FILE * | fp | ||
| ) |
◆ Cudd_SetSymmviolation()
| void Cudd_SetSymmviolation | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| int | symmviolation | ||
| ) |
Sets the value of the symmviolation parameter used in group sifting.
This parameter is used in group sifting to decide how many violations to the symmetry conditions f10 = f01 or f11 = f00 are tolerable when checking for aggregation due to extended symmetry. The value should be between 0 and 100. A small value causes fewer variables to be aggregated. The default value is 0.
- Side effects Changes the manager.
- See also
- Cudd_ReadSymmviolation
◆ Cudd_SetTimeLimit()
| unsigned long Cudd_SetTimeLimit | ( | DdManager * | unique, |
| unsigned long | tl | ||
| ) |
Sets the time limit for the manager.
The time must be expressed in milliseconds.
- Returns
- the old time limit.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_SetVarMap()
Registers a variable mapping with the manager.
Registers with the manager a variable mapping described by two sets of variables. This variable mapping is then used by functions like Cudd_bddVarMap. This function is convenient for those applications that perform the same mapping several times. However, if several different permutations are used, it may be more efficient not to rely on the registered mapping, because changing mapping causes the cache to be cleared. (The initial setting, however, does not clear the cache.) The two sets of variables (x and y) must have the same size (x and y). The size is given by n. The two sets of variables are normally disjoint, but this restriction is not imposeded by the function. When new variables are created, the map is automatically extended (each new variable maps to itself). The typical use, however, is to wait until all variables are created, and then create the map.
- Returns
- 1 if the mapping is successfully registered with the manager; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects Modifies the manager. May clear the cache.
- Parameters
-
manager DD manager x first array of variables y second array of variables n length of both arrays
◆ Cudd_SharingSize()
| int Cudd_SharingSize | ( | DdNode ** | nodeArray, |
| int | n | ||
| ) |
Counts the number of nodes in an array of DDs.
Shared nodes are counted only once.
- Returns
- the total number of nodes.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_DagSize
◆ Cudd_ShortestLength()
Find the length of the shortest path(s) in a DD.
f is the DD we want to get the shortest path for; weight[i] is the weight of the THEN edge coming from the node whose index is i. All ELSE edges have 0 weight.
- Returns
- the length of the shortest path(s) if such a path is found; a large number if the function is identically 0, and CUDD_OUT_OF_MEM in case of failure.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_ShortestPath
◆ Cudd_ShortestPath()
| DdNode* Cudd_ShortestPath | ( | DdManager * | manager, |
| DdNode * | f, | ||
| int * | weight, | ||
| int * | support, | ||
| int * | length | ||
| ) |
Finds a shortest path in a DD.
f is the DD we want to get the shortest path for; weight[i] is the weight of the THEN arc coming from the node whose index is i. If weight is NULL, then unit weights are assumed for all THEN arcs. All ELSE arcs have 0 weight. If non-NULL, both weight and support should point to arrays with at least as many entries as there are variables in the manager.
- Returns
- the shortest path as the BDD of a cube.
- Side effects support contains on return the true support of f.
- If support is NULL on entry, then Cudd_ShortestPath does not compute the true support info. length contains the length of the path.
- See also
- Cudd_ShortestLength Cudd_LargestCube
◆ Cudd_ShuffleHeap()
| int Cudd_ShuffleHeap | ( | DdManager * | table, |
| int * | permutation | ||
| ) |
Reorders variables according to given permutation.
The i-th entry of the permutation array contains the index of the variable that should be brought to the i-th level. The size of the array should be equal or greater to the number of variables currently in use.
- Returns
- 1 in case of success; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects Changes the variable order for all diagrams and clears
- the cache.
- See also
- Cudd_ReduceHeap
- Parameters
-
table DD manager permutation required variable permutation
◆ Cudd_SolveEqn()
| DdNode* Cudd_SolveEqn | ( | DdManager * | bdd, |
| DdNode * | F, | ||
| DdNode * | Y, | ||
| DdNode ** | G, | ||
| int ** | yIndex, | ||
| int | n | ||
| ) |
Implements the solution of F(x,y) = 0.
The return value is the consistency condition. The y variables are the unknowns and the remaining variables are the parameters. Cudd_SolveEqn allocates an array and fills it with the indices of the unknowns. This array is used by Cudd_VerifySol.
- Returns
- the consistency condition if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects The solution is returned in G; the indices of the y
- variables are returned in yIndex.
- See also
- Cudd_VerifySol
- Parameters
-
bdd CUDD manager F the left-hand side of the equation Y the cube of the y variables G the array of solutions (return parameter) yIndex index of y variables n numbers of unknowns
◆ Cudd_SplitSet()
Returns m minterms from a BDD.
Returns m minterms from a BDD whose support has n variables at most. The procedure tries to create as few extra nodes as possible. The function represented by S depends on at most n of the variables in xVars.
- Returns
- a BDD with
mminterms of the on-set of S if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_Srandom()
| void Cudd_Srandom | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| int32_t | seed | ||
| ) |
Initializer for the portable random number generator.
Based on ran2 in "Numerical Recipes in C." The input is the seed for the generator. If it is negative, its absolute value is taken as seed. If it is 0, then 1 is taken as seed. The initialized sets up the two recurrences used to generate a long-period stream, and sets up the shuffle table.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_Random
◆ Cudd_StdPostReordHook()
| int Cudd_StdPostReordHook | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| const char * | str, | ||
| void * | data | ||
| ) |
Sample hook function to call after reordering.
Prints on the manager's stdout final size and reordering time.
- Returns
- 1 if successful; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_StdPreReordHook
◆ Cudd_StdPreReordHook()
| int Cudd_StdPreReordHook | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| const char * | str, | ||
| void * | data | ||
| ) |
Sample hook function to call before reordering.
Prints on the manager's stdout reordering method and initial size.
- Returns
- 1 if successful; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_StdPostReordHook
◆ Cudd_SubsetCompress()
Find a dense subset of BDD f.
Density is the ratio of number of minterms to number of nodes. Uses several techniques in series. It is more expensive than other subsetting procedures, but often produces better results. See Cudd_SubsetShortPaths for a description of the threshold and nvars parameters.
- Returns
- a pointer to the result if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- Parameters
-
dd manager f BDD whose subset is sought nvars number of variables in the support of f threshold maximum number of nodes in the subset
◆ Cudd_SubsetHeavyBranch()
Extracts a dense subset from a BDD with the heavy branch heuristic.
This procedure builds a subset by throwing away one of the children of each node, starting from the root, until the result is small enough. The child that is eliminated from the result is the one that contributes the fewer minterms. The parameter numVars is the maximum number of variables to be used in minterm calculation and node count calculation. The optimal number should be as close as possible to the size of the support of f. However, it is safe to pass the value returned by Cudd_ReadSize for numVars when the number of variables is under 1023. If numVars is larger than 1023, it will overflow. If a 0 parameter is passed then the procedure will compute a value which will avoid overflow but will cause underflow with 2046 variables or more.
- Returns
- a pointer to the BDD of the subset if successful. NULL if the procedure runs out of memory.
- Side effects None
- Parameters
-
dd manager f function to be subset numVars number of variables in the support of f threshold maximum number of nodes in the subset
◆ Cudd_SubsetShortPaths()
| DdNode* Cudd_SubsetShortPaths | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| DdNode * | f, | ||
| int | numVars, | ||
| int | threshold, | ||
| int | hardlimit | ||
| ) |
Extracts a dense subset from a BDD with the shortest paths heuristic.
This procedure tries to preserve the shortest paths of the input BDD, because they give many minterms and contribute few nodes. This procedure may increase the number of nodes in trying to create the subset or reduce the number of nodes due to recombination as compared to the original BDD. Hence the threshold may not be strictly adhered to. In practice, recombination overshadows the increase in the number of nodes and results in small BDDs as compared to the threshold. The hardlimit specifies whether threshold needs to be strictly adhered to. If it is set to 1, the procedure ensures that result is never larger than the specified limit but may be considerably less than the threshold. The value for numVars should be as close as possible to the size of the support of f for better efficiency. However, it is safe to pass the value returned by Cudd_ReadSize for numVars. If 0 is passed, then the value returned by Cudd_ReadSize is used.
- Returns
- a pointer to the BDD for the subset if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- Parameters
-
dd manager f function to be subset numVars number of variables in the support of f threshold maximum number of nodes in the subset hardlimit flag: 1 if threshold is a hard limit
◆ Cudd_SubsetWithMaskVars()
| DdNode* Cudd_SubsetWithMaskVars | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| DdNode * | f, | ||
| DdNode ** | vars, | ||
| int | nvars, | ||
| DdNode ** | maskVars, | ||
| int | mvars | ||
| ) |
Extracts a subset from a BDD.
Extracts a subset from a BDD in the following procedure.
- Compute the weight for each mask variable by counting the number of minterms for both positive and negative cofactors of the BDD with respect to each mask variable. (weight = # positive - # negative)
- Find a representative cube of the BDD by using the weight. From the top variable of the BDD, for each variable, if the weight is greater than 0.0, choose THEN branch, othereise ELSE branch, until meeting the constant 1.
- Quantify out the variables not in maskVars from the representative cube and if a variable in maskVars is don't care, replace the variable with a constant(1 or 0) depending on the weight.
- Make a subset of the BDD by multiplying with the modified cube.
- Side effects None
- Parameters
-
dd manager f function from which to pick a cube vars array of variables nvars size of varsmaskVars array of variables mvars size of maskVars
◆ Cudd_SupersetCompress()
Find a dense superset of BDD f.
Density is the ratio of number of minterms to number of nodes. Uses several techniques in series. It is more expensive than other supersetting procedures, but often produces better results. See Cudd_SupersetShortPaths for a description of the threshold and nvars parameters.
- Returns
- a pointer to the result if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_SubsetCompress Cudd_SupersetRemap Cudd_SupersetShortPaths Cudd_SupersetHeavyBranch Cudd_bddSqueeze
- Parameters
-
dd manager f BDD whose superset is sought nvars number of variables in the support of f threshold maximum number of nodes in the superset
◆ Cudd_SupersetHeavyBranch()
Extracts a dense superset from a BDD with the heavy branch heuristic.
The procedure is identical to the subset procedure except for the fact that it receives the complement of the given function. Extracting the subset of the complement function is equivalent to extracting the superset of the function. This procedure builds a superset by throwing away one of the children of each node starting from the root of the complement function, until the result is small enough. The child that is eliminated from the result is the one that contributes the fewer minterms. The parameter numVars is the maximum number of variables to be used in minterm calculation and node count calculation. The optimal number should be as close as possible to the size of the support of f. However, it is safe to pass the value returned by Cudd_ReadSize for numVars when the number of variables is under 1023. If numVars is larger than 1023, it will overflow. If a 0 parameter is passed then the procedure will compute a value which will avoid overflow but will cause underflow with 2046 variables or more.
- Returns
- a pointer to the BDD of the superset if successful. NULL if intermediate result causes the procedure to run out of memory.
- Side effects None
- Parameters
-
dd manager f function to be superset numVars number of variables in the support of f threshold maximum number of nodes in the superset
◆ Cudd_SupersetShortPaths()
| DdNode* Cudd_SupersetShortPaths | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| DdNode * | f, | ||
| int | numVars, | ||
| int | threshold, | ||
| int | hardlimit | ||
| ) |
Extracts a dense superset from a BDD with the shortest paths heuristic.
The procedure is identical to the subset procedure except for the fact that it receives the complement of the given function. Extracting the subset of the complement function is equivalent to extracting the superset of the function. This procedure tries to preserve the shortest paths of the complement BDD, because they give many minterms and contribute few nodes. This procedure may increase the number of nodes in trying to create the superset or reduce the number of nodes due to recombination as compared to the original BDD. Hence the threshold may not be strictly adhered to. In practice, recombination overshadows the increase in the number of nodes and results in small BDDs as compared to the threshold. The hardlimit specifies whether threshold needs to be strictly adhered to. If it is set to 1, the procedure ensures that result is never larger than the specified limit but may be considerably less than the threshold. The value for numVars should be as close as possible to the size of the support of f for better efficiency. However, it is safe to pass the value returned by Cudd_ReadSize for numVar. If 0 is passed, then the value returned by Cudd_ReadSize is used.
- Returns
- a pointer to the BDD for the superset if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- Parameters
-
dd manager f function to be superset numVars number of variables in the support of f threshold maximum number of nodes in the subset hardlimit flag: 1 if threshold is a hard limit
◆ Cudd_Support()
Finds the variables on which a DD depends.
- Returns
- a BDD consisting of the product of the variables if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- Parameters
-
dd manager f DD whose support is sought
◆ Cudd_SupportIndex()
Finds the variables on which a DD depends.
- Returns
- an index array of the variables if successful; NULL otherwise. The size of the array equals the number of variables in the manager. Each entry of the array is 1 if the corresponding variable is in the support of the DD and 0 otherwise.
- Side effects None
- Parameters
-
dd manager f DD whose support is sought
◆ Cudd_SupportIndices()
Finds the variables on which a DD depends.
- Returns
- the number of variables if successful; CUDD_OUT_OF_MEM otherwise.
- Side effects The indices of the support variables are returned as
- side effects. If the function is constant, no array is allocated.
- Parameters
-
dd manager f DD whose support is sought indices array containing (on return) the indices
◆ Cudd_SupportSize()
Counts the variables on which a DD depends.
- Returns
- the variables on which a DD depends.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_Support Cudd_SupportIndices
- Parameters
-
dd manager f DD whose support size is sought
◆ Cudd_SymmProfile()
| void Cudd_SymmProfile | ( | DdManager * | table, |
| int | lower, | ||
| int | upper | ||
| ) |
Prints statistics on symmetric variables.
The information is accurate only if this function is called right after reordering with methods CUDD_REORDER_SYMM_SIFT or CUDD_REORDER_SYMM_SIFT_CONV.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_T()
◆ Cudd_TimeLimited()
| int Cudd_TimeLimited | ( | DdManager * | unique | ) |
Returns true if the time limit for the manager is set.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_tlcInfoFree()
| void Cudd_tlcInfoFree | ( | DdTlcInfo * | t | ) |
◆ Cudd_TurnOffCountDead()
| void Cudd_TurnOffCountDead | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Causes the dead nodes not to be counted towards triggering reordering.
This causes less frequent reorderings. By default dead nodes are not counted. Therefore there is no need to call this function unless Cudd_TurnOnCountDead has been previously called.
- Side effects Changes the manager.
◆ Cudd_TurnOnCountDead()
| void Cudd_TurnOnCountDead | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Causes the dead nodes to be counted towards triggering reordering.
This causes more frequent reorderings. By default dead nodes are not counted.
- Side effects Changes the manager.
◆ Cudd_UnderApprox()
| DdNode* Cudd_UnderApprox | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| DdNode * | f, | ||
| int | numVars, | ||
| int | threshold, | ||
| int | safe, | ||
| double | quality | ||
| ) |
Extracts a dense subset from a BDD with Shiple's underapproximation method.
This procedure uses a variant of Tom Shiple's underapproximation method. The main difference from the original method is that density is used as cost function. The parameter numVars is the maximum number of variables to be used in minterm calculation. The optimal number should be as close as possible to the size of the support of f. However, it is safe to pass the value returned by Cudd_ReadSize for numVars when the number of variables is under 1023. If numVars is larger than 1023, it will cause overflow. If a 0 parameter is passed then the procedure will compute a value which will avoid overflow but will cause underflow with 2046 variables or more.
- Returns
- a pointer to the BDD of the subset if successful; NULL if the procedure runs out of memory.
- Side effects None
- Parameters
-
dd manager f function to be subset numVars number of variables in the support of f threshold when to stop approximation safe enforce safe approximation quality minimum improvement for accepted changes
◆ Cudd_UnregisterOutOfMemoryCallback()
| void Cudd_UnregisterOutOfMemoryCallback | ( | DdManager * | unique | ) |
Unregister an out-of-memory callback.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_UnregisterTerminationCallback()
| void Cudd_UnregisterTerminationCallback | ( | DdManager * | unique | ) |
◆ Cudd_UnsetTimeLimit()
| void Cudd_UnsetTimeLimit | ( | DdManager * | unique | ) |
Unsets the time limit for the manager.
Actually, sets it to a very large value.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_UpdateTimeLimit()
| void Cudd_UpdateTimeLimit | ( | DdManager * | unique | ) |
Updates the time limit for the manager.
Updates the time limit for the manager by subtracting the elapsed time from it.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_V()
| CUDD_VALUE_TYPE Cudd_V | ( | DdNode * | node | ) |
◆ Cudd_VarsAreSymmetric()
◆ Cudd_VectorSupport()
Finds the variables on which a set of DDs depends.
The set must contain either BDDs and ADDs, or ZDDs.
- Returns
- a BDD consisting of the product of the variables if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_Support Cudd_ClassifySupport
- Parameters
-
dd manager F array of DDs whose support is sought n size of the array
◆ Cudd_VectorSupportIndex()
Finds the variables on which a set of DDs depends.
The set must contain either BDDs and ADDs, or ZDDs.
- Returns
- an index array of the variables if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- Parameters
-
dd manager F array of DDs whose support is sought n size of the array
◆ Cudd_VectorSupportIndices()
Finds the variables on which a set of DDs depends.
The set must contain either BDDs and ADDs, or ZDDs.
- Returns
- the number of variables if successful; CUDD_OUT_OF_MEM otherwise.
- Side effects The indices of the support variables are returned as
- side effects. If the function is constant, no array is allocated.
- Parameters
-
dd manager F DD whose support is sought n size of the array indices array containing (on return) the indices
◆ Cudd_VectorSupportSize()
Counts the variables on which a set of DDs depends.
The set must contain either BDDs and ADDs, or ZDDs.
- Returns
- the number of variables on which a set of DDs depends.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_VectorSupport Cudd_SupportSize
- Parameters
-
dd manager F array of DDs whose support is sought n size of the array
◆ Cudd_VerifySol()
Checks the solution of F(x,y) = 0.
This procedure substitutes the solution components for the unknowns of F and returns the resulting BDD for F.
- Side effects Frees the memory pointed by yIndex.
- See also
- Cudd_SolveEqn
- Parameters
-
bdd CUDD manager F the left-hand side of the equation G the array of solutions yIndex index of y variables n numbers of unknowns
◆ Cudd_Xeqy()
Generates a BDD for the function x==y.
This function generates a BDD for the function x==y. Both x and y are N-bit numbers, x[0] x[1] ... x[N-1] and y[0] y[1] ... y[N-1]. The BDD is built bottom-up. It has 3*N-1 internal nodes, if the variables are ordered as follows: x[0] y[0] x[1] y[1] ... x[N-1] y[N-1].
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_addXeqy
- Parameters
-
dd DD manager N number of x and y variables x array of x variables y array of y variables
◆ Cudd_Xgty()
Generates a BDD for the function x > y.
This function generates a BDD for the function x > y. Both x and y are N-bit numbers, x[0] x[1] ... x[N-1] and y[0] y[1] ... y[N-1], with 0 the most significant bit. The BDD is built bottom-up. It has 3*N-1 internal nodes, if the variables are ordered as follows: x[0] y[0] x[1] y[1] ... x[N-1] y[N-1]. Argument z is not used by Cudd_Xgty: it is included to make it call-compatible to Cudd_Dxygtdxz and Cudd_Dxygtdyz.
- Side effects None
- Parameters
-
dd DD manager N number of x and y variables z array of z variables: unused x array of x variables y array of y variables
◆ Cudd_zddChange()
Substitutes a variable with its complement in a ZDD.
- Returns
- a pointer to the result if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_zddComplement()
Computes a complement cover for a ZDD node.
For lack of a better method, we first extract the function BDD from the ZDD cover, then make the complement of the ZDD cover from the complement of the BDD node by using ISOP. The result depends on current variable order.
- Returns
- a pointer to the resulting cover if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects The result depends on current variable order.
◆ Cudd_zddCount()
Counts the number of minterms in a ZDD.
Returns an integer representing the number of minterms in a ZDD.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_zddCountDouble
◆ Cudd_zddCountDouble()
Counts the number of minterms of a ZDD.
This procedure is used in Cudd_zddCountMinterm.
- Returns
- the count. If the procedure runs out of memory, it returns (double) CUDD_OUT_OF_MEM.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_zddCountMinterm Cudd_zddCount
◆ Cudd_zddCountMinterm()
Counts the number of minterms of a ZDD.
Counts the number of minterms of the ZDD rooted at node. This procedure takes a parameter path that specifies how many variables are in the support of the function.
- Returns
- the count. If the procedure runs out of memory, it returns (double) CUDD_OUT_OF_MEM.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_zddCountDouble
◆ Cudd_zddCoverPathToString()
| char* Cudd_zddCoverPathToString | ( | DdManager * | zdd, |
| int * | path, | ||
| char * | str | ||
| ) |
Converts a path of a ZDD representing a cover to a string.
The string represents an implicant of the cover. The path is typically produced by Cudd_zddForeachPath. If the str input is NULL, it allocates a new string. The string passed to this function must have enough room for all variables and for the terminator.
- Returns
- a pointer to the string if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_zddForeachPath
- Parameters
-
zdd DD manager path path of ZDD representing a cover str pointer to string to use if != NULL
◆ Cudd_zddDagSize()
| int Cudd_zddDagSize | ( | DdNode * | p_node | ) |
Counts the number of nodes in a ZDD.
- Deprecated:
- This function duplicates Cudd_DagSize and is only retained for compatibility.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_DagSize
◆ Cudd_zddDiff()
Computes the difference of two ZDDs.
- Returns
- a pointer to the result if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_zddDiffConst()
Performs the inclusion test for ZDDs (P implies Q).
No new nodes are generated by this procedure.
- Returns
- empty if true; a valid pointer different from empty or DD_NON_CONSTANT otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_zddDiff
◆ Cudd_zddDivide()
Computes the quotient of two unate covers.
Computes the quotient of two unate covers represented by ZDDs. Unate covers use one ZDD variable for each BDD variable.
- Returns
- a pointer to the resulting ZDD if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_zddWeakDiv
◆ Cudd_zddDivideF()
Modified version of Cudd_zddDivide.
This function may disappear in future releases.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_zddDumpDot()
| int Cudd_zddDumpDot | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| int | n, | ||
| DdNode ** | f, | ||
| char const *const * | inames, | ||
| char const *const * | onames, | ||
| FILE * | fp | ||
| ) |
Writes a dot file representing the argument ZDDs.
Writes a file representing the argument ZDDs in a format suitable for the graph drawing program dot. Cudd_zddDumpDot does not close the file: This is the caller responsibility. Cudd_zddDumpDot uses a minimal unique subset of the hexadecimal address of a node as name for it. If the argument inames is non-null, it is assumed to hold the pointers to the names of the inputs. Similarly for onames. Cudd_zddDumpDot uses the following convention to draw arcs:
- solid line: THEN arcs;
- dashed line: ELSE arcs.
The dot options are chosen so that the drawing fits on a letter-size sheet.
- Returns
- 1 in case of success; 0 otherwise (e.g., out-of-memory, file system full).
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_DumpDot Cudd_zddPrintDebug
- Parameters
-
dd manager n number of output nodes to be dumped f array of output nodes to be dumped inames array of input names (or NULL) onames array of output names (or NULL) fp pointer to the dump file
◆ Cudd_zddFirstPath()
Finds the first path of a ZDD.
Defines an iterator on the paths of a ZDD and finds its first path.
A path is represented as an array of literals, which are integers in {0, 1, 2}; 0 represents an else arc out of a node, 1 represents a then arc out of a node, and 2 stands for the absence of a node. The size of the array equals the number of variables in the manager at the time Cudd_zddFirstCube is called.
The paths that end in the empty terminal are not enumerated.
- Returns
- a generator that contains the information necessary to continue the enumeration if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects The first path is returned as a side effect.
◆ Cudd_zddIntersect()
Computes the intersection of two ZDDs.
- Returns
- a pointer to the result if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_zddIsop()
Computes an ISOP in ZDD form from BDDs.
Computes an irredundant sum of products (ISOP) in ZDD form from BDDs. The two BDDs L and U represent the lower bound and the upper bound, respectively, of the function. The ISOP uses two ZDD variables for each BDD variable: One for the positive literal, and one for the negative literal. These two variables should be adjacent in the ZDD order. The two ZDD variables corresponding to BDD variable i should have indices 2i and 2i+1. The result of this procedure depends on the variable order. If successful, Cudd_zddIsop returns the BDD for the function chosen from the interval. The ZDD representing the irredundant cover is returned as a side effect in zdd_I. In case of failure, NULL is returned.
- Returns
- the BDD for the chosen function if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects zdd_I holds the pointer to the ZDD for the ISOP on
- successful return.
- See also
- Cudd_bddIsop Cudd_zddVarsFromBddVars
◆ Cudd_zddIte()
Computes the ITE of three ZDDs.
- Returns
- a pointer to the result if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_zddIthVar()
Returns the ZDD variable with index i.
Retrieves the ZDD variable with index i if it already exists, or creates a new ZDD variable.
- Returns
- a pointer to the variable if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_bddIthVar Cudd_addIthVar
◆ Cudd_zddNextPath()
| int Cudd_zddNextPath | ( | DdGen * | gen, |
| int ** | path | ||
| ) |
Generates the next path of a ZDD.
Generates the next path of a ZDD onset, using generator gen.
- Returns
- 0 if the enumeration is completed; 1 otherwise.
- Side effects The path is returned as a side effect. The generator is
- modified.
◆ Cudd_zddPortFromBdd()
Converts a BDD into a ZDD.
This function assumes that there is a one-to-one correspondence between the BDD variables and the ZDD variables, and that the variable order is the same for both types of variables. These conditions are established if the ZDD variables are created by one call to Cudd_zddVarsFromBddVars with multiplicity = 1.
- Returns
- a pointer to the resulting ZDD if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_zddVarsFromBddVars
◆ Cudd_zddPortToBdd()
Converts a ZDD into a BDD.
- Returns
- a pointer to the resulting ZDD if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_zddPortFromBdd
◆ Cudd_zddPrintCover()
Prints a sum of products from a ZDD representing a cover.
- Returns
- 1 if successful; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_zddPrintMinterm
◆ Cudd_zddPrintDebug()
Prints to the standard output a ZDD and its statistics.
The statistics include the number of nodes and the number of minterms. (The number of minterms is also the number of combinations in the set.) The statistics are printed if pr > 0. Specifically:
- pr = 0 : prints nothing
- pr = 1 : prints counts of nodes and minterms
- pr = 2 : prints counts + disjoint sum of products
- pr = 3 : prints counts + list of nodes
- pr > 3 : prints counts + disjoint sum of products + list of nodes
- Returns
- 1 if successful; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_zddPrintMinterm()
Prints a disjoint sum of product form for a ZDD.
- Returns
- 1 if successful; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_zddPrintDebug Cudd_zddPrintCover
◆ Cudd_zddPrintSubtable()
| void Cudd_zddPrintSubtable | ( | DdManager * | table | ) |
Prints the ZDD table for debugging purposes.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_zddProduct()
Computes the product of two covers represented by ZDDs.
The result is also a ZDD. The covers on which Cudd_zddProduct operates use two ZDD variables for each function variable (one ZDD variable for each literal of the variable). Those two ZDD variables should be adjacent in the order.
- Returns
- a pointer to the result if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_zddUnateProduct
◆ Cudd_zddReadNodeCount()
| long Cudd_zddReadNodeCount | ( | DdManager * | dd | ) |
Reports the number of nodes in ZDDs.
This number always includes the two constants 1 and 0.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_zddRealignDisable()
| void Cudd_zddRealignDisable | ( | DdManager * | unique | ) |
Disables realignment of ZDD order to BDD order.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_zddRealignEnable()
| void Cudd_zddRealignEnable | ( | DdManager * | unique | ) |
Enables realignment of ZDD order to BDD order.
Enables realignment of the ZDD variable order to the BDD variable order after the BDDs and ADDs have been reordered. The number of ZDD variables must be a multiple of the number of BDD variables for realignment to make sense. If this condition is not met, Cudd_ReduceHeap will return 0. Let M be the ratio of the two numbers. For the purpose of realignment, the ZDD variables from M*i to (M+1)*i-1 are reagarded as corresponding to BDD variable i. Realignment is initially disabled.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_zddRealignmentEnabled()
| int Cudd_zddRealignmentEnabled | ( | DdManager * | unique | ) |
Tells whether the realignment of ZDD order to BDD order is enabled.
- Returns
- 1 if the realignment of ZDD order to BDD order is enabled; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_zddReduceHeap()
| int Cudd_zddReduceHeap | ( | DdManager * | table, |
| Cudd_ReorderingType | heuristic, | ||
| int | minsize | ||
| ) |
Main dynamic reordering routine for ZDDs.
Calls one of the possible reordering procedures:
- Swapping
- Sifting
- Symmetric Sifting
For sifting and symmetric sifting it is possible to request reordering to convergence.
The core of all methods is the reordering procedure cuddZddSwapInPlace() which swaps two adjacent variables.
- Returns
- 1 in case of success; 0 otherwise. In the case of symmetric sifting (with and without convergence) returns 1 plus the number of symmetric variables, in case of success.
- Side effects Changes the variable order for all ZDDs and clears
- the cache.
- Parameters
-
table DD manager heuristic method used for reordering minsize bound below which no reordering occurs
◆ Cudd_zddShuffleHeap()
| int Cudd_zddShuffleHeap | ( | DdManager * | table, |
| int * | permutation | ||
| ) |
Reorders ZDD variables according to given permutation.
The i-th entry of the permutation array contains the index of the variable that should be brought to the i-th level. The size of the array should be equal or greater to the number of variables currently in use.
- Returns
- 1 in case of success; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects Changes the ZDD variable order for all diagrams and clears
- the cache.
- See also
- Cudd_zddReduceHeap
- Parameters
-
table DD manager permutation required variable permutation
◆ Cudd_zddSubset0()
Computes the negative cofactor of a ZDD w.r.t. a variable.
In terms of combinations, the result is the set of all combinations in which the variable is negated.
- Returns
- a pointer to the result if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_zddSubset1
◆ Cudd_zddSubset1()
Computes the positive cofactor of a ZDD w.r.t. a variable.
In terms of combinations, the result is the set of all combinations in which the variable is asserted.
- Returns
- a pointer to the result if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_zddSubset0
◆ Cudd_zddSupport()
Finds the variables on which a ZDD depends.
- Returns
- a BDD consisting of the product of the variables if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_Support
- Parameters
-
dd manager f ZDD whose support is sought
◆ Cudd_zddSymmProfile()
| void Cudd_zddSymmProfile | ( | DdManager * | table, |
| int | lower, | ||
| int | upper | ||
| ) |
Prints statistics on symmetric ZDD variables.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_zddUnateProduct()
Computes the product of two unate covers represented as ZDDs.
Unate covers use one ZDD variable for each BDD variable.
- Returns
- a pointer to the result if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_zddProduct
◆ Cudd_zddUnion()
Computes the union of two ZDDs.
- Returns
- a pointer to the result if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
◆ Cudd_zddVarsFromBddVars()
| int Cudd_zddVarsFromBddVars | ( | DdManager * | dd, |
| int | multiplicity | ||
| ) |
Creates one or more ZDD variables for each BDD variable.
If some ZDD variables already exist, only the missing variables are created. Parameter multiplicity allows the caller to control how many variables are created for each BDD variable in existence. For instance, if ZDDs are used to represent covers, two ZDD variables are required for each BDD variable. The order of the BDD variables is transferred to the ZDD variables. If a variable group tree exists for the BDD variables, a corresponding ZDD variable group tree is created by expanding the BDD variable tree. In any case, the ZDD variables derived from the same BDD variable are merged in a ZDD variable group. If a ZDD variable group tree exists, it is freed.
- Returns
- 1 if successful; 0 otherwise.
- Side effects None
- Parameters
-
dd DD manager multiplicity how many ZDD variables are created for each BDD variable
◆ Cudd_zddWeakDiv()
Applies weak division to two covers.
Applies weak division to two ZDDs representing two covers. The result of weak division depends on the variable order. The covers on which Cudd_zddWeakDiv operates use two ZDD variables for each function variable (one ZDD variable for each literal of the variable). Those two ZDD variables should be adjacent in the order.
- Returns
- a pointer to the ZDD representing the result if successful; NULL otherwise.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_zddDivide
◆ Cudd_zddWeakDivF()
Modified version of Cudd_zddWeakDiv.
This function may disappear in future releases.
- Side effects None
- See also
- Cudd_zddWeakDiv
 1.8.14
1.8.14